Kanban: Definition, 6 Rules, and its Benefits
Kanban is a crucial part of the Just in Time (JIT) system, which we discussed…
Sean Thobias
May 17, 2025The company’s warehouse plays a vital role in storing its products—essential tasks like picking and receiving occur there.
Companies need to reduce travel time and unnecessary steps to make warehouses more efficient. The proper warehouse layout can help achieve this. Designing the best layout requires paying close attention to details and analyzing data.
Consultants and companies specializing in handling materials and setting up racks can assist in determining the most suitable warehouse layout based on the available space. In this chapter, we will explore the concept of warehouse layouts, essential factors to consider when designing them, and the benefits they offer.
A warehouse is an integral part of manufacturing and the supply chain. It’s where all the materials, from raw to finished goods, are stored. Companies need to organize the layout properly to make things run smoothly in the warehouse.
Warehouse layout involves planning how to arrange things in the warehouse for efficient operations. A well-designed design improves production and distribution processes.
Because there are many tasks in the warehouse, like receiving goods, shipping them out, and storing inventory, companies need to figure out the best way to set up the warehouse. Organizing the layout well allows companies to make the most of the space and keep costs low.
Managing warehouse activities is complicated, so companies often use Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) to automate things in the warehouse.
Read more: Understanding Warehouses: Definition and its Importance
You need to consider three important things to create an efficient warehouse layout. Let’s take a look at each of these aspects:
According to a survey conducted by Cranfield University in 2008 (Baker and Perotti), allocation in the warehouse floor area is as follows: 52% for storage, 17% for pick/pack operations, 16% for receiving and shipping, 7% for value-adding services, and an additional 7% for storage areas like battery charging, empty pallet storage, and other uses.
Different operations determine the distribution of these areas. To ensure the warehouse is efficient, the company must collect data on the other sites it needs for its operations.
A company warehouse requires various areas for smooth operations. These areas include:
For accurate analysis, it is crucial to consider current and past data and future volumes and changes in product or area characteristics. This comprehensive approach allows for a more reliable understanding of the data.
Different companies have varying needs, which affect the calculation of required space. Below, you’ll find several commonly used formulas for space calculation.
To calculate the space needed for arranging vehicles at a vehicle manufacturing company, you can use this simple formula:
| Space = hours to (unload cargo) / Shift time x (number of pallets × space per pallet) |
For example, let’s say the company receives 20 vehicles each day. Each load has 26 pallets, each measuring 1.2 meters by 1.0 meters. It takes 45 minutes to unload a load and 30 minutes to inspect it. The company operates for eight hours.
Using the formula, we can calculate the space requirement like this:
| Space = {rounded((20 × 1.25) ÷ 8) × (26 × (1.2 × 1))} = 4 × 31.2 = 124.8 square meters |
In addition to this space, we also need to consider the work and travel space around the pallets. The amount of this space depends on the type of forklift or pallet truck used for unloading and loading the vehicles. It might be necessary to double the shipping area’s space to provide enough room to access the pallets.
First, you need to evaluate and record the properties of each item and the attributes of the potential storage options. Calculate how many goods can be stored per product line and convert that into the number of pallets required. It will help you determine the pallets needed for each product line.
Next, create a chart that details the number of pallet locations needed and their height requirements. Remember that the height of the pallets may vary depending on the products.
Look at the table below, which shows the characteristics of each item and the different storage options we considered. The table also includes as much information as possible about storing and ordering the products. This information will guide you in choosing the most suitable storage and handling options for your needs.
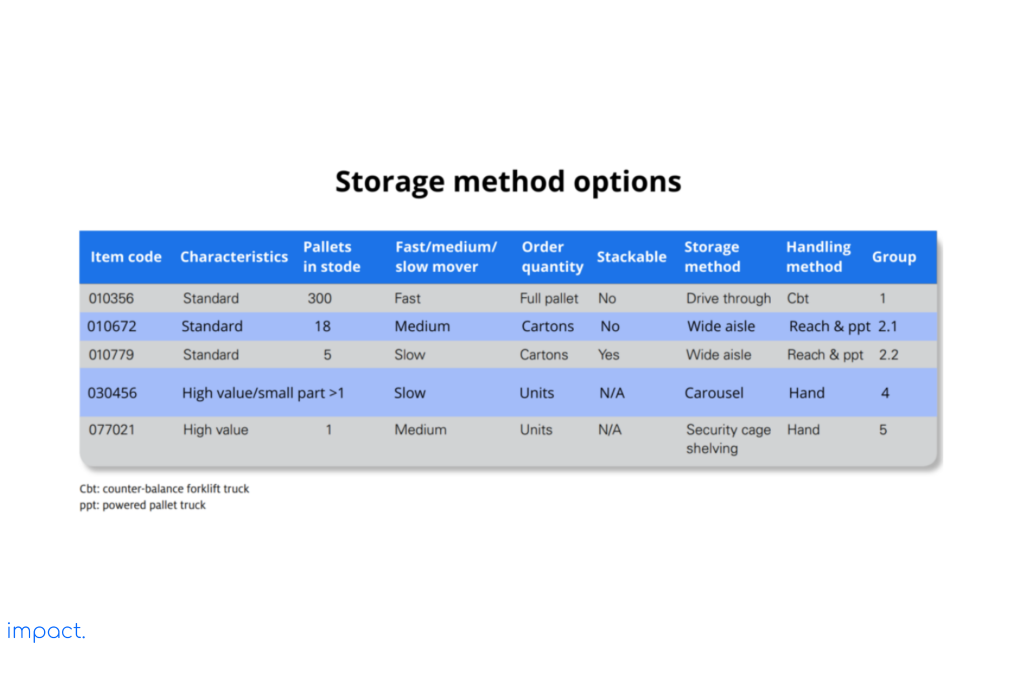
One important thing to consider when planning a warehouse layout is the width of the aisles. The aisle width is simply the distance between racks next to each other. To ensure everyone stays safe, companies must figure out how much space is needed between pallets once they are on the shelves. The aisle width depends on how much the forklift truck can turn and the size of the pallets it carries.
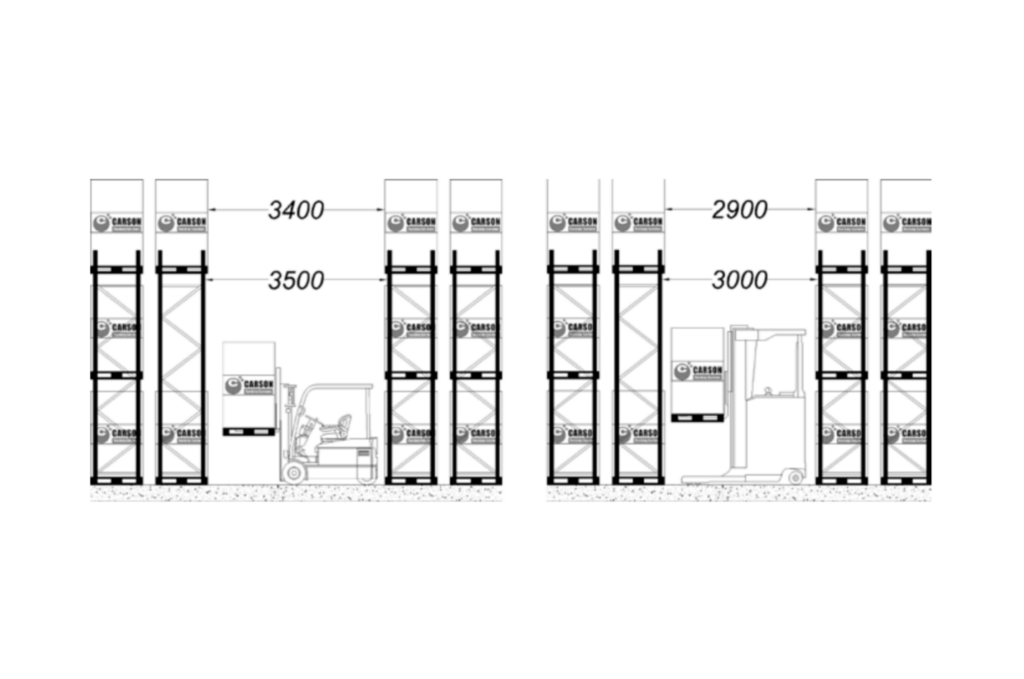
Source: Richard G. 2011. Warehouse Management. Aisle widths (courtesy of Carson Racking Systems Limited)
To keep things safe and efficient, it’s a good idea to add about 100 mm of space on each side of a typical pallet, making a total of 200 mm. This extra space helps with quickly storing and getting pallets when needed. Another thing to consider is the overall width of the forklift truck as it moves along the stacking aisle.
When choosing the aisle width, it’s crucial to find the best balance between productivity, making the most of the available space, flexibility, safety, and the cost of the equipment needed for the specific job.
In addition to the aisles, the warehouse reserves specific areas for tasks such as packing, enhancing product value, and managing returns. The size of these areas depends on factors such as the level and type of work, the number of people involved, and the equipment used.
When planning warehouse space, people sometimes forget to consider specific areas. These areas include the storage, recharging, and replacement spots for forklift batteries or gas cylinders, as well as parking spaces for equipment when it’s not in use. Remembering these things is crucial for using the warehouse space efficiently.
To determine the suitable warehouse layout for your needs, analyze your gathered information and goals. The flow of your warehouse relies heavily on the available space and how things will move in the entire operation.
Companies employ three warehouse layouts to organize their operations effectively: U-shaped, I-shaped, and L-shaped.
Companies commonly utilize the U-shaped warehouse flow because it effectively serves beginners. This layout arranges all the parts semi-circle, with the sending and receiving areas on opposite sides. In contrast, the storage area occupies the middle.
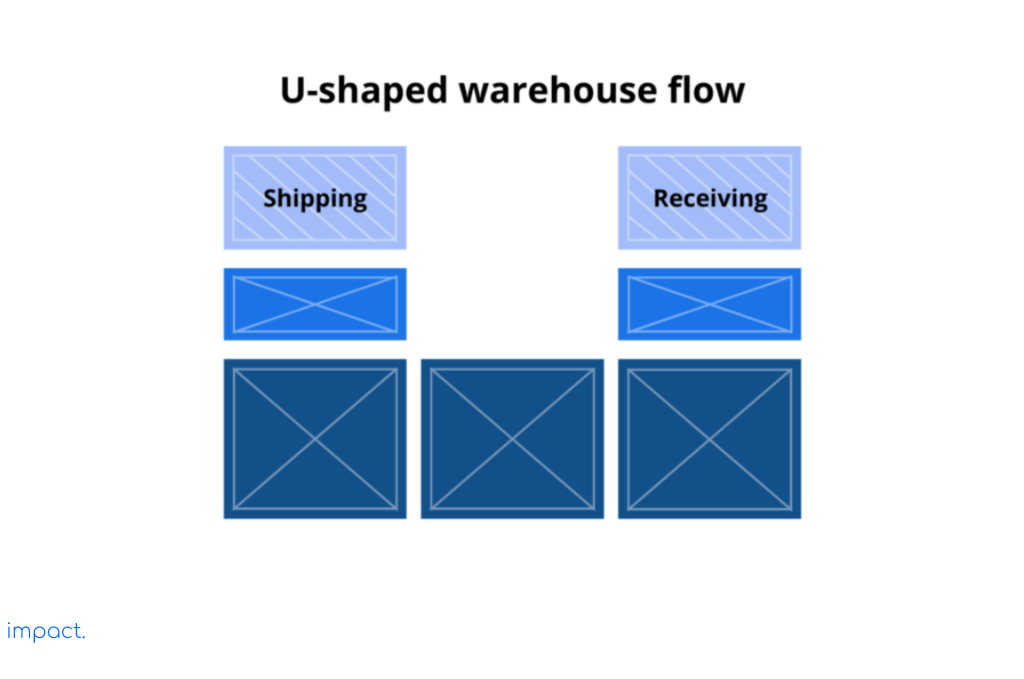
The U shape helps to keep the main traffic flows in the warehouse separate and efficient. By having the material come in and go out on different sides, we avoid jams and keep things running smoothly. This flow of goods also helps to save space.
The entrances and exits on the same side of the building reduce the need for ample package space. It enables our employees to swiftly transfer products between the reception and delivery areas. However, one drawback of the U-shaped flow is that it can create issues when the sending and receiving sites are nearby and share similar functions. These circumstances can result in production bottlenecks.
Big companies with large storage spaces prefer this type of warehouse flow. They like it because these companies usually have many things to make and need a straightforward way to bring something in and take them out.
The shape of this kind of warehouse goes straight from where things come into, where they go out, and the other way around. This type is the best way to make the most of the whole length of the warehouse.
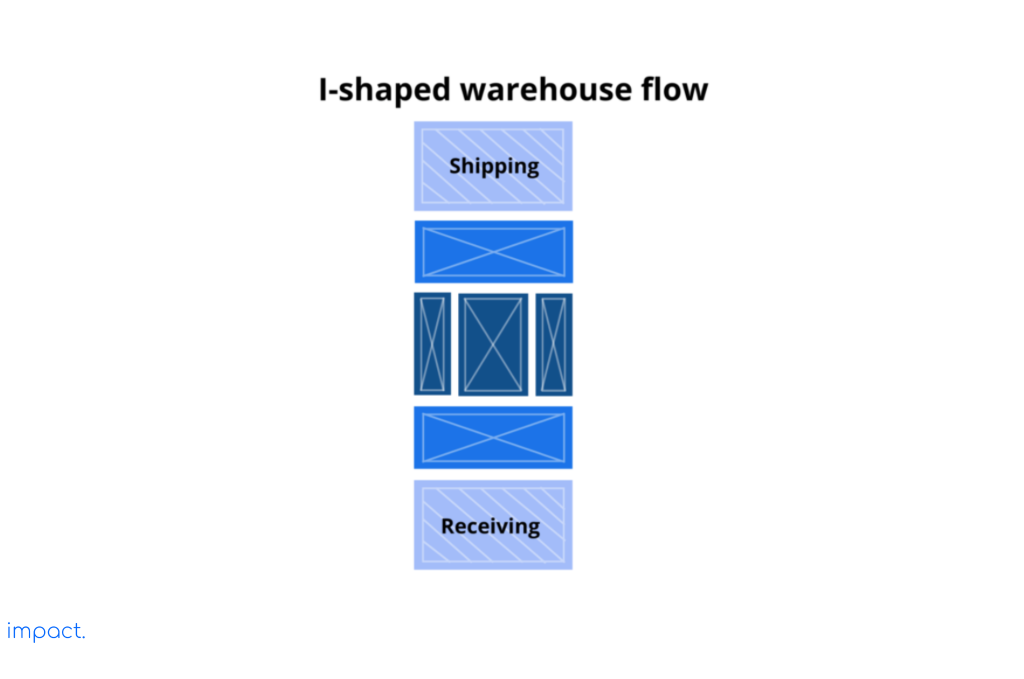
It also keeps similar things apart, like on an assembly line, so working with them is more manageable. This way, there are fewer places where things can get stuck or delayed because they have to go back and forth.
But there’s a downside to this type of warehouse. The company needs enough space on both sides of the building for loading and unloading. It can cost more money to buy equipment for bringing things in and taking them out. Also, things often have to travel through the whole warehouse to get where they need to go.
The least common flow type is this one, used for buildings with an L shape. The L shape consists of a shipping area on one side and a receiving site on the adjacent side, forming a 90-degree angle. L-shaped flow and I-shaped flow share similar advantages.
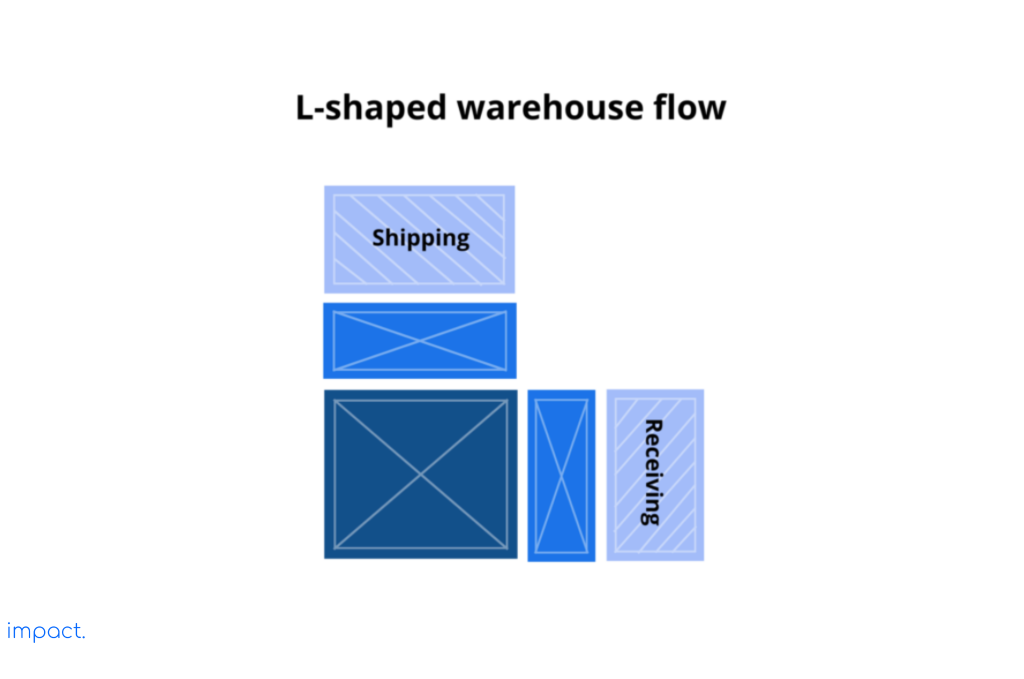
The L shape helps prevent congestion by avoiding back-and-forth movement. It effectively separates products by placing inbound and outbound docks on opposite sides. However, the main downside of the L-shaped warehouse design is that it needs much space to work well.
Read more: 7 Tips for Selecting the Ideal WMS
Designing a warehouse involves considering all the crucial areas a company requires and using the available space best. Here are the steps to develop a warehouse:
Before you decide, take some time to create a visual tool that will help you estimate the available space. It involves marking areas where you can place shipping docks and accommodate recipients. Blueprints will assist you in seeing the warehouse as a blank canvas.
Begin by planning how to prepare the different components of the warehouse. This process involves considering offices, employee living areas, and shipping and receiving docks. Consider all the main areas, such as assembly lines, manufacturing materials, workstations, conveyor belts, and other equipment needing space.
Once you have carefully examined the room, you can determine which designs will naturally meet your needs. If you want to keep the shipping and receiving areas close together, you can opt for a U-shaped warehouse flow.
Suppose your priority is to maintain a smooth workflow with minimal space usage. In that case, you may prefer an I-shaped warehouse flow. If you have a warehouse with a unique shape, an L-shaped warehouse flow would be suitable.
Once you’ve decided on the ideal flow for your requirements, it’s time to buy and assemble all the equipment needed to optimize movement within the warehouse. This equipment comprises forklifts, racks, bins, pallet racks, rolling ladders, picking and packing stations, processing technology, and other machinery essential for efficient warehouse operations.
When you’re unsure, test your proposed plan. Track the most profitable traffic flows before installing equipment into the warehouse layout. Consider the opinions and concerns of the warehouse staff and other participating employees actively involved in the workflow.
Here are some of the benefits of implementing warehouse layouts in companies:
The main aim of designing a warehouse layout is to optimize warehouse space utilization. By effectively using the available space, companies can reduce the time required for product manufacturing and streamline processes at every stage.
It is essential to make the most of every inch of the warehouse. The size and area of the warehouse play a significant role as they directly impact the overall efficiency and productivity of the space.
The main objective of creating a practical warehouse layout is to optimize operations, enhance productivity, and minimize the chances of congestion or errors. Surveys have shown that 67% of customers take their business elsewhere when they receive notification that an item they ordered is out of stock.
The warehouse management team actively collaborates with the operations management team to ensure a seamless production process from start to finish and efficient and accurate order fulfillment.
Some warehouse layouts can be more expensive to construct and maintain, depending on the available floor space. Understanding the materials on hand and determining the appropriate staff positioning are essential factors in finding a suitable design.
By implementing a suitable warehouse layout, companies can allocate resources more efficiently. It includes using the budget for warehouse maintenance and hiring the correct number of employees to carry out the operations in the warehouse environment.
Maintaining tidiness and avoiding significant problems in the warehouse is possible by implementing an efficient warehouse layout. An appropriate floor plan for the warehouse reduces the risk of goods being misplaced or mishandled, ensuring that everything has its designated place in the flow of the operations.
Efficiency is critical to organizing all warehouse operations. The design of a warehouse plays a vital role in effective warehouse management. It actively creates an environment where it effectively manages inventory, swiftly replenishes stock, treats staff fairly, and efficiently fulfills orders.
When you face a space shortage in a warehouse, you have several options. You can expand the warehouse, rent additional space, or make more room in the existing building.
Another way to increase available space is by reducing inventory levels. However, the warehouse manager may not have the authority to do this. Nevertheless, the warehouse manager can identify slow or stagnant stock and collaborate with the sales and finance departments to dispose of it as agreed.
Here are some options you might have missed:
Read more: 7 Warehouse Picking Methods: How to Choose the Right One
To create an efficient warehouse layout, we need to minimize the number of travel and labor touchpoints. It will help us avoid congestion and traffic jams as much as possible, ensuring that movement occurs logically.
There are three types of flow warehouses that companies can use. The most common one is the U-shaped flow, which makes it easier for warehouse traffic to move smoothly.
Furthermore, we can automate all of our company’s business processes by using an ERP system. Impact ERP also includes a WMS module that reduces waste and streamlines the picking process. In addition to the WMS module, ERP has various other modules, such as inventory, accounting, sales, and HCM.
Richard G. 2011. Warehouse Management. Great Britain: Kogan Page Limited.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
See how our ERP provides better value.
Speak with our consultant to explore how we can improve your accounting, processes, and people.
