Kanban: Definition, 6 Rules, and its Benefits
Kanban is a crucial part of the Just in Time (JIT) system, which we discussed…
Sean Thobias
May 17, 2025A distributor is someone or a company that helps to sell and deliver goods and services from the producers to the customers. They are necessary for many industries, such as electronics and pharmaceuticals, as they link the manufacturers and customers.
As technology advances, customers want goods delivered quickly, and distributors become more critical in the supply chain.
This article provides a complete understanding of distributors, including their types, functions, and benefits. It also outlines what businesses need to consider when selecting a distributor so that they can make informed choices about their distribution channels.
A distributor is a middleman that helps transfer products or services from manufacturers or suppliers to retailers and end-users.
Distributors typically work with many manufacturers and downstream entities and act as an agent for each manufacturer, agreeing to sell their products to retailers, value-added resellers (VAR), or wholesalers.
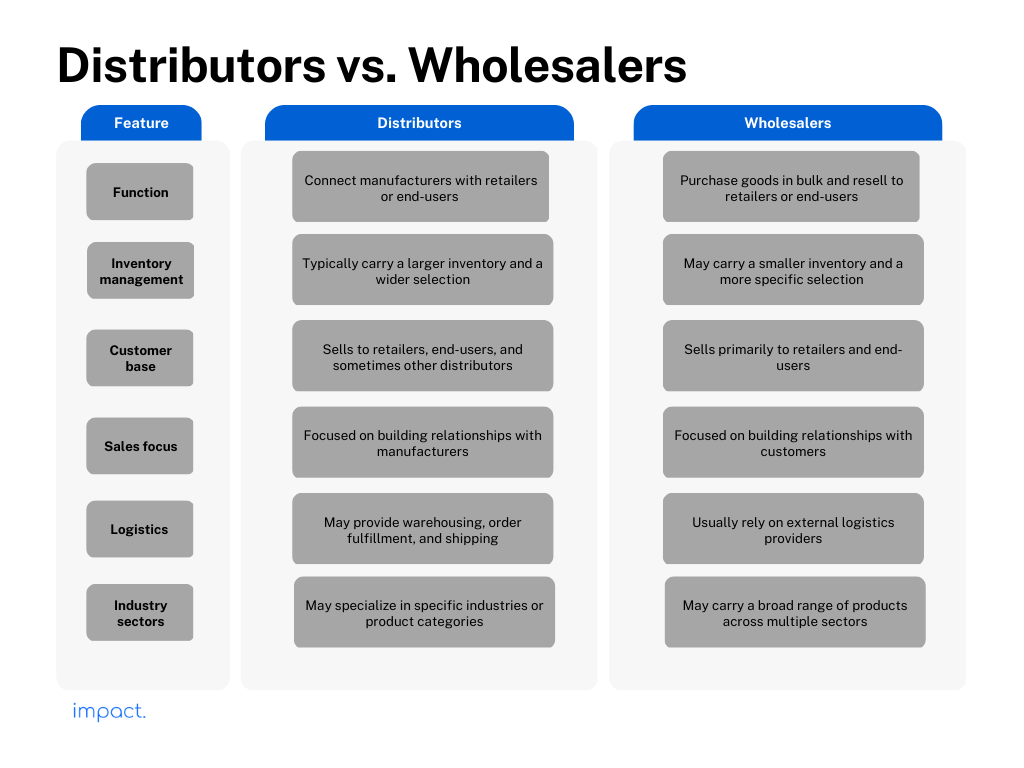
People sometimes mix up distributors and wholesalers, but they are pretty different.
Wholesalers mainly purchase goods in bulk from manufacturers and sell them to retailers. On the other hand, distributors have a more extensive range of responsibilities, including marketing, warehousing, and financing.
Read More: What is a Wholesaler? Definition, Benefits, and 4 Challenges
Depending on their strategy, distribution can be simple or complicated. Sometimes companies use several distribution channels or techniques. Here are five different types of distributors in the supply chain:
This type of distributor is sometimes called a one-level channel. They provide a simple way to get products to customers without using intermediaries. Manufacturers are an example of direct distributors because they give out their products themselves.
Direct distributors sell their products in different ways, such as online shops, physical stores, door-to-door sales, or directly from the factory. This type of distribution is helpful for businesses because it helps customers trust the brand and improves their experience. Direct distribution is widespread in industries such as cars, technology, and agriculture.
Indirect distributors involve other people or businesses that buy products from manufacturers and sell them to consumers. These distributors could be wholesalers, brokers, or agents.
Sometimes manufacturers don’t have the resources to distribute their products, so they use indirect distribution. This type of distribution also helps businesses reach more customers and make more sales because their intermediaries might have established connections with buyers and customers.
But there are also some downsides to indirect distribution. It adds extra costs, meaning customers pay more for the products. It also slows down the delivery of the products and gives less control to the manufacturer.
This type of distributor gets the exclusive right to sell certain products in a specific area for a set amount of time. Distributors that get this exclusivity are the only ones allowed to sell those products in that area during that time.
The manufacturer and the exclusive distributor make an agreement that outlines everything they need to do, such as pricing, marketing, and sales targets.
For example, a luxury bag manufacturer might only allow a few stores in certain areas to sell their bags through an exclusive distributor. This limited availability gives the distributor much control over how they sell and distribute the bags.
In an intensive distribution model, the distributor distributes products to as many places as possible, unlike an exclusive distributor.
Manufacturers usually use this strategy for products in high demand but sold at a low price, like snacks, drinks, and other fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG).
Businesses use intensive distributors to make their products more visible and accessible to customers. Companies can convert leads to more sales and a more significant market share for the manufacturer.
The role of distributors is critical in the supply chain, as they perform various functions vital to the success of manufacturers and suppliers. Here are the five essential functions of distributors.
Distributors play an essential role in managing inventory levels and stock levels. The function of a distributor is to keep an eye on how much stock they have and ensure they have enough of the right products to meet customer needs.
To guarantee on-time delivery of products to the correct location, distributors need to maintain proper inventory and stock levels. For example, if a retailer requires a specific product, the distributor must have sufficient stock to fulfill the order. Inadequate inventory can delay the delivery of the product to the retailer, leading to dissatisfied customers and missed sales opportunities.
Read more: Just in Time (JIT) adalah: Definisi & 8 Cara Penerapannya
Distributors provide warehousing and storage facilities to store products that they receive from manufacturers. The distributors design these facilities to keep the products safe, secure, and in good condition until they are ready to ship them to retailers or end customers.
While the products are in the warehouse, the distributor is responsible for any possible losses. For example, products may get damaged, expire, or become outdated. It is crucial for distributors to properly handle and dispose of any goods that have expired or are damaged.
Read More: Apa itu gudang? 12 Alasan Mengapa Gudang Dibutuhkan
One function of a distributor is to receive orders from retailers and consumers, process them quickly, and ensure timely delivery. Distributors checks if the products ordered are available and look for additional instructions. Next, the distributor packs the products, generates shipping labels, and schedules the delivery.
Distributors may combine orders from different retailers and consumers into one shipment to save money on transportation costs, called order consolidation. This method is cost-effective as it reduces the number of trips required.
Another function of distributors is the transporting and delivery of goods. Distributors transport products from their warehouses to the buyers who have purchased them. This means that distributors must figure out how to move the products from their warehouse to the buyer’s location.
When a buyer orders products, the distributor makes sure the products are packaged and labeled correctly for shipping. They may hire a shipping company or use their delivery trucks to transport the products.
The distributor is responsible for ensuring that the products are delivered to the buyer safely and in good condition. This involves tracking the products during transit, monitoring temperature and humidity levels, and preventing damage during loading and unloading.
Not many people know that promoting and selling products is an essential aspect of the role of distributors in the supply chain. Distributors must possess market expertise and knowledge of customer needs, which helps them develop customized marketing strategies and sales programs.
Distributors collaborate with manufacturers to create marketing materials and incentivize retailers to sell more products. They use their market expertise to identify new opportunities and work with online and specialty stores to expand sales channels. Additionally, they support retailers by providing product information, training, and merchandising.
Distributors make sure customers are satisfied by handling their questions and complaints. They act as the go-between for the manufacturer and the customer to resolve possible problems.
Distributors assist customers with product issues by coordinating with the manufacturer for a refund or replacement in case of damages. Additionally, they inform customers about product features and warranties. Customer support is crucial for building customer loyalty and trust, benefiting the manufacturer and retailer.
Distributors play a critical role in the supply chain as they provide a range of benefits to both manufacturers and retailers. However, they also have their disadvantages. The table below shows the pros and cons of utilizing distributors.
| Category | Pros | Cons |
| Market Reach | Distributors can help reach a wider market through their established network and relationships with retailers and customers. | Distributors may not prioritize your brand if it is not one of their top performers, and they may not always have the same passion for a business’s product. |
| Logistics | Distributors can take care of the logistical tasks, such as warehousing, shipping, and delivery, allowing you to focus on other business areas. | Businesses may have less control over the shipping and delivery process, and additional costs may be associated with using a distributor. |
| Sales | Distributors can provide sales support and help increase your product’s visibility in the market. | The distributor’s sales force may not always have the same level of knowledge or enthusiasm for your product as you do, and they may not be able to provide the same level of personalized attention to customers. |
| Cost | Distributors can help to reduce costs by allowing businesses to share expenses with other brands, such as warehousing and shipping costs. | Distributors may charge a commission or other fees that can eat into your profits. |
| Risk | Distributors can help reduce risk by assuming responsibility for inventory and sales. |
Companies may have less control over their product’s branding and marketing when using a distributor, and there is always the risk of the distributor going out of business or not performing as expected. |
A distributor’s role can be crucial in determining the success of a business. Whether a company is a newly-established startup or an established corporation does not matter.
Businesses must identify a partner who comprehends their business and has the expertise to assist them in achieving success.
Here are some factors to consider when choosing a distributor:
Customer service: When selecting a distributor, it is crucial to consider their customer service. This refers to the level of support they will provide customers, including handling any issues or complaints they may have promptly and professionally. Good customer service can help build and maintain a positive reputation for businesses. In contrast, poor customer service can lead to negative reviews, lost sales, and damage to brand reputation.
Below are examples of Indonesian and global distributors, categorized based on their areas of specialization.
Distributors from the F&B sector include PT Infofood Sukses Makmur Tbk, PT Mayora Indah Tbk, The Coca-Cola Company, Dole plc, and General Mills.
Distributors from the retail sector include Unilever plc, PT Sinergi Inti Plastindo Tbk, PT Erajaya Swasembada Tbk, PT Mitra Adiperkasa Tbk, and PT Mustika Ratu Tbk.
Distributors from the healthcare sector include PT Kimia Farma Trading & Distribution, McKesson Corporation, Cardinal Health, Alfresa Holdings, and AmerisourceBergen Corp.
Distributors in this sector include PT Pertamina (Persero), PT Perusahaan Gas Negara Tbk, Shell plc, Weatherford International, and Schlumberger Limited.
As the demand for quick delivery continues to rise, the role of distributors becomes more crucial in the supply chain by linking manufacturers and customers.
This article has effectively highlighted distributors’ indispensable role in business by providing readers with a comprehensive overview of their functions, benefits, and different types.
Businesses must consider various factors when selecting a distributor to make informed decisions about their distribution channels. In summary, companies rely heavily on distributors for their success, and one cannot overemphasize their significance.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.
