Best ERP Software for Indonesian Businesses in 2025
There is no such thing as the best ERP software. ERP exists to automate and…
Nindy
July 9, 2025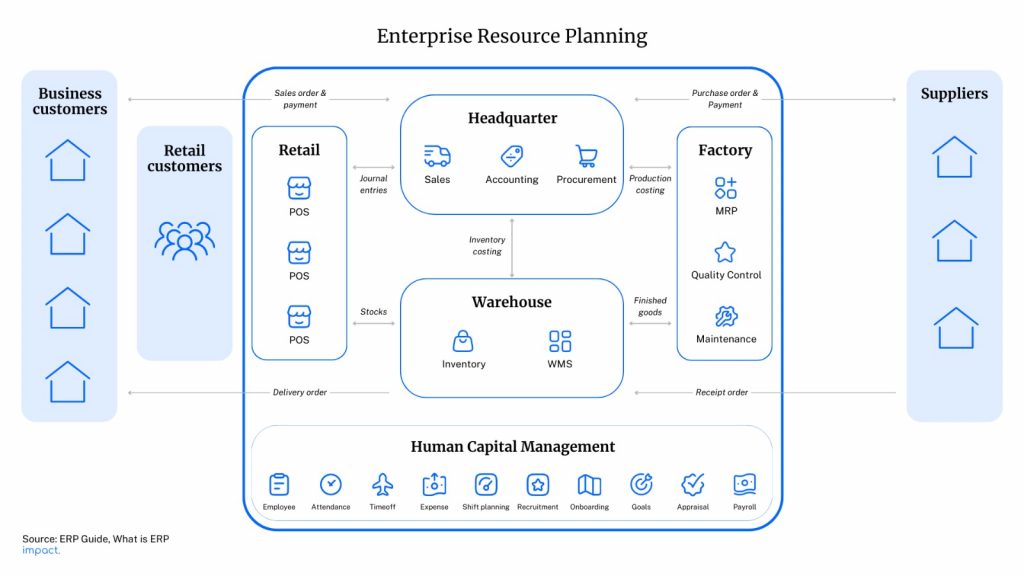
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is the integrated management of key business processes, often in real-time, facilitated by software and technology.
ERP is usually referred to as a category of business management software, typically a suite of integrated applications, that an organization can use to collect, store, manage and interpret data from many business activities.
ERP systems are designed to streamline and automate business activities across different departments and are often used in digital transformation efforts.
ERP vs CRM
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is software tools designed to manage and analyze interactions and relationships with customers and potential customers throughout the customer lifecycle.
The difference between CRM and ERP is that CRM is a software used by the sales team while ERP is a suite of integrated softwares used by different teams within a company, typically accounting, inventory management, warehouse management, procurement management, customer relationship management, and human resources.
So it can be said that CRM can be a part of ERP while it can exist on its own.
ERP vs SCM
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the process of managing the flow of goods and services to and from a business, including every step involved in turning raw materials and components into final products and getting them to the ultimate customer.
The difference between SCM and ERP is that SCM is a business process, while ERP is a software that supports the automation of business processes (including SCM).
ERP vs SAP
SAP is a German multinational software company founded in 1972 that develops ERP software. Many consider SAP ERP as a legacy system. In Indonesia, it is commonly used among enterprises, manufacturing companies, and BUMNs. However, many companies are switching to more affordable modern, easy-to-use ERP systems since COVID-19 pandemic due to its high monthly costs.
Learn more about the difference between legacy systems and modern ERPs.
The difference between SAP and ERP is that SAP is one of the many brands of ERP, while ERP refers to the system itself. However, due SAP’s long-standing presence in Indonesia (SAP has been around in Indonesia since 1997 when no other ERP systems were around at that time), SAP has become a household name synonymous with ERP, especially among the older generations.
1960s: Birth of MRP
J.I. Case, a manufacturer of tractor and construction machinery, worked with IBM to develop what is believed to be the first MRP system. While they were expensive to create, required a team of experts to maintain and took up a lot of space, early MRP systems enabled businesses to track inventory and production.
That helped manufacturers manage raw materials procurement and delivery of product to the factory so they could better plan production runs. Although adoption of MRP systems gained traction in the 1970s, the technology remained limited to large companies that had the budgets and resources for in-house development.
Eventually several large software providers, including Oracle and JD Edwards, set out to make this software accessible to more businesses.
1980s: Birth of MRP II
The more sophisticated manufacturing resource planning (MRP II) systems that supported manufacturing processes beyond inventory and raw materials procurement first appeared.
MRP II systems allowed the various departments involved in manufacturing to coordinate, and they had more advanced production scheduling capabilities.
It wasn’t long until other industries realized that manufacturing firms were onto something.
1990s: Birth of ERP
By 1990, research firm Gartner coined the term “enterprise resource planning.” The new name recognized that many businesses—not just manufacturing—were now using this technology to increase the efficiency of their entire operations.
This was when ERP systems took on their current identity: a unified database for information from across the company. ERP systems brought in other business functions, like accounting, sales, engineering and human resources (HR), to serve as a single source of accurate data for all employees.
Back then all ERPs were based on-premise, which means companies need to have the right hardware, server, and IT staff to maintain. Due to the high implementation and maintenance costs, only large enterprises have access to ERP systems.
One major breakthrough happened in 1998 when NetSuite introduced cloud ERP where companies no longer have to pay for the high implementation and maintenance costs, thus allowing medium-sized businesses to enjoy the benefits of ERP systems.
2000: Birth of ERP II and open source ERP
ERP systems initially focused on automating back office functions that did not directly affect customers and the public.
However, front office functions such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM), ecommerce and marketing automation, and back-end applications like Supply Chain Management (SCM) and Human Capital Management (HCM) became integrated later, when the internet simplified communication with external parties.
In 2000, Gartner introduced the idea of ERP II – ERP that integrates with third party software through the internet.
At the same time, many companies had realized the benefits of ERP systems for their businesses, however, the ERP industry was dominated by SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft Dynamics. Therefore, the costs of implementing an ERP system remain relatively high and many small and medium-sized businesses are unable to afford them.
This was when Compiere, the first truly viable open source ERP solution was born. Although Compiere was not perfect in any way, and it is no longer available today (in 2005, Consona Corporation purchased Compiere and discontinued advancing the community edition), it gave birth to other open source ERP projects like Odoo.
2010: Birth of AI and IOT
The 2010s saw the beginning of ERP vendors incorporating advanced technology such as artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT).
AI can enhance ERP systems by adding new capabilities, such as advanced analytics and forecasting.
This can be useful for large manufacturing companies that have lots of data to make predictions and recommendations for various operational activities, such as production planning, inventory management, demand forecasting, and sales performance.
IoT in ERP is the network of physical objects (“things”) that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies and connecting them with an ERP system over the internet.
IoT devices connected to ERPs deliver real-time updates on enterprise assets, equipment and products, helping companies detect the root causes of issues and become more responsive.
This can be useful for healthcare (to control patients off-site), manufacturing (to control production process and machine conditions), agriculture (to control conditions of crops and livestocks), and banking (reduce ATM frauds, track customer spending habits, process automations).
Although AI and IoT sounds very useful, it is hard to implement (need big data, sensors, integrations, etc.) and costs a lot, therefore it only makes sense for large enterprises. In Indonesia, the problem is mainly in the business process, so AI and IoT does not help much for 99% of businesses.
2020: Modern ERP
Modern ERP is a term popularized by Netsuite. Although there is no official definition, we feel that appropriate characteristics of a modern ERP are:
One example of a modern ERP is Impact ERP.
License fees are paid to the company who owns the ERP, not the implementer. Usually there are server and maintenance fees to the implementer in addition to license fees.
Many companies in Indonesia have trouble with the lack of communication between different team (sales, warehouse, procurement, accounting, HR, etc.) causing revenue losses, unnecessary spendings, and inefficiencies (product delivery time, accounting team busy doing reconciliations, inventory unavailability when customers want to buy certain products, etc.). ERP reduces the need for the different teams to manually communicate since the data that they need are already available on the system.
There are two business processes that are automated: sales to cash and procure to pay. Sales to cash is the process from when a customer makes an order, gets the product delivered, gets an invoice, and pays for it, while procure to pay is the process when a company purchases an inventory to be sold, receives the product, gets billed, and pays for it. E
ach business process requires the involvement of creating an order document (sales order, delivery order, etc) and passing the document to other teams for follow up. An ERP system automates those processes, so when a team creates an order, the other team will automatically get notified of that and can immediately process the order. An order that usually may take 2 weeks can be done in 2 days. This is crucial for companies that have a lot of orders since it affects customer satisfaction.
Since every process is managed by the ERP system real-time, business leaders will get the data real-time, too. This is crucial because business leaders can take immediate action when things go wrong. In addition, in the case of non-performance of certain teams that happen repeatedly (eg. sales team), business leaders can analyze the data to figure out why, thereby making the necessary changes to ensure it doesn’t happen again.
An ERP system comes with user access restrictions, allowing only qualified personnel to view, create, edit, or delete certain sensitive data. Changes to data are also recorded, so employees involved with fraudulent activities can get identified quickly (eg. sales team hiding customer orders).
Although this is an indirect benefit of an ERP system, it is a crucial one. When business processes get more efficient (and data), it brings about transformation in the company, which is the first step to having a more sustainable company with self-improvement culture.
We find this to be crucial because then the employees don’t rely too much on the business leaders on every little thing and the business leaders have the time to focus on more impactful long-lasting activities (eg. company growth, analyzing data to find out the reasons why teams are not performing, creating standard operating procedures, performing skill gap analysis, fixing hiring, etc.).
Impact is a cloud-based modern ERP software designed ready-to-use for Indonesian companies, yet flexible, customizable, and scalable. It has 4 different versions built for 4 different businesses: wholesale distribution, manufacturing, retail, and small businesses.
The small business version is free to use and mobile-only with zero implementation fee, which is great for companies trying out ERP for the first time (or for students who are considering a career as a Business Analyst).
Odoo is a cloud-based modern ERP system with 2 editions: Odoo Community and Odoo Enterprise. Odoo Community is the open-source edition while Odoo Enterprise is the licensed version.
The major differences between the two is that Odoo Community doesn’t have an accounting module (among others), mobile version, barcode, and limited MRP features. Odoo is popular in Indonesia because of its affordability and flexibility, however, choosing an Odoo partner can be tricky.
SAP has been enjoying its first mover advantage for many years in Indonesia, with SAP Business One being the most popular among medium-sized companies, and SAP HANA being the most popular among enterprises.
It is a reliable ERP system, especially for complex manufacturing companies, despite being a legacy system.
Oracle, like SAP, has been in Indonesia since the 1990s. They were strong for companies in service industries. Oracle Fusion Middleware is popular among enterprises in service industries, and Oracle Netsuite is relatively popular among medium-sized companies.
Microsoft Dynamics has been popular in Indonesia among enterprises within the Microsoft ecosystem (Microsoft servers using Microsoft Windows), especially Dynamics NAV (Navision).
Now the old generations of Dynamics (GP, NAV, SL, and AX) were forked into Dynamics 365 to allow Microsoft to focus on its SaaS suites.
There are 4 pricing components of ERP:
ERP prices are highly dependent on your industries, modules, business processes, customizations required, and other factors. However, as a general rule, small businesses can expect to pay Rp 100-500 million, medium-sized from Rp 500 million to Rp 1 billion, while enterprises start from Rp 1 billion.
ERP works by automating and integrating two core business processes: sales to cash and procure to pay.
Sales to cash refers to all the steps involved in processing customer orders from the moment a customer places the order to when the payment is received.
Order to cash process involves different teams working together to ensure customers get their goods on time and companies get paid on time. It is really difficult to coordinate the different teams without an automated system since a lot of things can go wrong in the day-to-day operations.
Without an ERP system, sales to cash process may take 1-6 months, however, with an ERP system, it can be shortened to under 1 month. This huge efficiency boost will allow the company to send orders to customers faster (and they will be happier) and give the company better cash flows.
Procure to pay refers to all steps involved in processing purchase orders from the moment the procurement team places the order to when the bill is paid.
Common problems that happen when companies don’t have an ERP system are:
Production process involves the following activities:
Production process involves different teams working together to ensure raw materials needed are available on time, the production process is efficient (low Cost of Goods Manufactured through minimizing wastage and overhead costs), and manufactured goods are of high quality.
It is really difficult to coordinate the different teams without an automated system, since one mistake by one person can affect the whole process (eg. if the purchasing manager doesn’t buy raw materials on time, the whole factory can’t produce anything).
Therefore an ERP system with an MRP module is really crucial for manufacturing companies.
In retail, the key to operational efficiency is in the stores and the supply chain (warehouse and logistics), especially in retail with multiple stores. Each store has different product demands, and to be able to maximize revenue, retailers need to know what products should be available (fast-moving vs slow-moving) and at what quantity for each store. This sounds easy, but in reality, inventory management and planning is a nightmare.
In addition, promotions and loyalty programs, if done correctly (but unfortunately often not the case), can boost revenue (as well as clear out slow-moving goods to give space for faster-moving goods with better margins).
Moreover, store management and human resources for retail are really time-consuming, since there are a lot of unexpected day-to-day operational dramas.
Most retailers just get POS software since they are affordable. However, there are a few things only an ERP software can do:
50-75% of ERP implementation projects fail to meet their objectives. Considering the amount of money companies spend on ERP implementation, this is seriously a waste of resources.
There are many reasons for ERP implementation failures, however the top 3 are:
About 42% of organizations report a lack of clarity in business goals as an issue during their ERP implementation.
When we ask companies we’ve met why they are looking for an ERP system, their answers were generally “we just want to upgrade from excel/accounting software”. Most of them can’t even explain their own pain points, let alone setting business goals.
As a result, they just look for the most affordable ERP software and go with the most affordable ERP implementer. Also, since they don’t have clear goals, they will try to get the most out of their new systems (eg. asking for unnecessary customizations) which don’t add value to their business. This often causes a huge mess (they end up abandoning the new system and go with the old system), and all the time, effort, and money going down the drain.
For these companies, ERP implementation is simply “buying another software” and they are not prepared to redesign business processes, change standard operating procedures, re-training employees, changing company culture, and so on.
We try to avoid these companies since their ERP implementation will most likely end up in failures and they will eventually blame the ERP implementer.
Around 26% of ERP implementations fail due to a lack of a detailed project plan. A detailed project plan is the responsibility of the ERP implementer (assuming the information needed is fully provided by the company). Therefore, choosing the right ERP vendor who has industry knowledge, understands business processes, best practices, and accounting (since every transaction will have an impact to accounting), and not just IT knowledge, is so crucial.
Lack of top management involvement is reported as a main factor in 45% of failed ERP implementations. In order to understand this point, let’s take a step back.
The goal of an ERP system is to automate and integrate the different processes and teams for efficiency purposes. For companies who implement an ERP system for the first time, it involves a huge change to the company.
It requires identifying all the different pain points of all the teams that cause inefficiencies, discussing with the team to find practical solutions to those inefficiencies, and basically changing the way they work.
The messy part is, the change of one team will affect other teams since the processes are interrelated.
Therefore, companies need to be ready to make major changes since this requires heavy commitment (time, effort, and money). For example, companies may have to restructure their organization, removing unnecessary positions, changing employee job descriptions, changing warehouse layout, changing supplier selection process, and changing employee goals, KPI, and appraisals.
This is a digital transformation process which definitely requires top management involvement to resolve employees’ resistance to change (especially the not so open minded ones who have been around for a long time).
Most companies are already comfortable with the way they work and they look for an ERP system to make their companies slightly more efficient without changing anything major.
However, when this happens in real-life, we sometimes think that it will be much better if they just continue using the old system, because they are totally missing the benefits of having an ERP system.
The short answer is: when it can increase net profit and when company leaders can commit (because there may be other more urgent things that can increase net profit that leaders can focus on).
Also read: 4 Steps to Calculate your ERP Return on Investment
ERP is quite different from other business software because it’s the automation and integration that you are looking for. If you think team integration and process automation is not necessary for you, don’t get an ERP system. Just get accounting, crm, or hr software separately. They are much cheaper.
The majority of ERP implementation failures are not due to the ERP system, but the lack of planning and top management involvement. Don’t choose an ERP system based on brand or hearsay. When you hear someone with bad experience badmouthing a certain ERP system, it is most probably because they choose the wrong implementer (most often with freelancers or IT consultants who don’t understand accounting and business processes).
Most often, the actual cost of implementing an ERP system ends up more than the initial assessment, so it’s better to start from ERP systems that cost half of your actual budget. Starting with Odoo vendors or a local ERP vendor is a good start. Go with the more expensive ERP software only when you know the affordable ones are not a good fit for you (only if you know you need certain features and the cost to customize those features are more than getting another more expensive ERP software.
If you are getting an ERP system for the first time, we always recommend businesses to implement the system without any customization in advance. This is because during your implementation process, companies often realize they have to change their business processes. When this happens, oftentimes their earlier concerns are already solved so there is no need to customize, or they realize there are more important features to customize.
We’ve heard a lot of stories where companies try to cut costs by hiring internal software developers or freelancers because they think those are cheaper. Majority of them ended up in failures (freelancers disappear with bugs unfixed, internal software developers are unclear of what to build while companies blame them thinking it’s their jobs, etc.) and they ended up starting all over again with professional ERP implementers. It took them years longer and a lot of money going down the drain.
This is how we recommend you to filter your ERP vendors:
Start with the most affordable ERP system like Odoo or Impact. Find out who they are (visit their websites) and contact them to learn more about their ERP software. They may already have the customizations you are looking for without you paying for it.
Assess if they understand your pain points and are able to convince you that they can solve your pain points. A good ERP implementer can tell you exactly how from the point of view of software, business process, and accounting. You should avoid those who tell you that their ERP can do whatever you need without explaining how. Most often, they themselves don’t really understand what you are talking about.
Although this is not a bad way to do an initial assessment, it does not guarantee future success, either. Similar past clients can have different pain points, and you don’t really know if their implementation is a success or a failure. But there is no harm in asking.
Understanding how consulting companies hire their employees can oftentimes tell you about how much they value their customers’ success.
It is much better to choose the more expensive ERP vendor that is more likely to bring you ERP implementation success, than to choose the cheaper option but they end up in a mess and you end up paying 2-3 times the price.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.
