Transportation Management 101: Benefits, Key Success Factors & Metrics to Track
In the previous chapter, we discussed in full how important effective order fulfillment is to…
Insight Team
December 18, 2023In today’s digital age, the importance of efficient order fulfillment cannot be overstated. 80% of customers say the delivery experience influences their future buying decisions and 75% of consumers are willing to pay more for faster shipping. These figures clearly demonstrate the critical role order fulfillment plays in customer satisfaction, brand loyalty, and ultimately, business success.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of order fulfillment, exploring order fulfillment process, best practices for optimizing the process, and insights into ensuring your customers receive their orders quickly and efficiently.
Order fulfillment refers to the entire process of receiving, processing, and delivering customer orders for products or services. It encompasses a series of steps that take place from the moment an order is placed until the customer receives the ordered items.
The goal of order fulfillment is to efficiently and accurately meet customer demands while minimizing errors and delivering a positive customer experience.
Timely and accurate order fulfillment is directly tied to customer satisfaction. When customers receive their orders promptly and in good condition, it contributes to a positive experience and fosters customer loyalty.
Satisfied customers are more likely to become repeat customers. Efficient order fulfillment builds trust and confidence in the reliability of a business, encouraging customers to return for future purchases.
The order fulfillment process reflects directly on a company’s reputation. Consistent and reliable fulfillment contributes to a positive brand image, while errors or delays can lead to negative reviews and damage a company’s reputation.
In today’s competitive market, businesses are constantly striving to differentiate themselves. Efficient order fulfillment system can be a key differentiator, attracting customers who prioritize a seamless buying experience.
Streamlining order fulfillment processes can lead to cost savings. This includes optimizing inventory management, reducing errors that result in returns, and improving overall efficiency in picking, packing, and shipping.
Effective order fulfillment requires accurate inventory management. Maintaining optimal stock levels ensures that products are available when customers place orders, minimizing stockouts and overstock situations.
Meeting or exceeding customer expectations during order fulfillment contributes to customer retention. Happy customers are more likely to stay loyal to a brand, reducing the need for businesses to constantly acquire new customers.
An optimized order fulfillment process ensures efficient use of resources, including raw materials, labor, warehouse space, and transportation. This leads to better resource utilization and cost-effectiveness.
Positive order fulfillment experiences can contribute to word-of-mouth referrals and positive reviews, helping a business expand its customer base. Satisfied customers may recommend the brand to others, contributing to organic growth.
The order fulfillment process generates valuable data that can be analyzed to identify trends, forecast demand, and make informed business decisions. This data-driven approach is essential for staying competitive in the market.
An efficient order fulfillment process allows businesses to adapt more quickly to changes in market demand, product trends, and customer preferences. This agility is crucial in dynamic business environments.
Meeting or exceeding customer expectations in terms of delivery times, order accuracy, and overall service quality is essential for sustaining positive customer relationships.
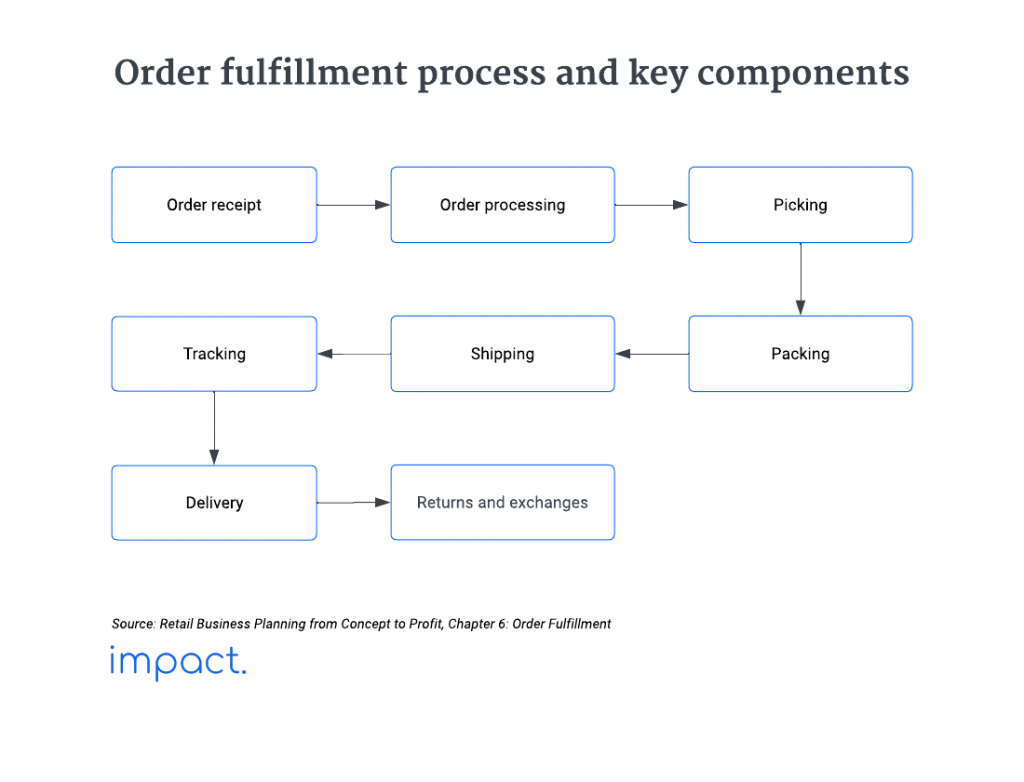
The process begins when a customer places an order through a sales channel, such as a website, phone, or in-person. The order information, including the items purchased, quantity, and customer details, is recorded.
The order is then processed within the organization’s system. This involves checking inventory levels to ensure the items are in stock, verifying pricing, applying any discounts or promotions, and confirming payment.
After processing, the items are picked from the warehouse shelves or designated storage locations. The picking process can be done manually by employees, or it may involve Material Handling Equipments (MHE) or automated systems, such as conveyor belts or robots, for more significant operations.
Once the items are picked, they are packed securely for shipment. This includes placing the items in packaging materials, labeling the package, and including any necessary documentation, such as invoices or packing slips.
The packed orders are then transferred to the shipping department for delivery to the customer. Shipping methods can vary and may include options such as standard ground shipping, express shipping, or third-party carriers.
Customers are often provided with tracking information so they can monitor the progress of their orders in real-time. This enhances transparency and allows customers to anticipate the delivery date.
The final step involves delivering the package to the customer’s specified address. This can be done through in-house delivery services or third-party carriers, depending on the organization’s logistics strategy.
Handling returns and exchanges is an integral part of the order fulfillment process. Organizations need to have established procedures for return management, inspecting returned items, and restocking inventory.
Implement a robust inventory management system that provides real-time visibility into stock levels. This helps prevent stockouts, overstock situations, and improves overall accuracy.
Automate order processing workflows to minimize manual errors and accelerate the order-to-shipment cycle. Utilize technology such as Order Management Systems (OMS) to streamline the process.
Optimize the order picking process by using efficient picking strategies such as batch picking, zone picking, or wave picking. This reduces travel time and enhances overall productivity.
Implement barcode or RFID technology to enhance accuracy in order picking, packing, and shipping. These technologies also support real-time tracking of inventory and orders.
Implement dynamic slotting strategies to organize inventory based on demand patterns. This minimizes travel time for pickers and optimizes space utilization in the warehouse.
Implement quality control checks at various stages of the order fulfillment process to ensure that the right products are picked, packed accurately, and meet quality standards.
Standardize packing processes to improve consistency and reduce errors. Utilize packaging materials that provide adequate protection for products during transit.
Choose shipping carriers based on factors such as cost, delivery speed, and reliability. Utilize multiple carriers to offer flexible shipping options to customers.
Provide customers with real-time order tracking information. Transparency in the shipping process enhances the customer experience and reduces inquiries to customer support.
Develop efficient processes for handling returns and exchanges. Clearly communicate return policies to customers and strive to process returns quickly and accurately.
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) for order fulfillment and regularly analyze data to identify areas for improvement. Metrics may include order accuracy, on-time delivery, and order cycle time.
Cross-training employees to perform multiple tasks within the order fulfillment process. This flexibility ensures that staff can adapt to fluctuations in demand and peak seasons.
Foster a culture of continuous improvement. Encourage feedback from employees involved in order fulfillment, and regularly review and update processes to enhance efficiency.
Design order fulfillment processes with scalability in mind. Ensure that the system can handle increases in order volume without sacrificing accuracy or speed.
Communicate proactively with customers about order status, delays, or any issues that may arise. Clear and timely communication helps manage customer expectations and build trust.
Collaborate with suppliers to ensure a steady and reliable supply chain. Establish strong relationships to mitigate the risk of disruptions.
Order fulfillment is a critical process that spans the entire journey from order placement to product delivery. Its significance is rooted in fostering customer satisfaction, encouraging repeat business, and building a positive brand reputation.
Efficient order fulfillment not only contributes to reduced operating costs but also plays a key role in customer retention, market expansion, and adaptability to changing market dynamics. By automating the order fulfillment using WMS, businesses can improve inventory management, reduce errors, and optimize tracking through barcode and RFID features.
If you want to streamline overall business processes, from accounting, purchasing, sales, and many more, you can consider ERP implementation.
Learn more: What Is ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) – A Complete Guide
Supply chain
Competitive advantage
Customer retention
Inventory management
Quality control
Fulfillment center
Customer satisfaction
Packing materials
Order picking
Distribution center
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.
