12 Vital Retail Metrics & KPIs for Your Business Success
Our retail guide’s last chapter explored ways to boost your store’s success through innovative finance,…
Sean Thobias
November 19, 2024Kanban is a crucial part of the Just in Time (JIT) system, which we discussed in the preceding chapter. It serves as the wall of the House of Lean Production.
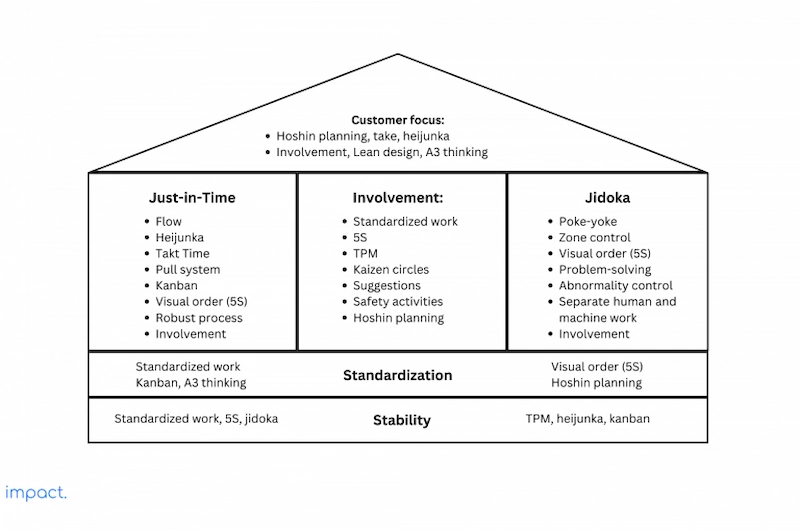
Kanban is a method that visualizes work, maximizes efficiency, and improves operations. A Kanban board displays jobs, enabling workers to handle complex projects in a single environment.
Below, we explain Kanban’s definitions, rules, and benefits when implemented in companies.
Kanban helps with JIT production. The term comes from Japan and means a visual board or sign. Toyota was the first to use this method as a schedule for Just-in-Time manufacturing.
However, “Kanban” refers to the “Kanban Method” that originated in 2007. It is a production process that operates on a pull system and encompasses pertinent information such as:
Other forms include:
Read more: Lean Manufacturing: Definition & 3 Advantages to Utilize
In practice, there are two commonly used types of Kanban:
These two types of Kanban work together, as shown in the figure below:
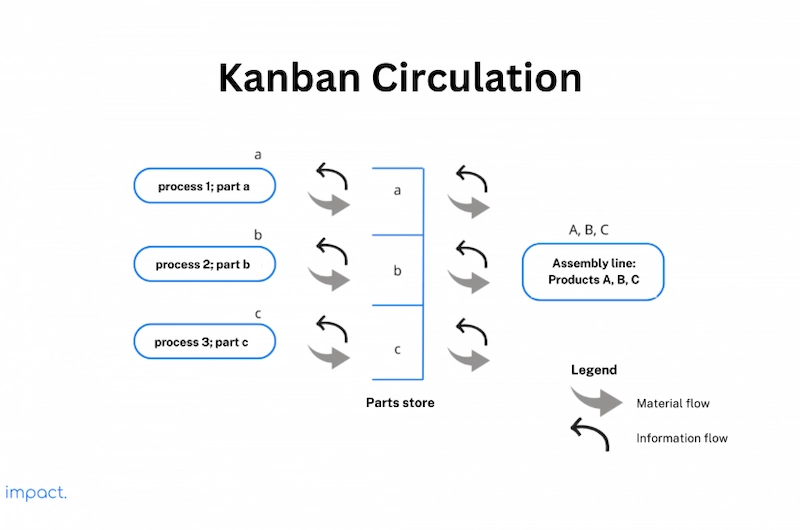
The assembly line produces goods A, B, and C by purchasing parts a, b, and c from the spare parts shop using Kanban withdrawal. Any shortage leads to the creation of production Kanban for processes 1, 2, and 3, which produce replacement parts. The company manufactures recalled items strictly in the order customers request, guaranteeing defect-free products are delivered.
If the parts store runs out of part A, the customer should submit the withdrawal Kanban to process 1. Process 1 will then schedule the work and fulfill the order. Below is an example of a withdrawal Kanban and a production Kanban:
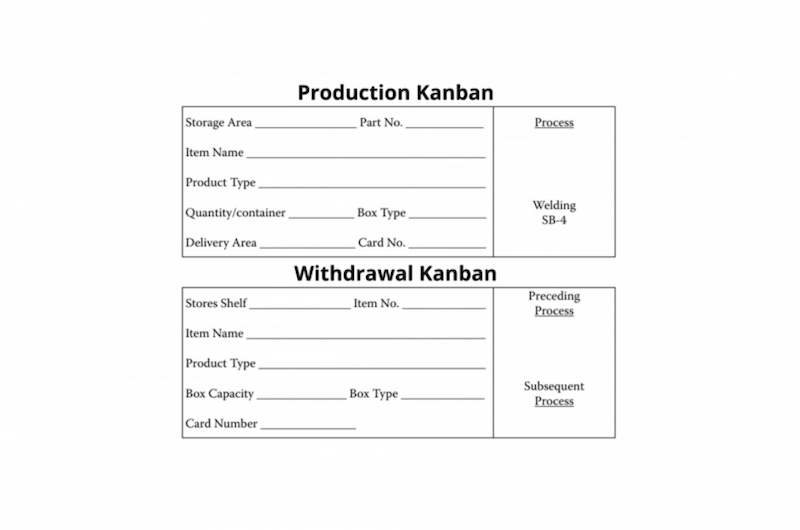
Source: Dennis, P. (2017). Lean production simplified; Production and withdrawal kanban
To effectively implement Kanban, workers, and supervisors require a profound understanding of its rules and strong problem-solving skills. The rules for Kanban implementation encompass the following:
Companies must follow Rule 1, which means they should avoid making defective products. If a company produces faulty products, it wastes labor, materials, and time as these items are unfit for sale. This hampers cost-reduction efforts and prevents them from achieving their goals. According to Rule 1, companies must:
The previous chapter discussed the concept of Just in Time. To address critical production problems, companies need to ensure they have product stock available in the required quantity when customers come to make a purchase. This way of thinking helps answer the following questions:
Rule 2 has the following consequences:
To avoid problems caused by producing too much, too soon, or with the wrong parts, it’s essential to be mindful. These mistakes can lead to unnecessary overtime, excess inventory, and wasted resources due to not realizing we already have enough capacity. It’s crucial to accurately assess and ensure that our existing capacity is sufficient to prevent these inefficiencies.
Rule 3 is based on rule 2, allowing production processes to work together like an assembly line. Kanban connects customers and suppliers. The following are the outcomes of rule 3:
We must design the production scheduling board to ensure transparency in order and quantity.
Companies must maintain stability in their orders to achieve accurate and timely production. Ordering 50 pieces in one hour and suddenly increasing it to 250 in the next hour would lead to overproduction. Therefore, companies must recall products on time, in fixed quantities, and in a predetermined order.
The Kanban system doesn’t suit many production changes. It serves as a tool for fine-tuning processes. For instance, when a customer pulls out pieces at an unstable rate (e.g., 100 pieces in the first hour, 200 pieces in the second hour, and 75 pieces in the third hour), it results in inventory buildup and overcapacity for the company.
Companies must apply the jidoka principle to improve process capability and actively address muda, mura, and muri. To accomplish this, you can:
Organizations must carefully follow six practical steps to implement the Kanban method successfully. Let’s go through each step in the Kanban implementation process:
Using this system, you can visualize work processes using board media with cards and columns. Each column on the board represents a step in the workflow, while each Kanban card represents a work item. The board accurately reflects the current state of the workflow, including all risks and specifications.
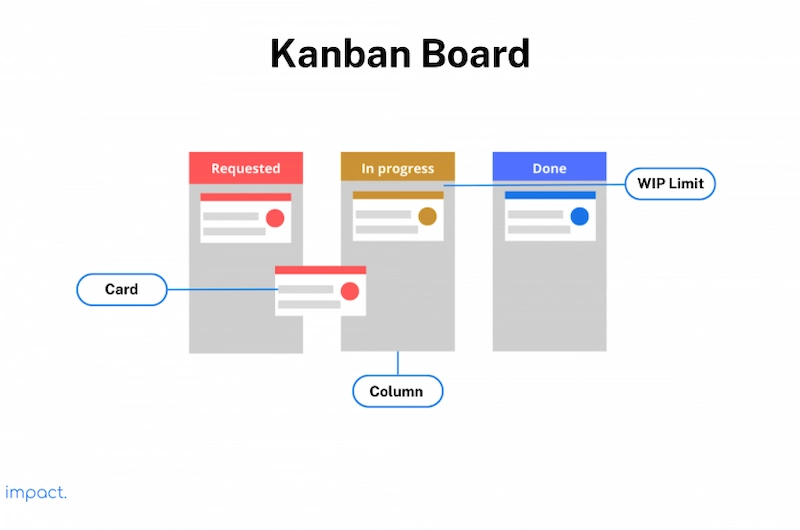
Firstly, it’s vital that you understand how to turn a request into a tangible end product. Understanding the flow of work within the system will enable you to embark on a journey of continuous improvement or kaizen, where necessary changes can be implemented and observed.
When you work on item X, drag it from the “Requested” column to the “Done” column upon completion. This action allows for effortless progress tracking and issue identification. Naturally, the appearance of your board may vary based on your unique requirements and workflows.
Kanban‘s primary purpose is to ensure you don’t have too many things in progress simultaneously. If you don’t limit the amount of work you can do, then you’re not using Kanban.
Changing what your team focuses on in the middle of a project is not a good idea because it can mess up the whole process. Trying to do multiple things simultaneously is also a waste of time and makes things less efficient.
Limiting your work in progress means you only move on to the next step when you have space. This action helps you see any problems and deal with them quickly.
Managing flow involves managing work items as they move through the production process at a predictable and continuous pace. When implementing a Kanban system, a key objective is establishing a smooth and efficient flow. Focus on managing work processes to speed advancement rather than excessive control and constant busyness. Consequently, your system will generate value more rapidly.
To improve something, you must first understand it. Therefore, clearly defining, publicizing, and socializing your process is crucial. People won’t engage with or support something they don’t believe in.
When everyone is familiar with the shared objectives, they can effectively collaborate and make decisions to create a positive impact. Implementing employment policies that are infrequent, visible, well-defined, and adaptable when needed can empower workers to regulate themselves.
The company ensures that the organization effectively responds to potential changes and helps share knowledge among stakeholders. Kanban recommends using cadence at the team and service levels.
To establish a team-level cadence, a daily meeting can be held. This meeting keeps track of the status and flow of work, allowing us to see how much capacity is available and find ways to improve delivery speed. It takes place in front of the Kanban board, and each member shares what they accomplished the previous day and their plans for today.
Having focused and regular meetings with fewer participants is a good practice. However, determining how long a specific Kanban cadence depends on your situation, team size, and the topic you’re discussing.
To keep improving and making organizational changes, we must work together, use methods we know work, listen to feedback, and measure our progress. It’s essential to evaluate the impact of every idea we have so we can create a culture that values new and better ways of doing things. This approach helps us develop a mindset focused on minor improvements over time.
According to the 1st State of Kanban report, companies use this methodology primarily to make work more visible and continuously improve. Here are some of the benefits companies gain from using Kanban:
The central concept of Kanban is to represent each job visually. The Kanban board transforms into a central information hub, ensuring everyone is aligned. All tasks are readily visible and never vanish, promoting transparency throughout the work process.
Kanban empowers companies to monitor and analyze work distribution information closely. Identifying stages with the most extended task durations and bottlenecks becomes effortless by providing a clear view of completed work items within a specific period. By doing this, the system improves workflow and speeds up how quickly products are delivered.
Kanban practices help companies align their big goals with everyday work by being transparent, giving feedback, and holding regular review meetings. This connection between the business direction and what gets done improves how quickly the organization can respond to changes. It allows the team to quickly adjust to new priorities, market changes, or what customers want.
Once you make a board and add work items, you can learn more about the process using flow metrics. You can improve your predictions about future work by analyzing how much time tasks spend in the workflow (cycle time). Understanding how consistent your delivery rates are (throughput) will help you make better estimates and decisions based on past data.
The Kanban method originates from the pull system, which ensures work completion upon request. In simpler terms, it strives to minimize waste by focusing solely on necessary tasks. You can guarantee that the outcome meets customer expectations by utilizing visualization techniques and implementing work limits.
Also read: Manufacturing Computer Software: 3 Types & How to Choose
Kanban is a method that makes work more visible and controllable. It helps companies identify inefficient business processes and find solutions. To implement Kanban effectively, follow the six rules mentioned in this chapter.
After grasping this concept, the following chapter will delve into production leveling, also referred to as heijunka, another crucial element of Just in Time.
Dennis, P. (2017). Lean production simplified: a plain-language guide to the world’s most powerful production system. Crc press.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

Our retail guide’s last chapter explored ways to boost your store’s success through innovative finance, operations, and customer relations practices. As you manage your store, pay close attention to critical metrics and KPIs for a clearer picture of performance.
These retail metrics include sales, inventory, and customer data. Discover why these metrics are crucial, which ones to focus on, and get practical tips to enhance their effectiveness.
Measuring metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for evaluating individual and team performance in your business. This assessment guides performance reviews, goal setting, and improvement efforts.
Monitoring metrics and KPIs in retail is vital to assess overall business performance and alignment with strategic goals. The practice helps identify successes and areas for improvement.
Retail business owners, it’s vital to base your decisions on data for effective planning and execution. Metrics and KPIs offer valuable insights, showing what works well and pointing out areas that need improvement.
Use metrics and KPIs to optimize resource allocation. Identify high-impact areas so you can deploy resources effectively. It ensures your time, manpower, and financial investments go where they’ll contribute the most to your business success.
Keeping a close watch on significant numbers is essential for retail business owners. Check your cash flow and liquidity ratios regularly. These indicators can give you an early heads-up about economic ups and downs.
Keep an eye on your supply chain metrics, too. These metrics help you spot weaknesses, diversify suppliers, and be ready with backup plans. Taking these steps upfront lessens the hit if there are any bumps in the road for your business.
Boost your employees’ performance using metrics and KPIs to measure their satisfaction and productivity. These metrics serve as a straightforward scorecard, giving your employees a clear picture of their performance.
Equip your team with essential metrics to help them establish and achieve meaningful goals. This accountability fosters a culture of responsibility and continuous improvement in your retail business.
Conversion rate is a must-watch metric for retail, whether online or in-store. It shows the percentage of visitors who purchase, giving you more insight than just counting transactions.
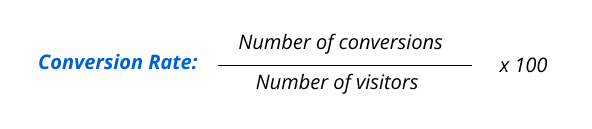
A high conversion rate means many visitors become customers, pointing to successful marketing and retail sales tactics. Keep an eye on this metric to spot where you can enhance the customer experience, like improving product displays, making your website more user-friendly, or smoothing out the checkout process.
Foot traffic means the number of people entering your store. You can track it using electronic counting systems or manually counting during peak hours.
Analyzing foot traffic alongside metrics like the conversion rate is crucial, as it helps you gauge how well your store turns visitors into customers. Also, comparing foot traffic across various periods unveils seasonal patterns and reveals the impact of marketing efforts.
Sales per square foot tells you how well you use your store space to make money. It’s a measure of how productive your layout, where you put products, and your overall use of space is in bringing in retail sales.

A high sales per square foot means your store setup is good, and customers enjoy shopping there. Check if all your stores or departments are doing well. If this number continues, your retail strategies work, and you use your space effectively.
ATV is the average amount a customer spends in one transaction. It’s critical for grasping customer buying habits and how well sales strategies work.
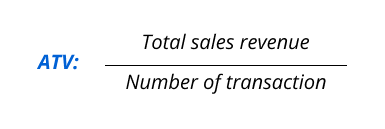
Increase your retail earnings by cross selling or having discounts on larger purchases to boost the average transaction value (ATV). Monitor trends and customer groups to make targeted improvements for maximum profitability.
Customer Retention Rate measures the percentage of customers a business retains over a specific period. It provides insights into customer satisfaction, loyalty, and the effectiveness of efforts to keep existing customers.

A rising CRR signals satisfied customers; if it drops, address product quality or customer service. Strive to balance acquiring new customers and retaining existing ones to ensure sustained retail success.
Gross profit margin is the percentage of money you make from selling your products after accounting for how much it costs to make or buy them.
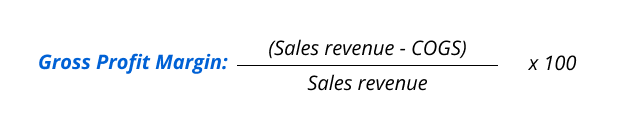
Aim for a higher gross profit margin because you manage costs well and effectively pricing your products. Keep an eye on this number to catch any issues with costs or pricing that might affect your overall profit.
Year-over-year (YoY) growth is a way to measure the percentage change in a specific business metric from this year compared to the previous year. This comparison provides a solid understanding of your business’s performance trends and helps evaluate how well your strategies work.

Analyze year-over-year (YoY) growth across sales, revenue, and customer acquisition for a comprehensive view. Positive YoY growth is encouraging, but understanding the reasons is crucial, while negative growth prompts a thorough examination of strategies and operations for improvement.
Inventory turnover shows how fast a business sells and restocks its products, telling you how well you manage inventory and if there’s demand for your goods.
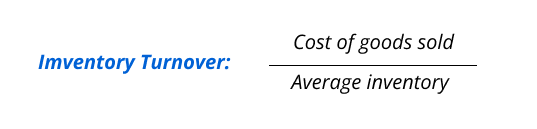
A higher turnover is good, meaning products are selling fast. Yet, if it’s very high, you might be running out of stock, and if it’s low, you could have too much stock or slow-selling items. Keep an eye on this to balance your inventory right.
The sell-through rate is a tool that helps retail business owners understand how efficiently they sell the products they have in stock. It’s calculated by dividing the units sold by the initial inventory quantity, providing a percentage that indicates the rate at which inventory turns into sales.
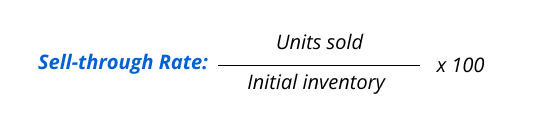
For retail businesses, a reasonable sell-through rate means products are selling fast, but be cautious of an excessively high rate that could lead to stockouts or a low rate indicating overstock. Regularly track this metric to fine-tune inventory strategies, ensuring optimal retail sales without excess or shortages.
The stockout rate is how often a retailer faces inventory shortages or runs out of a specific product, directly influencing customer satisfaction and potential retail sales.
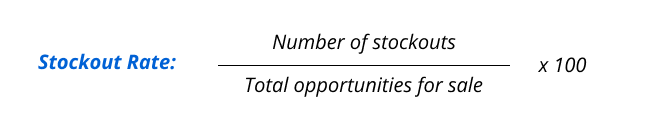
A low stockout rate in retail signals effective inventory management, preventing lost sales and maintaining customer satisfaction. Reviewing stockout data is crucial for optimizing inventory levels and strategically adjusting procurement or supply chain processes.
Shrinkage is the difference between the recorded and actual stock on hand, usually expressed as a percentage. It includes losses from theft, errors, and other unaccounted factors.

Excessive shrinkage can negatively impact retail profits, making it vital to monitor trends and address areas for improvement, such as security measures, inventory management, and employee training. Retailers must thoroughly investigate and address the root causes of shrinkage to minimize financial losses effectively.
GMROI is a key metric that helps you assess how profitable your inventory is by looking at the relationship between the gross margin and the average inventory investment.
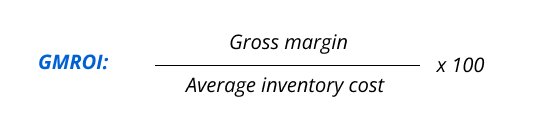
A higher GMROI indicates a superior return on inventory investment. Optimize profitability by balancing high gross margins, swift inventory turnover, and regularly adjusting product assortments and pricing strategies.
Choose metrics and KPIs that directly relate to your business objectives. It’s better to focus on several key indicators that provide actionable insights rather than measuring everything.
When assessing metrics for your retail business, focus on what truly helps you improve. Get rid of metrics that don’t contribute to your goals, concentrate on the ones that do, and skip unnecessary measurements to save time and resources.
Setting clear targets for your KPIs is crucial to measure your retail business’s performance effectively. Know your business goals and avoid setting too ambitious or unattainable targets.
When setting targets, consider realistic values that make sense for your specific retail context and look at industry benchmarks for guidance. Doing this will ensure your goals are practical and achievable, preventing frustration or setbacks caused by setting too high or unrealistic targets.
Once you’ve selected your metrics and KPIs, transform them into actionable insights instead of just numbers. Opt for visually engaging formats when presenting data, as 65% of the population learns better through visuals.
Streamline comprehension for stakeholders by incorporating dashboards and visualizations. Take advantage of tools that offer diverse dashboard options for a centralized presentation of your KPIs and metrics.
For retail business owners, integrating real-time monitoring is a game-changer. It gives you instant insights into crucial metrics like sales and operations, making it easier to make timely decisions and tackle issues as they arise.
Utilize ERP software to streamline real-time monitoring by consolidating data, ensuring accuracy, and facilitating informed decision-making for overall business improvement.
Ensure your retail metrics and KPIs stay current with your business goals and challenges. It sharpens your monitoring system, allowing for swift adjustments in response to market shifts.
Updating your metrics isn’t a mere formality — it’s a practical step to enhance your retail business’s agility. By fine-tuning your metrics based on real-time insights, you can proactively address issues and keep your store agile, ready to seize emerging opportunities.
Running a successful retail business requires careful attention to metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs). Yet, manual tracking can be cumbersome and challenging due to the real-time nature and many variables.
For a more efficient approach, consider investing in an ERP system to streamline your operations. In the next chapter of our guide, we’ll delve into the various types of software and technology essential for retail businesses, highlighting their significance and providing insights on what to consider when purchasing.
Ramsey, D., & Ramsey, J. (2010). The Everything Guide to starting and running a retail store: All you need to get started and succeed in your own retail adventure. Adams Media.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

The last chapter explored the essential steps of creating a web startup, using steps from “The Startup Owner’s Manual” by Steve Blank and Bob Dorf. Now, let’s dive into a crucial tool pivotal in your startup journey: the Business Model Canvas.
As your startup progresses through the customer development process, you’ll rely on the Business Model Canvas as your trusty scorecard. It’s your guide, helping you track and refine your business hypotheses for each critical component.
In this article, we aim to explain the Business Model Canvas. We’ll break it down into nine key components, giving you a clear understanding of how this canvas can be your compass on the path to startup success.
Read more: Building a Company: 4-Step Customer Development Guide
A business model is like a roadmap that shows how a company creates, delivers, and makes money from its products or services. But sometimes, it’s tough for everyone in a company to understand this roadmap clearly.
That’s where the Business Model Canvas comes in. It’s a handy tool developed by Alexander Osterwalder that helps you figure out how your company will make money. Think of it as a strategic tool for startups. It enables you to plan, adapt, and change your business idea.
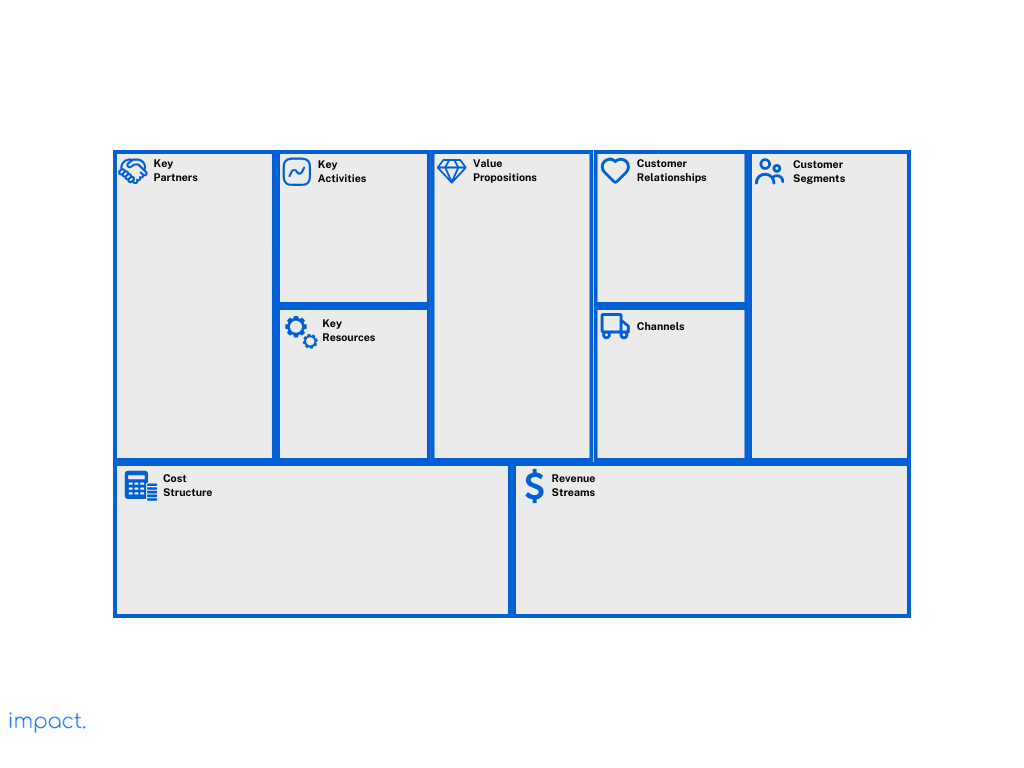
Unlike a typical company chart that shows how things work inside, the Business Model Canvas is more like a treasure map. It helps you explore the unknowns that many startups face. There are nine boxes on the canvas, each representing a crucial part of your business idea. (We will explain each component later on in this article).
As your startup goes through the customer development process, the Business Model Canvas becomes your scorecard. You put your ideas about each part of your business model on it.
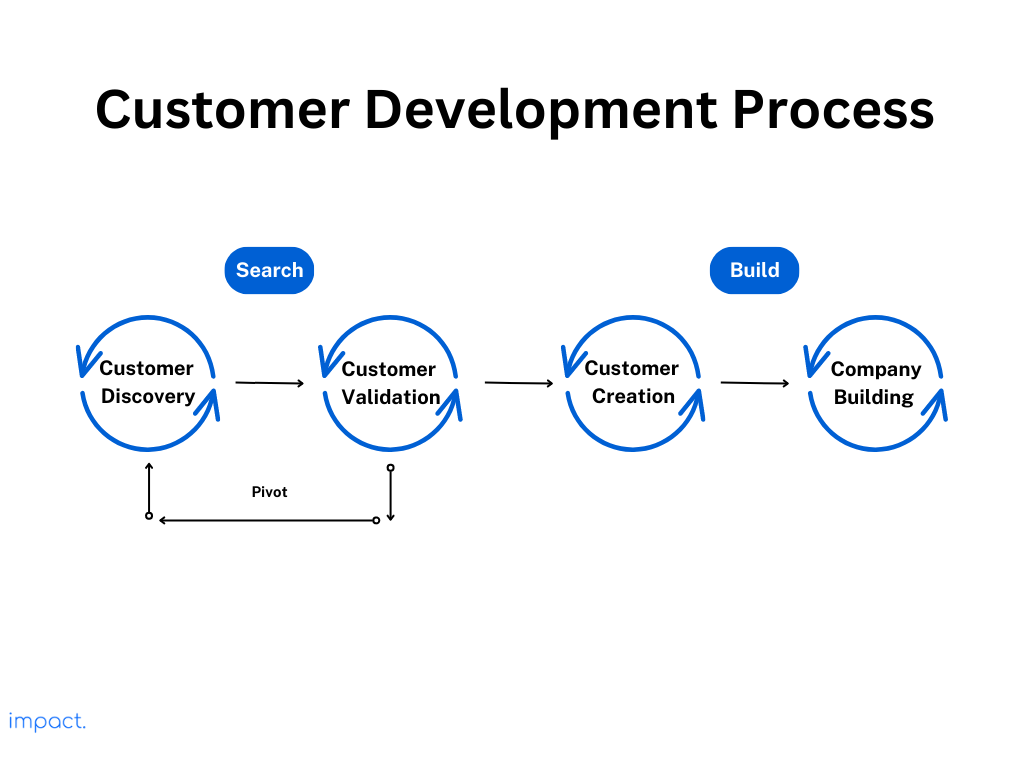
Then, as you learn more from your customers, you update those ideas. It’s like starting with a map of where you think the treasure is, and then, as you explore, you adjust your course based on what you find.
Read more: Customer Development Process: 4-Step Framework for Startups
By leveraging the Business Model Canvas, you can unlock numerous benefits that pave the way for a more structured, adaptable, and successful startup journey. Here are some benefits that you can gain when using this strategic tool:
The Business Model Canvas is like a blueprint for your business. It breaks down the essential parts of your business into clear blocks. These blocks help you see how everything fits together.
Using the Business Model Canvas, you can organize your business thoughts neatly. It ensures that you don’t miss anything important. Plus, it shows how different parts of your business connect.
Simply put, it’s a tool that helps you create a clear plan for your business. It makes you think deeply about each part, ensuring your strategy is well-defined.
The Business Model Canvas is like a flexible blueprint for your startup. It lets you begin with your ideas, even if they are only assumptions. You can improve your plan as you learn more and get feedback. It’s all about making your business better bit by bit.
This canvas not only simplifies and streamlines but also accelerates the development of your business strategies. Think of it like a rough sketch that you refine over time as your business vision evolves. The canvas encourages a flexible mindset where you plan, check, and make changes as needed.
Imagine the Business Model Canvas as a set of educated guesses. You need to check for these guesses by talking to real customers. Why? Because as your business grows and gets more customers, your plan will need to change. So, the canvas is like a fluid tool that moves and adapts to your business journey.
By mapping your ideas on the canvas early on, you can quickly identify any potential risks and assumptions that may arise. It’s similar to spotting potholes on the road before driving into them.
The Business Model Canvas serves as a helpful guide for taking your idea to the market. It connects your value, target audience, and revenue generation strategy. This information is crucial for developing your marketing, positioning, and sales plans. Additionally, it’s faster and more efficient than creating a lengthy business plan, providing you with a competitive advantage.
The canvas highlights a crucial factor for startup success: knowing what your customers want and what issues they face. This understanding is essential because it guides your decisions and actions.
When you know your customers’ needs and problems, you can effectively tailor your products or services to meet those demands. It increases your chances of success and helps you create a more meaningful and valuable solution for your target audience. So, remember that understanding your customers is a fundamental step toward a successful startup.
Now that we’ve grasped the essence of the Business Model Canvas, let’s delve deeper into its nine critical components in more detail. These components are the building blocks of your business strategy, each playing a unique and essential role in shaping your startup’s success.
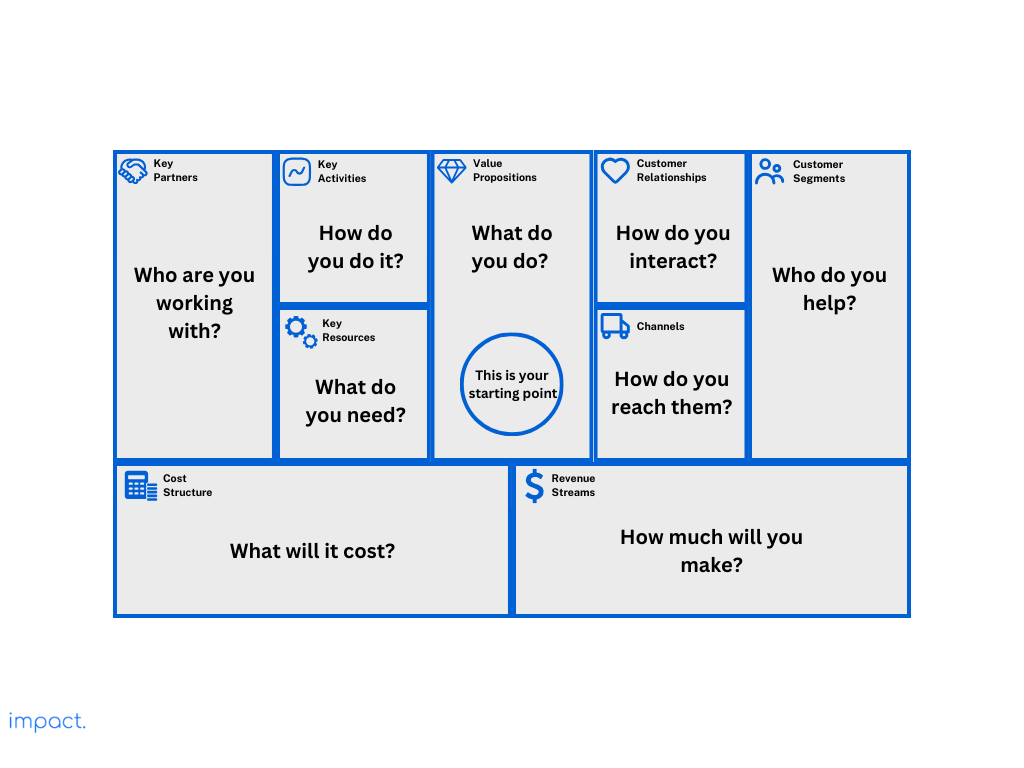
The value proposition is the core of your startup. It’s what makes your business stand out and provides solutions to your customers’ problems. It answers the question, “Who are you creating your startup for?” Simply, it’s about solving your customers’ problems and meeting their needs.
Customers aren’t interested in your fancy technology or all your cool features. What matters to them is how you can make their lives easier or better. In this part of the Business Model Canvas, you should define how your product or service benefits your customers. Think of it as a list of how your startup will solve their problems and fulfill their needs. That’s what the value proposition is all about.
Who are your customers, and why do they buy from you? In this part of the Business Model Canvas, you group your customers based on similarities like age, gender, interests, and spending habits.
Identifying these customer groups is crucial. You must understand their needs, behaviors, and unique traits to create customer personas. Startups often have multiple customer segments, each requiring a tailored approach. Always remember that your company’s purpose is to cater to the needs of its customers, not the other way around.
Distribution channels are the paths your product takes to reach your customers. Think of them as the routes to deliver what you’re selling. These channels are part of your marketing plan. Picking the right ones ensures your product gets to the right people.
Today, there are various methods to deliver your product to reach customers. Here are a few: Search Engine Marketing (SEM), Search Engine Optimization (SEO), content marketing, traditional ads, and working with blogs that match your target audience.
Read more: Unlocking Growth: 19 Traction Channels for Business Success
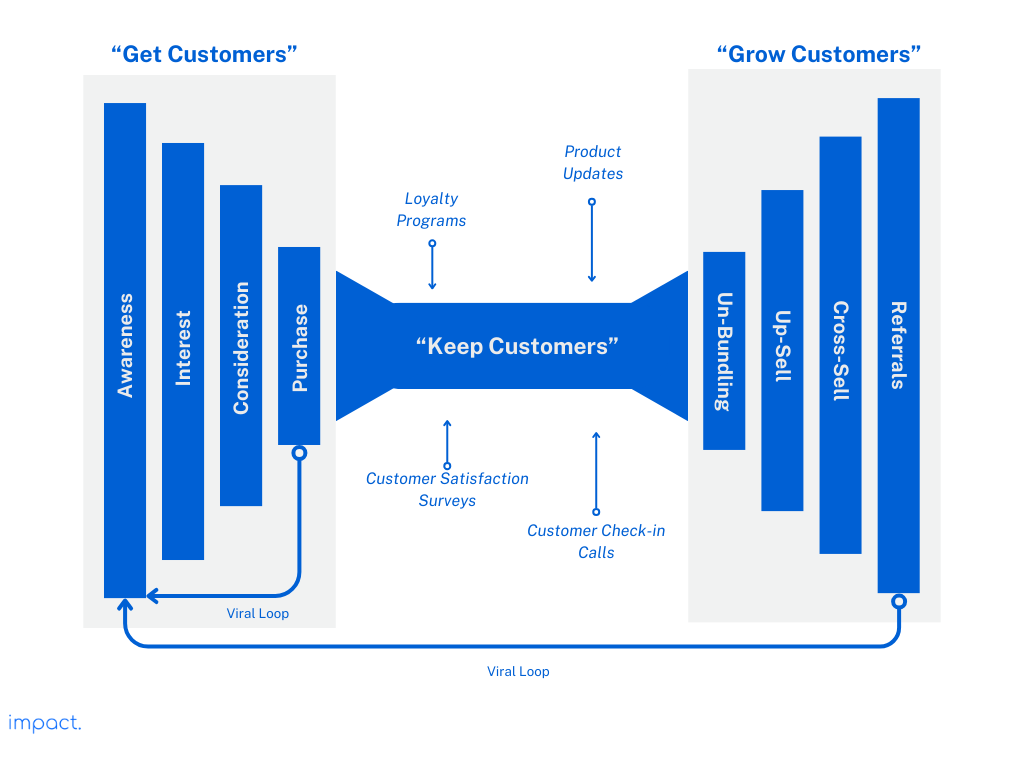
The customer relationships part of the Business Model Canvas is about how you connect with your customers, make them stay, and buy more from you. Imagine it as a two-sided funnel.
The revenue streams component is about how your business earns money by selling your product or service to customers. It’s about figuring out what customers are willing to pay for and how to get them to pay. Knowing your revenue streams is crucial for your business to survive and grow.
It’s also essential to set the right price for your offering. You need to consider how much customers are willing to spend compared to the problem your product or service solves. You can use various pricing models, such as direct sales, subscription, or freemium (giving basic services for free and charging for premium features).
The resources component of the Business Model Canvas deals with what your startup needs to get things done. It’s about the essential assets your business relies on to offer its products or services and run smoothly. These assets could be financial, physical (machines, vehicles), technological (software), intellectual (like patents), and your team.
The key partners component is about whom you need to work with from external companies or suppliers to make your business work. These partners help you do the essential tasks and provide what you need to make your customers happy.
It’s important to consider what your partners will contribute and when they will do it. Your business may require assistance from others, and understanding their role is crucial.
Many startups think they must partner with other companies immediately because big companies do it. However, partnering in your first year differs from when your startup has grown into a mature company. So, think carefully about when and who to partner with.
The key activities in your business or product are your actions to make your customers happy. This part of the Business Model Canvas is all about the essential tasks your startup must do to provide value to customers. It includes everyday jobs and big strategic moves that help your business grow. To make your business work, focus on these actions.
In the Business Model Canvas, all the components come together to form the cost structure. This part represents the money you need to run your business.
Your cost structure includes two main types of expenses:
Understanding your cost structure is crucial for effective financial management and ensuring the profitability of your business. Here are key aspects to consider:
When running your business, it’s crucial to consider the opportunity cost. Consider the potential earnings you might have had if you were doing something else instead. By understanding all these costs, you can make informed financial decisions for your startup.
The Business Model Canvas is an invaluable tool for startups on their journey to success. It provides a clear and concise roadmap, allowing companies to visualize how they create, deliver, and monetize their products or services. Its nine essential components serve as a strategic companion, helping entrepreneurs adapt and refine their business ideas as they navigate the often uncharted waters of the market.
As we conclude our startup guide, remember that the journey doesn’t end here. The Business Model Canvas is not just a one-time map; it’s a dynamic tool that evolves with your startup’s growth. Continuously update your canvas based on the insights gained from your customers, much like adjusting your course while on a treasure hunt.
With dedication, adaptability, and a well-mapped strategy, your startup is poised for success. Embrace the adventure, stay agile, and keep refining your business model to unlock the treasures of entrepreneurship.
Blank, Steve, and Bob Dorf. The Startup Owner’s Manual: The Step-By-Step Guide for Building a Great Company. 2020.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

Companies are always searching for new ways to set themselves apart as the business world becomes increasingly competitive. With the rise of technology, it is clear that Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM) is the way of the future.
What is E-CRM exactly? It is a solution that leverages digital channels to manage customer interactions.
This article will examine what this solution is, how it works, and why it is essential for businesses today. We will also explore its benefits and factors for implementing this system.
Understanding this application will help you develop stronger client interactions regardless of how big or tiny your business is. Long-term success as a result of this can be enormous.
E-CRM is a method of managing customers using digital technology. It can include emails, websites, chat rooms, and forums to achieve CRM goals.
This solution is not only software. It combines software, hardware, and the commitment to support the strategy to achieve business goals.
Its is growing in various business fields. It improves consumer interactions and helps businesses select products and services that meet client needs.
To enhance client relations, E-CRM makes use of technology. For the following reasons, this application is crucial for businesses:
In today’s digital era, customer expectations for business interactions are increasing. Customers expect a seamless, personalized, and comfortable experience interacting with businesses. Companies must utilize E-CRM to be able to meet customer demands adequately.
E-CRM streamlines corporate operations. The system automates lead management, sales monitoring, and customer service. With this system in place, manual tasks will be minimal.
Data is valuable in business today. E-CRM simplifies the collection, storage, and analysis of customer data. Companies can leverage this data for improved operations by gaining insights into customer behavior.
E-CRMs are flexible systems that meet changing requirements and an expanding client base. It aids businesses in maintaining customer focus while growing and managing client relationships effectively.
E-CRM uses digital platforms to expand global reach and surpass spatial customer limits. It creates options for the expansion and growth of the worldwide market.
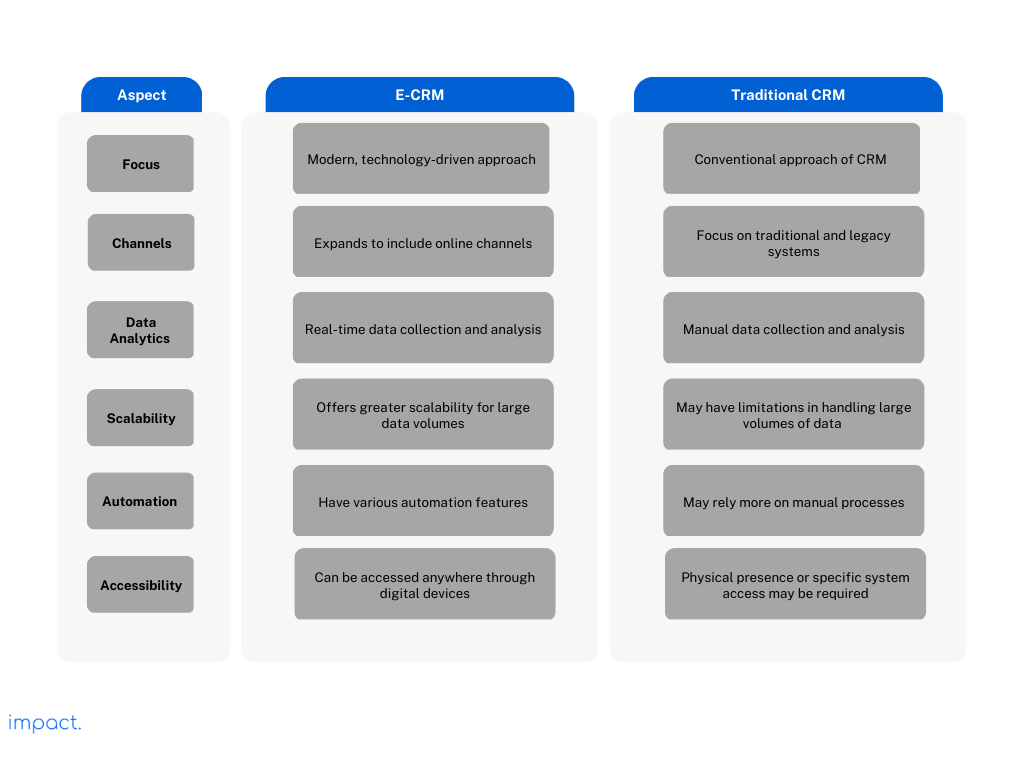
In this high-tech era, the Internet has transformed almost every aspect of our lives. With the rise of E-CRM, the traditional approach of CRM has been replaced.
As a result, this application has significantly impacted business growth. Therefore, you must know the differences between these two approaches.
CRM involves manual processes or legacy systems for managing customer interactions. E-CRM is a step ahead of that. It is the adaptation of a CRM using the Internet; all contacts are online.
Here we have compiled the differences between the two using the table below.
Electronic Customer Relationship Management uses digital technologies to manage and optimize customer interactions. Here are some key features of the system:
Automation tools are integral to E-CRM systems and can significantly improve efficiency in managing customer relationships.
E-CRM can automate the following:
This tool helps you save time and improve accuracy. However, you need to balance its use for a personalized CRM approach.
An essential element of E-CRM is customer data management. It enables commercial businesses to gather and arrange client data in one place. With the data available, companies can communicate effectively with clients. Additionally, it aids in tailoring services to meet individual customer needs.
E-CRM systems are highly customizable. You can modify the system to match your company’s requirements. This adaptability offers a more individualized method of managing consumer interactions.
E-CRM offers customizable reporting options, enabling businesses to identify successful and ineffective actions. These records provide valuable insights that can help companies make data-driven decisions. Furthermore, it can also assist in improving overall business strategies.
E-CRM empowers businesses to gain a competitive edge by always offering customer service and support. Companies can proactively increase engagement and promptly address concerns by remaining available to customers.
E-CRM integrates multiple communication channels to interact with customers, such as email, social media, chatbots, and mobile apps. This feature enables seamless and consistent customer engagement across preferred channels.
By implementing an E-CRM system, businesses can reap multiple advantages due its various features. Here are five of them:
With this system, your business can effortlessly manage customer inquiries, complaints, and feedback through electronic channels. This technology allows faster response times, personalized interactions, and consistent service delivery. As a result, your customers enjoy a better service experience that keeps them returning for more.
When customers are happy, they become loyal to the brand. You can achieve this with E-CRM. The technology allows you to gain valuable insights into their preferences and interactions. Leveraging this information, can help you to create personalized and tailored communications to customers.
E-CRM streamlines routine tasks like data entry, tracking customer interactions, and generating reports. You would not have to worry about inputting data manually. As a result, your operations can focus on other complex issues, leading to higher efficiency and productivity levels.
If you are looking for a strategy that boosts sales and profits, E-CRM can be the solution. The technology helps identify and target potential customers accurately. You can also track customer habits closely. It enables data-driven decisions, drives growth, and fosters unparalleled success in today’s dynamic market.
Implementing this system in your company opens up customer service to work remotely. Your business can save operational costs as your team is not in the office full-time. It also opens you up to utilize a global talent pool.
If you are thinking about implementing an E-CRM system for your business, there are some important factors to consider. The system’s success increases when these factors come into play.
You must first define your objectives for using an E-CRM system. What do you want to achieve? Is it to improve customer service, increase sales, or streamline business processes?
Understanding your business objectives will help you align your implementation with your overall business strategy. If your goals do not align, the implementation will cause difficulty in achieving your desired outcomes.
Revamping your current infrastructure may be necessary when implementing an E-CRM system. It would be best to ask your team whether introducing new technology will disrupt current processes. Ignoring this can lead to employee resistance, inefficiencies, and suboptimal results.
Implementing an E-CRM system can result in significant transformations affecting multiple business areas. The process may require an overhaul of your current work processes. You must consider the implications, plan for process changes, provide employee training, and gain buy-in.
Selecting the right technology is crucial for a successful implementation. You must choose a system that aligns with your business requirements and meets current and future needs. Thoroughly evaluate scalability, customization, ease of use, integration, security, and support options.
Electronic Customer Relationship Management is a robust solution to manage customer interactions effectively using digital channels. Its implementation can lead to stronger client interactions and long-term success, regardless of business size.
If you want a CRM solution with online capabilities, consider Impact. Experience the power of a fully-integrated Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system with Impact, designed for Indonesian businesses.
Impact’s CRM tool seamlessly connects with essential modules, such as sales, purchasing, and omnichannel – simplifying your workflow.
Unlock your full potential in managing customer relationships with Impact’s CRM tool. Enjoy advanced customer tracking, improved sales performance, and data-driven insights for efficient sales and relationship management.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

In the previous chapter, we discussed the basics of retail business — its operations, various types, challenges, and opportunities. Let’s now focus on retail business planning in this chapter.
The ultimate goal of running a retail business is to make a profit. To ensure long-term success in serving customers, laying down the groundwork that will lead you to this goal is vital.
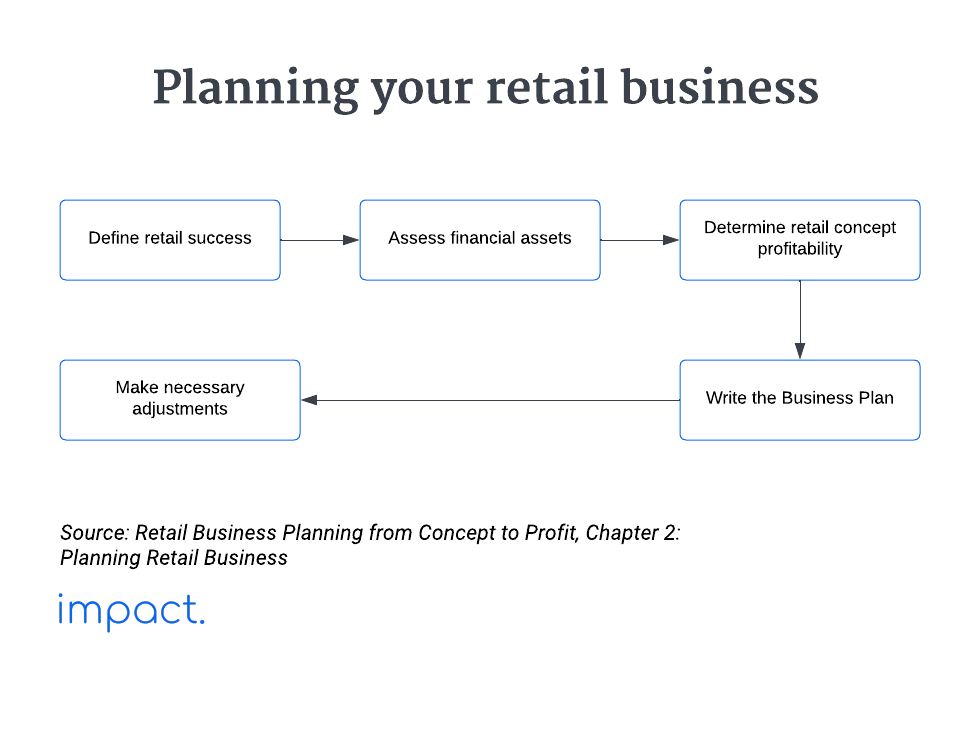
When launching your retail business, establish a clear business goal. According to Dan Ramsey in The Everything Guide to Starting and Running a Retail Store, success in retail falls into three main categories:
Cash flow issues are a common problem for businesses. According to a study, poor cash flow management accounts for 82% of business failures.
To thrive, prioritize growing your retail store’s financial assets. Before choosing a concept, assess your cash reserves, convertible equity, and available credit.
Businesses depend on liquid assets for flexibility and the ability to adapt to sudden market changes or settle debts. You use these assets to convert to cash without a significant loss of value easily.
Businesses must have enough liquid assets to handle responsibilities like buying inventory, paying bills, and dealing with unexpected expenses. These include cash on hand and easily accessible funds in bank accounts.
Although turning your home or property into cash may not be easy, you can leverage the equity in these assets. Equity is the gap between their current market value (after deducting selling expenses) and the remaining mortgage.
Utilize your home equity to get funds for everyday business needs such as equipment, technology, and operational vehicles, ensuring your business has the necessary working capital. But beware, if your business doesn’t succeed, you might risk your home and business.
Good credit is vital for your business — it helps you get loans, credit lines, and favorable terms with vendors. A strong credit rating in retail is crucial; it can make it easier to secure a store lease, set up utilities, get wholesale merchandise on credit, and open various business accounts.
If your credit isn’t great during the planning stage, it’s wise to delay opening your store until you’ve improved it. Good credit makes dealing with essential aspects of your retail business, like leases and vendor relationships, much smoother and more favorable.
Explore these alternative avenues to solidify your financial assets:
Consider opening a franchise store if you have assets but lack retail management experience. A franchise license lets you use another company’s business know-how, methods, and brand.
In this setup, you can sell a product or service using the original company’s name, usually for an initial startup fee and yearly licensing fees.
Pros:
Cons:
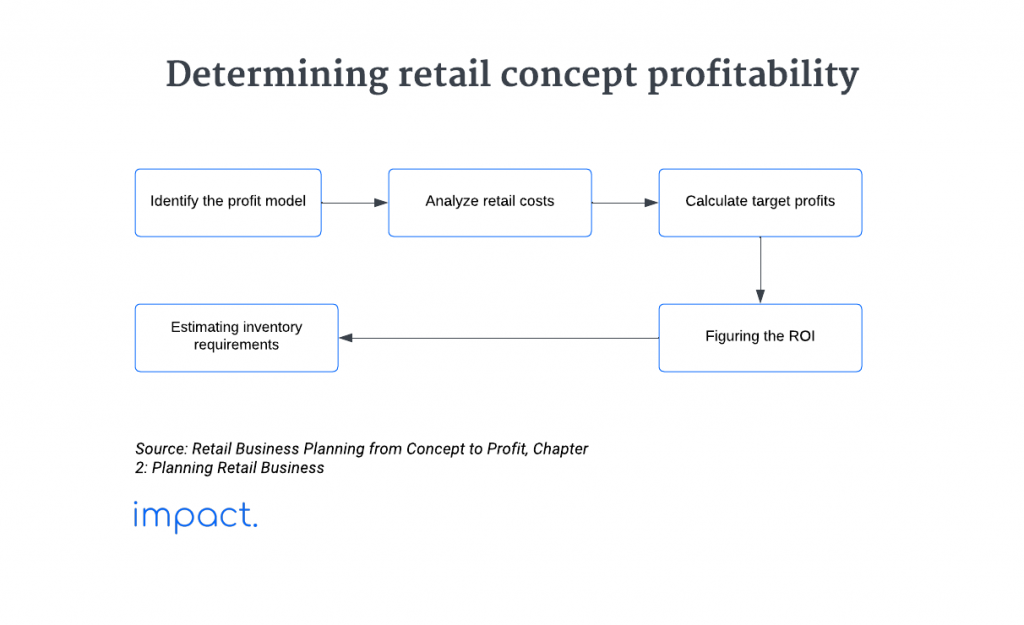
In the retail business, numbers are crucial. To run a store successfully, you must understand your profit model.
Here’s a simple breakdown: Profit is the money you have left after subtracting all your business expenses from your earnings. If you save more money after covering all costs, that’s your profit.
Tracking and managing your retail costs is crucial in the early stages of your retail business. When your business expenses go up, your profits go down.
To boost your retail store’s profitability, keep a tight rein on costs such as inventory, fixtures, equipment, overhead, taxes, and licenses.
Managing inventory is your store’s main expense; restock items promptly after selling them. If a product isn’t profitable, replace it with something more lucrative and better suited to your customers’ needs.
To ensure your store’s success, closely monitor your inventory, understanding what sells and what doesn’t. If you can cut costs without increasing expenses, your profits will rise.
When opening small retail stores, owners often invest in fixtures and equipment upfront for long-term utility. Retailers may choose to build, purchase used items, or lease to cut down on initial and ongoing expenses.
The expense for fixtures and equipment varies based on the type of retail store. For instance, a discount store may opt for simple or pre-owned fixtures, while a jewelry store could invest in top-of-the-line display cases, a sturdy safe, and high-quality lighting.
Running your store involves daily expenses known as overhead, which covers essentials like rent or lease payments. Certain overhead costs may fluctuate based on your store’s operating hours and utility usage.
In bigger retail setups, employee wages can significantly impact expenses. Yet, for small retailers, taking charge during operating hours and minimizing vacations can help cut costs and reduce income loss.
Inventory and equipment taxes are non-negotiable, whether you’re making a profit or not. Consider getting an accountant or tax advisor before starting your business. Neglecting taxes and licenses has led to the closure of many small businesses.
Boost your retail store’s success by ensuring you earn more than you spend. Keep a close eye on your profits to keep your business on track.
Ensure your retail store’s return on investment (ROI) exceeds the loan interest, as lenders will likely require it. Remember that the potential return is linked to business risk, so evaluate your venture’s risk profile to set realistic expectations for investment returns.
Based on the associated risks, anticipate an 8-12% return on your retail store investment. This return compensates you for your investment and work, while external investors receive their share.
Your most significant expense is inventory. As your business plan takes shape and your store is up and running, you’ll need more precise numbers. For now, use these figures to establish inventory targets.
Find your store’s inventory turnover rate by calculating how many times you sell your stock in a year. Aim for a typical turnover rate, like the common goal of 2X (twice a year) for small retail stores.
Get guidance on your expected turnover rate by consulting trade associations, wholesalers, or distributor salespeople, considering your store’s size and location.
Determine your desired turnover rate, then use it to calculate the initial inventory for your store’s opening day. The accuracy of your inventory estimate depends on how accurately you define the turnover rate; the more precise the rate, the better your estimate will be.
Replenish sold-out items with similar products based on sales patterns. Good managers analyze sales data to restock items with higher profit potential.
For example, if blue vases make $1.00 profit and green ones make $1.50, adjust the inventory by decreasing blues and increasing greens to boost the store’s growth.
Create a precise and accurate business plan to navigate the launch and operation of your retail store. Plan the specifics of how you will achieve your retail objectives.
Direct lenders, like banks, require a comprehensive business plan, while other investors need clarity on fund utilization and repayment. Major suppliers may request a business plan summary before offering credit for initial inventory.
Here are the key elements typically found in a successful retail business plan:
When you do retail business planning, changes are inevitable. Don’t just assume customers will come if you build something; instead, focus on building what customers want.
To guide your adjustments, you should consider these three questions:
Before you start a retail business, check essential things like market research, local demand, customer needs, competition, potential profit, and resources you need to succeed. Make intelligent choices so your investment of money and time pays off with a profitable retail business.
Think about improving your product. Identify changes that will attract more customers, increase profits, and help you reach a larger audience.
In retail, it’s crucial to meet your customers’ needs. Know your target customers, understand what they want, and adjust your business to serve them better and make more profit.
Stand out from competitors by giving customers a solid reason to choose your store. Create and implement a unique retail concept that makes your store genuinely distinctive.
New retailers may struggle to profit and satisfy customers without a solid plan. It’s crucial to assess finances and understand the store’s profitability to navigate the challenges of the business world effectively.
A well-thought-out business plan serves as a roadmap, enhancing the retailer’s ability to run their store successfully and succeed in the competitive retail landscape. In the next chapter, we’ll explore finding the ideal location for your business.
Ramsey, D., & Ramsey, J. (2010). The Everything Guide to starting and running a retail store: All you need to get started and succeed in your own retail adventure. Adams Media.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.
