Kanban: Definition, 6 Rules, and its Benefits
Kanban is a crucial part of the Just in Time (JIT) system, which we discussed…
Sean Thobias
May 17, 2025In 2015, McKinsey reported that supply chain finance (SCF) is a growing market. The consulting firm states that the financial practice has a potential global revenue of $20 billion.
Moving ahead six years later, the evidence of that growth is still present. Allied Market Research valued the SCF market at $6 billion in 2021. They even predict that it will reach $13.4 billion within this decade.
Many businesses have grown to accept this financial service which drove supply chain financing’s growth. Despite hiccups in 2020, the demand for SCF grew as companies preferred it for their supply chain security.
So, what is a supply chain finance?
In simple terms, supply chain financing eases suppliers to receive funding. A third party does the backing on your behalf.
If you want to know more about supply chain financing, continue reading this article. We will explain SCF in detail and its importance for your business performance. You will also understand ways to implement SCF successfully.
Supply chain finance (SCF) is a strategy that helps companies cut costs. SCF improves efficiency for everyone involved in a transaction — minimizing supply chain disruptions.
Think of it as a win-win solution.
With the buyer’s approval, suppliers receive early payment via a financier. Funding could be from a bank or other financial institution. This strategy provides short-term credit that boosts working capital and liquidity for all.
Supply chain finance is different from other types of financing. We compare it with a traditional bank loan and factoring.
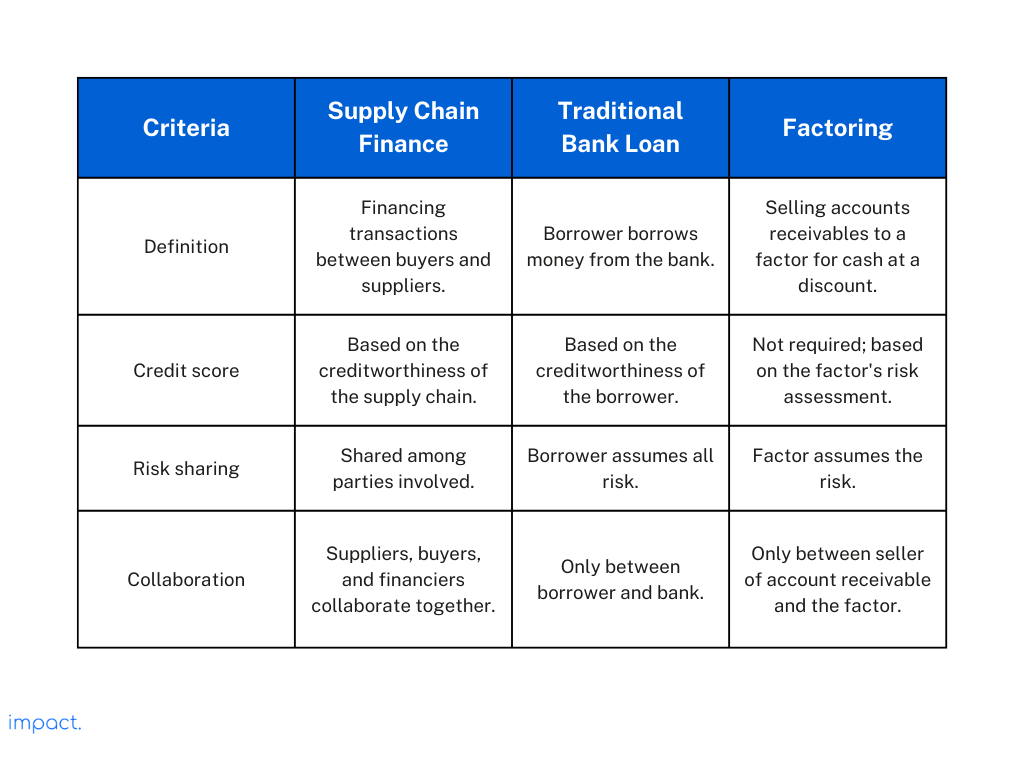
Unlike a bank loan, supply chain financing bases its credit score on the supply chain. Banks only base the credit score on the borrower.
Suppliers, buyers, and financiers collaborate to optimize the supply chain’s financial performance. Compared to a loan, there is a shared risk for all parties. In a traditional loan, the transaction is between the borrower and the bank.
Let us move on to its differences with factoring. Factoring is selling accounts receivables to a factor for cash at a discount. Factoring can improve a company’s short-term cash needs.
Factoring sells accounts receivable, while SCF finances transactions between buyers and suppliers. Factoring suits businesses with weaker credit as the factor assumes the risk. Factoring does not require an ongoing relationship between a company and its suppliers.
All supply chain financing programs are different. However, its platform and external financiers are involved. The process flow typically involves the following six steps:
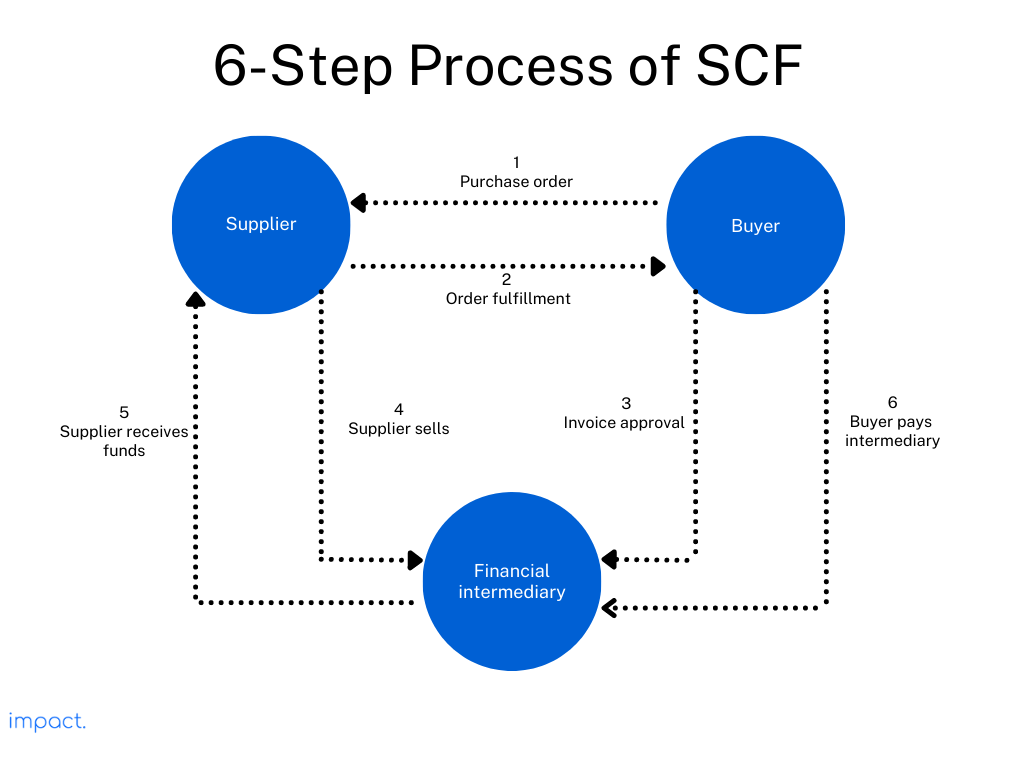
Purchase order: The buyer initiates an order with the supplier for the goods and services.
There are various types of supply chain finance that you need to know about. Each technique provides services that cater to different markets. We have compiled five of them for you.
We mentioned earlier that SCF differs from factoring. However, when you reverse it, the company arranges a financial institution to pay suppliers earlier.
The financial institution pays the company on the due date of the invoices. Reverse factoring allows the business to extend payment terms so suppliers can get paid earlier.
This method allows companies to use their good credit rating to help their suppliers improve their cash flow.
This financing strategy is when you offer suppliers an early payment for a discount on their invoices. The “dynamic” in dynamic discounting refers to the flexibility to adjust rates on payment dates to suppliers.
The company bases the markdown on the time value of money and the supplier’s cost of capital. The earlier the supplier accepts payment, the higher the discount they receive.
Dynamic discounting helps companies improve cash flow by paying suppliers earlier and decreasing the amount of money owed to suppliers.
This type of financing allows a company to use its inventory as collateral. The lender evaluates the estimated sales value of your inventory and offers a loan amount based on that assessment. The interest rate may also depend on your credit score.
They will hold your inventory and return it once you make full payment. However, if you fail to meet your obligations, the lender will sell your merchandise to recover funds.
TCI is a method that helps protect businesses from non-payment. This method is not a traditional form of supply chain financing. However, it does play an essential role in mitigating the risks involved.
When you get non-payment protection, you can offer better terms to suppliers. Your capital and cash flow are more stabilized. TCI can also help you secure better financing terms from banks. Your credit score will increase as there is confidence in the payment of accounts receivable.
This financing method provides funding to pay suppliers to fulfill customer orders. PO financing is helpful for small businesses that do not have enough inventory or cash to fulfill orders.
A lender provides funding based on a purchase order value. The business uses this to pay its suppliers. The customer pays the company directly upon order fulfillment to repay the lender.
Supply chain finance offers various gains to those involved. Below are some benefits for the buyers, suppliers, and financiers.
Read more: What is SRM? Definition, Benefits, & 3 Implementation Steps
Read more: What is a Supplier? Their role & 6 criteria to look out for
While there are some benefits that supply chain finance provides, some businesses are hesitant to implement it. Here are some reasons why.
Supply chain finance can be challenging to employ. It can be tough to implement without an understanding of how it works.
SCF involves tech-based processes that not all organizations are ready for. They must invest in technology platforms to handle transaction volumes and provide real-time data visibility.
Both suppliers and buyers must undergo an onboarding process to understand the processes. Training can take time and delay implementation.
Not many companies have the option to participate in supply chain financing. Top-tier suppliers with significant transactions and established credit histories can access SCF programs.
Companies with poor credit scores may not qualify for supply chain financing. Financial institutions might consider them high-risk borrowers.
Smaller-sized organizations may face challenges due to their resources. They might not meet the requirements set by banks and other financiers. Some now offer programs for smaller suppliers.
Buyers may worry that requesting extended payment terms through SCF could affect their ties with suppliers. Supply chain finance involves third-party involvement, and suppliers may feel pressured to accept the rates given. Such situations can create tensions in the buyer-supplier relationship.
Buyers could also exploit the program to make late payments. This action can harm the supplier’s cash flow and ability to operate effectively. Buyers that abuse supply chain financing can undermine the supplier’s trust.
Legal or governing restrictions can limit some industries from engaging in supply chain financing. Certain countries may limit SCF program availability due to financial instrument usage restrictions.
Legal or contract-related issues may need to be addressed, even if an industry permits supply chain financing. Contract limitations can affect SCF program feasibility, such as not allowing receivables sale or limiting payment terms.
Businesses realize the significance of managing working capital in tough times and seek ways to free up trapped cash within the financial supply chain. Supply chain finance has become the most preferred choice for improved cash flow. Companies must consider the following factors to benefit from supply chain financing.
Different financial institutions may have different types of supply chain finance programs. Identifying and researching which financial providers best suit your business requirements is vital. Consider the financing type, fees, reputation, and transaction volume handling ability.
Choosing the wrong financier can cause SCF to fail. When your backer does not align with your business goals, it can lead to inefficient processes and unnecessary costs.
Everyone in your company should work closely together to ensure a successful financing. These key stakeholders may include internal departments such as procurement, accounting, and IT.
Each department should align its objectives and KPIs. When everyone strives for the same goals, the program will run smoothly. There will be minimal conflicts and misunderstandings.
Transparency is critical in any business relationship and applies to supply chain finance. Be transparent with suppliers about the financing terms to avoid misunderstandings or conflicts.
Lack of transparency in supply chain finance can lead to a damaged relationship with your suppliers. Their trust in you will reduce, and they may hesitate about future collaborations.
All parties involved in supply chain financing should adhere to the applicable policies. Compliance means following rules to prevent fraud, bribery, corruption, and breaking trade sanctions.
Failing to comply with these regulations can have severe legal and reputation consequences. Everyone involved must implement appropriate measures to mitigate these activities. There should be regular audits of the program.
With technology, you can reduce manual processing and increase efficiency. Manual input is labor intensive, increasing the overall cost of supply chain financing.
ERP platforms, like Impact, can provide real-time visibility into transactions. Its accounting module allows you to see invoice, payment, and request statuses instantly. It also reduces human errors with its automated processes.
Supply chain finance emerged from the pandemic stronger than ever. It is now a piece of better equipment to challenge supply chain disruptions.
Further down the line, SCF will be a lucrative option for businesses of all sizes. Here are some potential trends to watch out for in this industry.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain technology has the potential to transform SCF. Businesses can use AI to analyze data and identify risks. Blockchain, on the other hand, can improve the security and transparency of transactions.
As technology improves, SCF becomes a more accessible financial solution. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) will likely adopt supply chain financing even more. They can access better financing and improve their supply chain operations.
In the future, relying solely on one finance provider may not be popular. Instead, programs will utilize a variety of financing options.
Right now, invoice financing is the primary focus of supply chain finance. However, there is a growing interest in expanding the range of financing options available – inventory and purchase order financing.
A broader approach to supply chain finance allows companies to optimize cash flow and manage risk effectively.
We will likely see more collaboration between traditional banks and fintech companies as the industry evolves. This union aids innovation, reduces costs, and improves financing access.
These partnerships can leverage the strengths of both for better supply chain financing. Fintechs are known for their agility, innovation, and technology expertise. Traditional banks have deep experience in financial regulations, risk management, and financing operations.
Supply chain finance is a strategy that has been growing steadily in recent years. As a financing option that benefits all involved parties, SCF is very lucrative.
Extended payment periods in supply chain finance benefit buyers and suppliers while creating investment opportunities for financiers. Using SCF, many companies have cut costs, improved efficiency, and minimized supply chain disruptions.
Supply chain finance can be adapted to meet the changing needs of businesses as the business landscape evolves. Its evolution creates new opportunities for companies of all sizes to optimize operations and secure supply chains.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.
