Best ERP Software for Indonesian Businesses in 2025
There is no such thing as the best ERP software. ERP exists to automate and…
Nindy
July 9, 2025Customer relationships are the lifeblood of a business’s success. However, we understand that it can be a daunting task.
That is where Customer Relationship Management (CRM) comes in.
CRM is a powerful strategy that helps your business manage customer interactions effectively. The solution helps boost sales and foster long-term loyalty with customers.
Indonesia’s CRM market offers many options, from established players to innovative newcomers. It makes choosing the right one an even more tricky task. We have created this comprehensive guide to help you choose the right system for your organization.
The guide includes information on what to look for in a CRM system. Also, it features a list of the top 20 CRM applications in Indonesia to aid your informed purchase decision.
A CRM application is a business tool that helps companies maintain and improve customer relationships. It is not just software but a strategic blend of people, processes, and technology.
Applications for CRM get up close and personal with customer-related processes. It aids in forecasting, customer service, sales, and the study of consumer trends.
Modern CRM software enhances customer experience like never before. A company’s success depends on satisfied clients.
CRM applications are essential for businesses for these five reasons:
CRM systems automatically collect your customer data. It includes their contact information, purchase history, and preferences. The available data empowers effective personalized marketing campaigns.
CRM tools enable you to request customer input, which aids in assessing their satisfaction with your business. Additionally, CRM platforms empower you to interact with clients actively — enhancing their appreciation for your brand and solidifying their relationship with it.
With the vast data available, CRM makes marketing easier. CRM’s analytic capabilities allow for campaign tracking. You can measure a campaign’s success and make adjustments through data-driven decisions.
CRM software seamlessly integrates with a variety of business channels. This function allows you to interact with customers across different touchpoints. As long as organizations have an all-encompassing view of their interactions, customers will enjoy a consistent experience.
CRM applications provide businesses with tools to automate the sales process. With this feature, your team can prioritize leads and track their sales progress. Using analytics, companies can pinpoint areas for improvement and make decisions based on data to increase sales.
There are various criteria to look out for before choosing a CRM system. Below are five critical capabilities of a CRM application that you need to consider.
A CRM application should be easy for your sales team and other stakeholders. Search for a CRM with an intuitive interface, easy navigation, and minimal learning curve. Your team should immediately adopt and utilize the CRM without extensive training.
Every business has unique processes and requirements. Look for a CRM that offers flexibility regarding custom fields, workflows, and automation options. You can customize the CRM to match your business processes and adapt to your evolving needs.
A CRM is an essential resource for overseeing contacts and sales tasks. When selecting a CRM, search for all-inclusive functions such as monitoring leads, managing opportunities, and forecasting sales. Additionally, it should record interactions, save files, and offer insights into the sales journey. These features enable your team to handle customer relations and finalize transactions promptly and efficiently.
A good CRM should offer robust reporting for insights into sales performance and business operations. Look for a CRM with pre-built and custom report options and data visualization features like charts and graphs. These tools will help you make informed decisions and identify areas for improvement in your business.
The perfect CRM effortlessly merges with your current workflows and systems like email, calendars, and marketing automation tools. Find a CRM with robust integration features and automation possibilities. Doing so will enhance sales procedures, increase productivity, and conserve precious time and resources for your company.
Read more: 16 Most Recommended Receipt Printer Software 2023!
You can now view our list of Indonesia’s 20 best CRM applications. We have provided details on the unique features and prices for each product.
Impact is a dynamic solution made for Indonesian businesses, offering comprehensive Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) capabilities. Impact’s CRM tool can integrate with its various modules, including sales, purchasing, and omnichannel. The CRM application suits MSME businesses, startups, and enterprises.
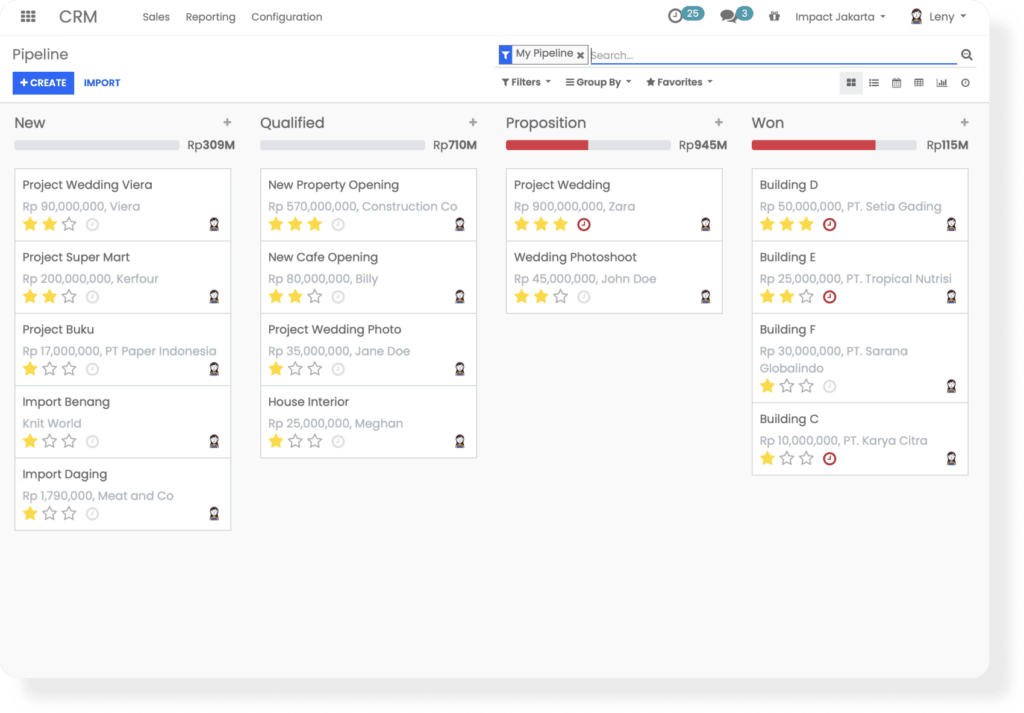
Features:
Price:
The basic package starts with a one-time fee of Rp99 million. Implementation costs an additional Rp50 million.
Microsoft Dynamics CRM is a tool to improve sales and marketing operations. It provides valuable social insights, business intelligence, and campaign management capabilities. It has three deployment options, cloud-based, on-premises, and hybrid.
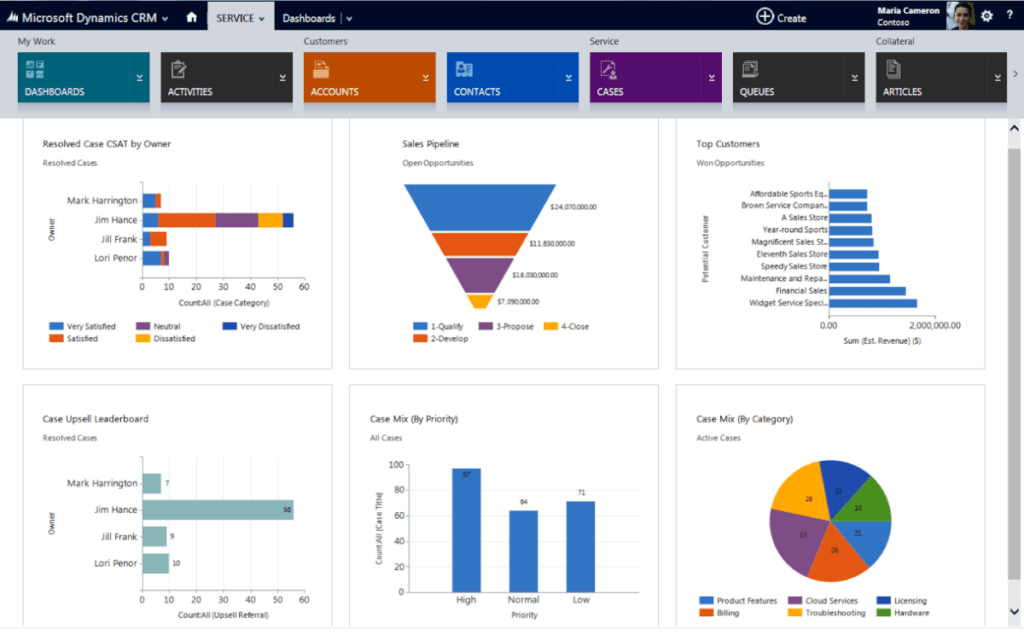
Features:
Price:
Ranges from $63/user/month.
Odoo is an ERP system that assists you in managing business processes. It is an open-source ERP with over 30 applications covering various business needs. Besides CRM, Odoo offers accounting, inventory, point-of-sales (POS) applications, and other modules.
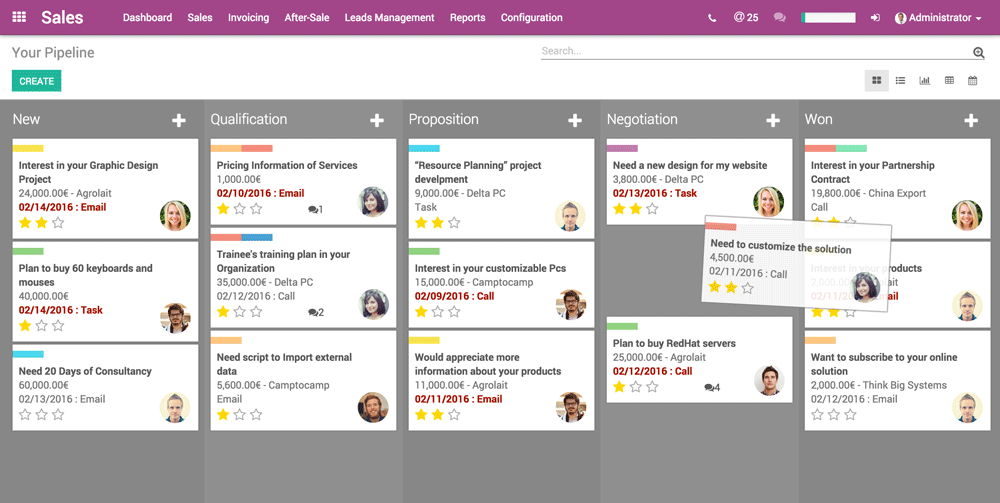
Features:
Price:
Odoo offers a free basic package for one application. However, its standard package charges $7.25/user/month.
HubSpot is a modern CRM application that has recently entered the market. It provides a unique tracking code for every HubSpot account, enabling users to monitor website traffic quickly.
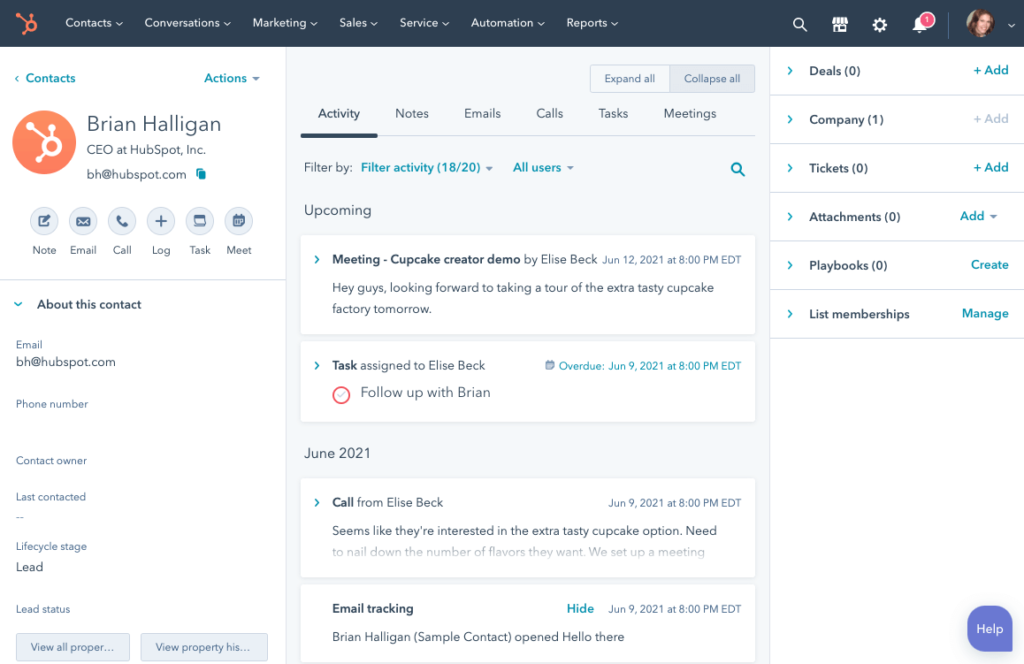
Features:
Price:
For large companies, HubSpot provides two packages – Professional and Enterprise. The Professional package starts at $1.781/month, while the Enterprise package starts at $5.000/month. The CRM suite is also available for individuals and smaller businesses. These start at $50/month.
Salesforce is a cloud-based software that facilitates connections between sales, service, marketing, and more. The CRM application enables you to uncover sales opportunities throughout your entire business.
Features:
Price:
Sales Cloud’s pricing starts at $25/month.
Zoho CRM enables businesses to connect, engage, and close deals smartly. With automation and comprehensive CRM tools, it streamlines operations for business growth.
Features:
Price:
Zoho offers four different packaging options – Standard, Professional, Enterprise, and Ultimate. The price range starts from $14/user/month to $52/user/month.
SAP CRM is a software suite that provides businesses with tools for managing and optimizing customer interactions and relationships. It offers functionalities for sales, marketing, and service processes. SAP initially offered on-premises CRM but shifted focus to cloud-based offerings for competitiveness.
Features:
Price:
SAP does not offer a specific price range for SAP CRM. For up-to-date information on their pricing models, it is advisable to contact their representatives directly.
Oracle CRM is a comprehensive software solution that empowers businesses to streamline sales processes and enhance customer engagement. With its robust suite of tools, organizations can improve loyalty, retention, and business performance.
Features:
Price:
The specific pricing details for Oracle CRM may vary depending on the edition and features needed. It is best to contact their team directly or visit their Global Price List.
Pipedrive CRM is a customer relationship management software specifically designed to cater to the needs of salespeople. Pipedrive CRM’s core function is to acquire, organize, and share vital customer information, thereby contributing to a more efficient and effective sales process. The platform is a versatile choice for businesses of all sizes.
Features:
Price:
Pipedrive offers pricing plans that range from $14.90/month to $99/month. Different price points offer varying features and options.
Freshsales CRM, developed by Freshworks, is a customer relationship management tool for different industry verticals. The subscription fee for Freshsales is affordable, making it a budget-friendly option for small to medium-sized businesses.
Features:
Price:
Freshsales offers three plans — Growth, Pro, and Enterprise. Payment is annual, ranging from $15/user/month to $69/user/month.
Read more: 21 Best Cashier App Recommendations for Business in 2023
Sugar CRM offers an overview of the customer journey, providing contextual intelligence for a complete customer view. Businesses can anticipate opportunities and make informed decisions when using this CRM.
Features:
Price:
SugarCRM offers a variety of pricing plans tailored to different business needs. Sugar Sell starts at $49/user/month. Sugar Serve starts at $80/user/month. Sugar Market starts at $1000/user/month.
Formerly BPM Online, Creatio is a no-code platform for CRM. Users can create apps, automate workflows, and more without coding. It merges CRM with industry workflows and offers templates and customization options.
Features:
Price:
From $30/user/month
Copper offers a CRM application that streamlines business operations by managing contacts, offers, emails, files, and more from a single dashboard. It also analyzes key metrics, such as sales revenue and lead tracking. With Copper’s automation capabilities, businesses can enhance productivity by automating almost any sales process.
Features:
Price:
The basic plan starts at $29/user/month.
Keap is a specialized software for small businesses that centralizes customer information and streamlines daily tasks, freeing time from repetitive work. This CRM allows companies to focus on growth and deliver excellent customer service.
Features:
Price:
Keap offers two pricing plans. The Pro plan costs $149/month for 1500 contacts and two users. The Max plan costs $249/month for 2500 contacts and three users. Additional users will cost an extra $29 each.
Insightly CRM is a user-friendly and customizable customer relationship management software for small to midsize businesses. It helps companies to manage sales, marketing, service, and app integration in one platform. Insightly streamlines sales, personalized marketing, and enhances customer support, making it a valuable tool for business growth.
Features:
Price:
Insightly is available in three plans. The Plus plan charges users $29/month. The Professional plan starts at $49/user/month. The Enterprise plan starts at $99/user/month.
Agile offers CRM software streamlining sales, marketing, and service in a single platform. Agile’s user-friendly applications are supported by cloud-based SaaS services for mobile access, enabling real-time data updates from anywhere.
Features:
Price:
Agile CRM offers four subscription plans –- Free, Starter, Regular, and Enterprise. Pricing ranges from $14.99/month to $79.99/month.
Scoro CRM software boosts sales processes and team performance. With its CRM module, you can easily manage the contact details of suppliers and customers in one place, simplifying filtering and searching.
Features:
Price:
From $26/user/month
Accelo CRM is a cloud-based software for small and medium-sized businesses. The system provides sales, project management, billing, and client service tools. With seamless sync for email, calendar, and contact tools, it streamlines operations and enhances productivity.
Features:
Price:
Pricing starts from $24/user/month for its Cloud plan. The Premium plan starts from $39/user/month.
NetSuite CRM is a robust cloud-based software for managing customer relationships, sales, marketing, and partner interactions. It provides vital features such as sales and marketing automation, customer service management, and additional functions to improve business capabilities.
Features:
Price:
NetSuite’s annual license fee comprises the core platform, optional modules, and user count. However, pricing details are unavailable on their website and require users to contact NetSuite for further information.
Zendesk Sell is a powerful sales force automation software that boosts productivity and streamlines processes. It provides enhanced pipeline visibility for sales teams.
Features:
Price:
Zendesk’s Basic plan starts from $19/user/month. Complete CRM capabilities would cost $99/user/month.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

If you are involved in business transactions, you may have encountered the term “proforma invoice.”
Many businesses typically issue these documents to customers post-negotiations. The invoice describes the agreed-upon deliverables.
What is a proforma invoice?
Its name comes from the Latin phrase “pro forma,” meaning “for the sake of form.” A proforma invoice serves as a provisional arrangement outlining the terms of an agreement.
People often confuse proforma invoices with standard invoices. Little do they realize that a proforma invoice is temporary and requires subsequent issuance of an official document.
If you still want to know more about proforma invoices, we encourage you to read through this article. It will show you its definition, practical applications, and business benefits.
A proforma invoice is a pre-sale document sent to buyers before the shipment or delivery of goods, serving as a preliminary bill of sale.
Sellers typically issue this document for the buyer to review. Once reviewed, the buyer will then agree on the purchase. The seller delivers the product or service that was agreed upon afterward.
The proforma invoice may be subject to change. It is a reasonable estimate to prevent buyer surprises from unexpected charges after transaction completion.
Proforma invoices give buyers a price illustration that includes an estimate of commissions, taxes, or shipping costs.
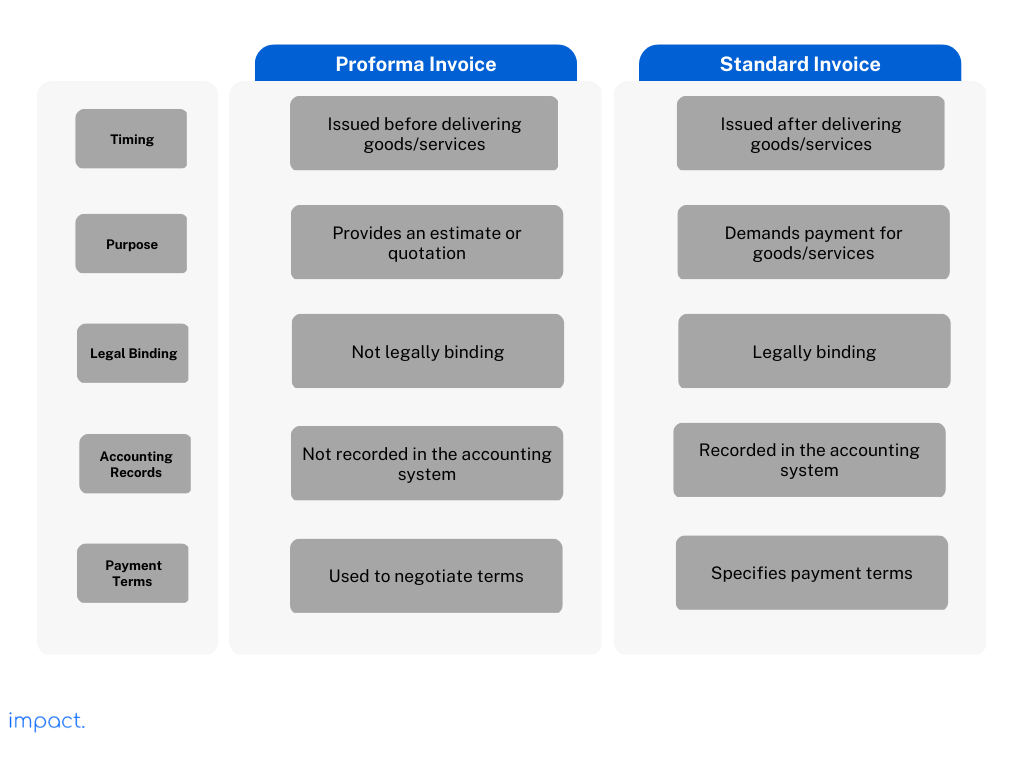
We mentioned in the introduction that people think a proforma invoice is the same as a standard invoice. However, the two documents are very different.
A proforma invoice is usually issued before a sale takes place. The seller often provides a pro forma invoice during a transaction’s negotiation or quoting stage. It is a tool to help buyers finalize the order details to decide whether to place the order based on the information provided.
Standard invoices are issued when the sale is complete. It is a formal payment request and includes the final agreed-upon prices, payment terms, and applicable taxes or fees.
As standard invoices formally ask buyers to make payments, it is legally binding. An issued invoice enforces the rights and responsibilities of the buyer and seller to meet the negotiated agreement.
Accounting books do not record proforma invoices. They are not considered completed transactions. Standard invoices, however, are recorded for accounting purposes by both the seller and buyer.
The table below should help you understand the main differences between the two invoices easily.
Proforma invoices have several uses in commercial transactions. Here are seven standard proforma invoice functionalities that you need to be aware of:
Proforma invoices provide a preliminary quotation or estimate to a potential customer. They can outline a possible transaction’s costs, terms, and details. The seller helps the customer understand the expected expenses of the goods or services.
Sellers use proforma invoices to request customer deposits before delivering goods/services. This function helps sellers mitigate risks in case of non-payment. Additionally, prepayment helps sellers manage working capital for production costs.
Read more: What is SCF? Definition, 6-Step Process, and its Benefits
Proforma invoicing can be a helpful tool for managing inventories in a business. You can efficiently plan and manage stock levels when you have a preliminary record of anticipated sales.
Businesses involved in international trade often use proforma invoices. This document assists the import/export process by providing accurate information to customs authorities. Information may include product description, quantity, value, and relevant trade agreements/licenses.
A proforma invoice is not legally binding. However, you can use it as a tentative contract agreement with buyers. Proforma invoices specify the transaction’s terms and conditions, including payment and delivery schedules. For both parties, this information offers a certain amount of security.
In many organizations, an internal approval process is standard practice. These procedures can take time since you must navigate numerous red tape levels. Giving an estimate before the acquisition gets cleared speeds up the process.
Pro forma invoices make it easier for the buyer and seller to communicate. All parties will be aware of the costs and conditions of the deal. The document promotes openness and trust between the parties, facilitating easier economic transactions.
There are several benefits for businesses in using proforma invoices. Here are six benefits that we have compiled for you:
A proforma invoice is given to clients or business partners to show their professionality. It creates an impression of security and trust by demonstrating how well-organized and open your company is.
All pertinent information regarding the order, such as the particulars of the items and the estimated cost, is included in a proforma invoice. The provided details make sure that both parties fully comprehend the transaction. Buyers and sellers will have less miscommunication, and they may manage their budgets more efficiently.
The use of proforma invoicing encourages buyers and sellers to commit more fully. It doubles as a quote or purchase order for customers, which in many cases may be necessary to get the sale approved and the final invoice paid.
Everyone hates having to go back and forth when trying to purchase something. Proforma invoices eliminate this process by documenting and agreeing upon the terms of a transaction upfront. The process can save time, effort, and resources for the sales process. Additionally, it also minimizes communication breakdowns between seller and buyer.
Proforma invoices are not complete invoices. The pricing that is displayed is liable to change at any time. This flexibility is advantageous in dynamic corporate settings where frequent changes to orders or transactions occur.
Proforma invoices provide a starting point for discussions and negotiations between buyers and sellers. Both parties can make changes according to their needs. Pro forma invoices also contribute to building long-term customer loyalty.
To better understand proforma invoices, here is a sample scenario in which a company utilizes this tool.
A small manufacturing company based in Indonesia receives an inquiry from a potential European buyer interested in purchasing many of their products. The company wants to provide the buyer with an accurate estimate of the costs and terms of the transaction before proceeding with the sale.
The Indonesian company creates a proforma invoice with detailed information about the products, quantities, unit prices, and applicable taxes or fees. They also outline the payment terms, shipping details, and other relevant terms and conditions.
The proforma invoice is a quote for the buyer, helping them review and confirm transaction details, assess total costs, and obtain financing. It also allows discussions and negotiations between the buyer and seller for any needed changes or clarifications.
Once the buyer approves the proforma invoice, they issue a purchase order to the seller, referencing the agreed-upon conditions. The seller then issues a formal commercial invoice based on the agreed terms, and the buyer proceeds with payment and shipment of the products.
This use case shows that the proforma invoice facilitates negotiation and agreement between the buyer and seller, ensuring transparency and accuracy. It helps establish a clear understanding of the sale terms and provides a basis for documentation and financial arrangements.
The primary purpose of a proforma invoice is to outline the details of a proposed transaction for the customer. Making one uses the same method as a standard invoice. Hence, it should contain identical information to the final invoice:
The unique invoice number.
Seller information (which includes full contact details of the entity/individual).
Buyer information (which includes full contact details of the entity/individual).
A detailed description of goods/services offered (includes quantity, unit price, and total price).
Payment & shipping terms that outline agreed-upon terms of payment and method of delivery.
If applicable, the pro forma invoice should show the expected added taxes & duties.
A validity period indicates the timeframe for which the quotation is valid.
However, unlike a final invoice, a proforma invoice should have the following:
Here is a proforma invoice sample to help you understand what it looks like.
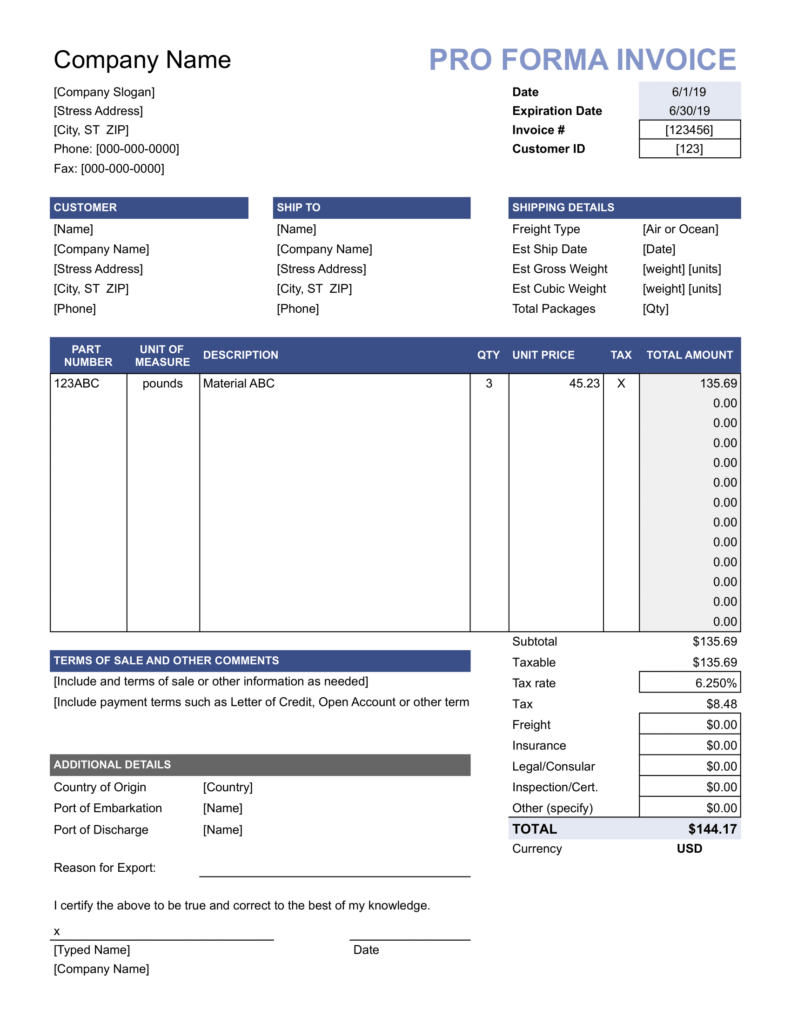
Unlike standard invoices, a proforma invoice is not a formal payment request and is subject to change. Understanding the distinction between the two is essential as they serve different purposes
Proforma invoices are provisional documents that outline the terms of an agreement. They provide a reasonable estimate of the costs involved in a transaction, allowing buyers to make informed decisions before placing an order.
By issuing a proforma invoice, sellers can ensure that their buyers are well-informed about the transaction’s terms and prevent surprises from unexpected charges.
If you are looking for an efficient way to manage your invoices and streamline your payment process, consider Impact’s invoicing software.
Take charge and optimize your business operations with the convenience of automated invoicing, streamlined payment adjustments, and a unified taxation system.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

YouTube is where creators and businesses thrive, reaching audiences worldwide through captivating videos, the ultimate tool for online engagement. From Facebook to LinkedIn and beyond, video is the top choice, adored, viewed, and shared across all social platforms.
This guide maps your journey to YouTube marketing triumph, guiding you from channel inception to content crafting and brand building. With over half of marketers (55%) already utilizing YouTube’s influence, grasping its methods, tactics, and top tips is critical to captivating your audience like never before.
Video and YouTube are huge on the internet, grabbing people’s attention with cool videos that spread everywhere. However, YouTube isn’t just about fun; it’s a powerful tool for marketing and connecting with others online.
Let’s explore ways how YouTube as a platform works:
Registered users upload videos to their YouTube channels. These creators can set privacy settings for their videos, making them public, private, or unlisted.
Users can engage with videos and creators in several ways:
Users can discover videos on YouTube through various means:
YouTube allows businesses and content creators to advertise and connect with their desired viewers. Advertisers can make campaigns using various ad types like pre-roll ads, display ads, and sponsored content, tailoring them to specific demographics, interests, and keywords.
YouTube offers various monetization options for creators to earn revenue from their content:
YouTube has tools like Content ID to safeguard copyrighted content and enforce intellectual property rights. Content ID scans videos for copyrighted material, letting rights holders claim or make money from their content. Users can also report copyright violations and settle disputes on YouTube.
YouTube is a vast social media platform with about 2.9 billion active monthly users globally in 2024. This number is predicted to grow by 200 million users, around 6.89%, from 2024 to 2025.
Businesses can benefit from this vast user base by using YouTube to reach potential customers worldwide. By consistently sharing quality content and teaming up with influential creators in your field, you can increase your brand’s exposure and attract more traffic to your business.
Backed by Google, YouTube videos frequently appear in search results, boosting visibility and attracting natural visitors. Many search result pages now showcase video carousels, with over 94% of those videos sourced from YouTube.
By leveraging YouTube marketing, you can score backlinks to your site, making it more visible on search engines. This approach also strengthens your business’s online reputation, directly influencing its ranking on Google’s search results.
In today’s digital age, video content captures attention quickly and effectively. YouTube marketing empowers businesses to convey their message through captivating videos, keeping viewers engaged.
Videos are a dynamic tool for storytelling, ideal for showcasing products, providing demos, and sharing customer experiences.
YouTube is an excellent platform for boosting your brand’s credibility. It’s the go-to spot for product research and buying decisions, with about six in ten people finding it trustworthy for shopping.
Creating valuable content on YouTube helps you establish authority in your field. Sharing industry knowledge and expert advice builds trust with your audience, positioning your business as a leader in the industry.
YouTube marketing can boost your profits — 81% of marketers credit videos for directly boosting their sales.
YouTube’s various shopping tools, such as cards, end screens, channel stores, and tagged products, give marketers ample opportunities to sell both within and outside the platform.
YouTube isn’t just a tool to enhance your marketing; it’s a potential money-maker in its own right. You can earn cash from views and engagement if your channel meets YouTube’s Partner Program requirements.
With compelling content that draws in viewers, your business can tap into YouTube as a source of passive income while also showcasing your offerings.
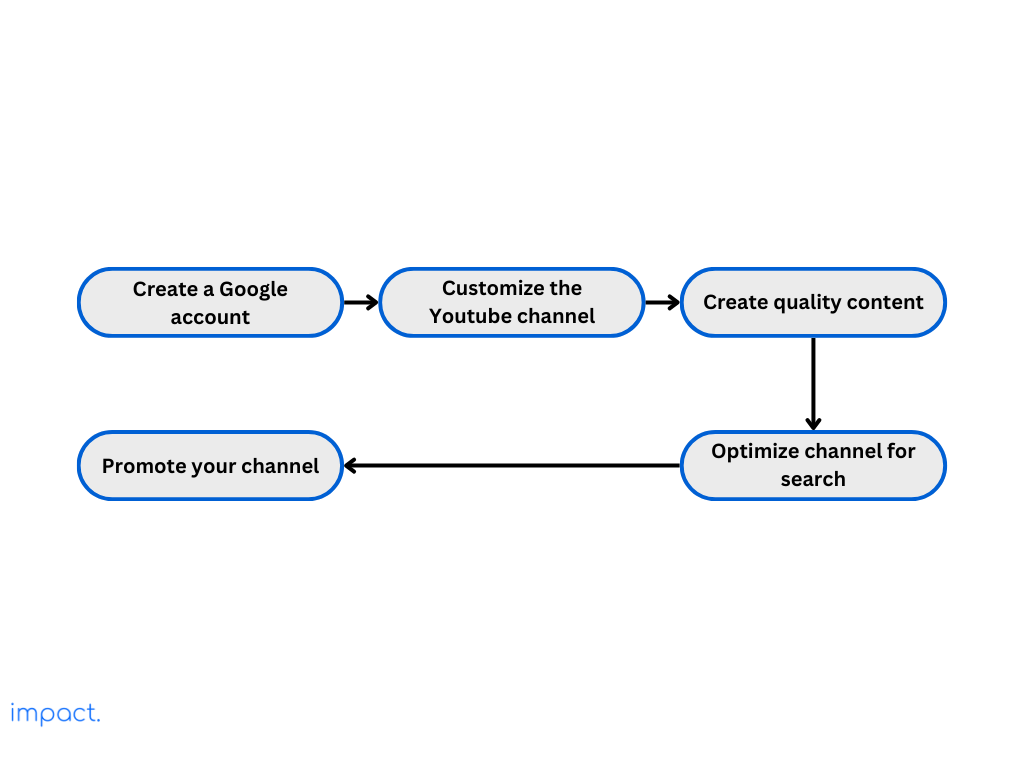
If you don’t have one already, create a Google account that you’ll use to manage your YouTube channel. Ensure it’s linked to an email address you check regularly.
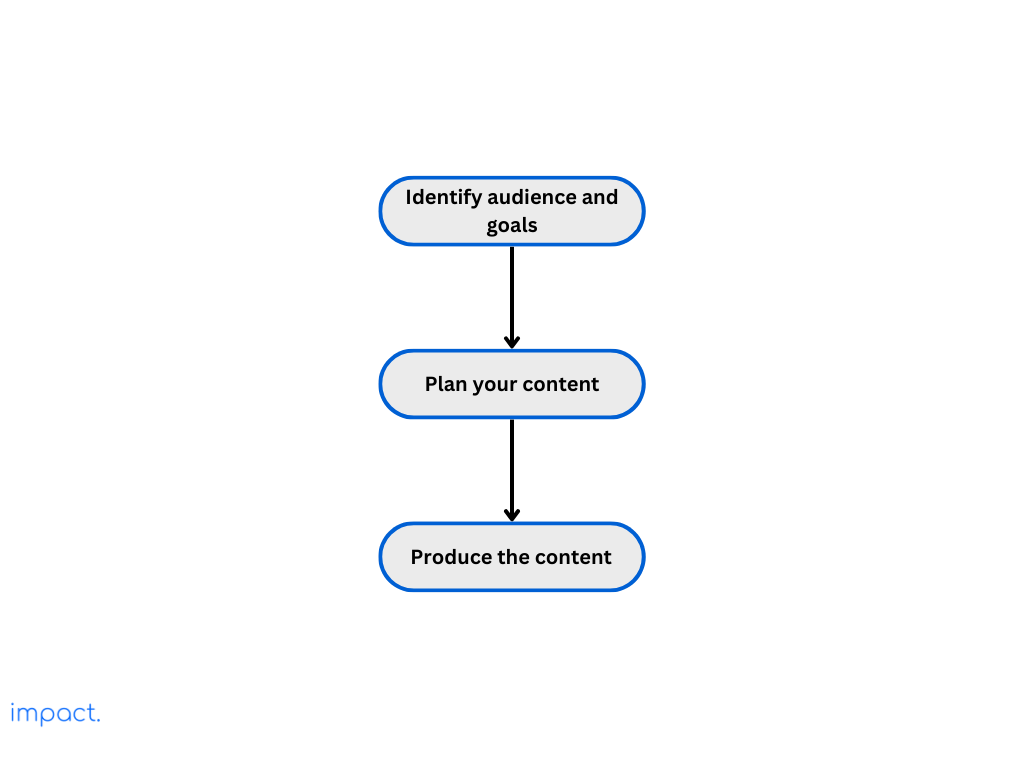
Know your target audience and what you want from your YouTube marketing. Set clear goals, such as raising brand awareness, bringing more people to your website, generating leads, or increasing sales.
Brainstorm ideas your audience will love and help your marketing goals. Make a content calendar to plan when you’ll post videos regularly so your audience knows when to expect new content.
Here are some popular content that are used for YouTube marketing:
Invest in making quality videos that grab people’s attention and provide helpful content for your followers. Consider your videos ‘ format, style, and length based on your audience preferences and the type of content you’re creating.
The YouTube algorithm tracks how users engage with videos, considering factors like watch time and user feedback to suggest similar content. By analyzing viewers’ preferences, the algorithm curates what the users might like.
Use keywords strategically in titles, descriptions, and tags to boost your video’s visibility. Create content encouraging likes, comments, and shares, and adapt the length and format to match your audience’s preferences.
Promote your video across different channels to maximize its reach and engagement. Share on social media, embed it in blog posts or emails and collaborate with influencers or fellow companies in your niche.
Engage with your viewers by responding to comments, addressing questions, seeking feedback, and showing appreciation for their support. Dedicate a specific time to check video interactions and engage with users to ensure you don’t overlook this crucial aspect.
Thumbnails are vital on YouTube because they’re what people see first and help get clicks — 90% of top videos have custom thumbnails. Create captivating and pertinent thumbnails showcasing your video on licks to enhance its appeal and engagement.
Use clear pictures, easy-to-read words, and exciting visuals to make good thumbnails. What people like in thumbnails can change, so it’s wise to stay updated on what’s popular in your community.
Studying your rivals’ YouTube channels is critical to understanding effective strategies in your field. You can enhance your approach by pinpointing successful content types, subjects, and engagement methods.
Identify gaps in their content that your brand can address. Seize opportunities your rivals might overlook and capitalize to stay ahead of the curve.
Consistency is vital to building a loyal YouTube audience. Establishing a regular upload schedule helps set expectations for your viewers and keeps them returning for more.
Consistency helps improve your channel’s visibility in YouTube’s algorithm and fosters trust and loyalty among your audience. Whether weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly uploads, stick to your schedule to maintain momentum and keep your audience engaged.
There are countless creators on YouTube, each with their dedicated followers. You can team up with these creators to showcase your offerings uniquely and engagingly.
Identify creators in your niche whose audience matches yours and suggest partnership ideas like co-hosting videos or cross-promotions. Collaborating exposes your channel to new viewers and spices up your content, keeping your audience hooked.
Keeping an eye on your YouTube stats is crucial to understanding who’s watching, how your videos are doing, and where you can improve. Focus on numbers like watch time, audience retention, demographics, where your viewers are coming from, and how engaged they are to figure out what works and what doesn’t.
With this information, you can tweak your content plan, make better videos, and reach your YouTube goals. It’s all about understanding your audience and using that insight to improve your YouTube marketing.
YouTube presents a prime chance for marketers to engage with vast audiences and boost brand credibility through captivating videos. Although it might seem daunting initially, YouTube makes sharing and watching videos easy, meeting your audience’s needs for learning, fun, and engaging with brands through video.
Integrating Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software can amplify YouTube marketing efforts by streamlining operations further and offering valuable insights into audience behavior and preferences. By leveraging this data, businesses can tailor content to meet audience needs, maximizing the impact of their marketing campaigns.
McDonald, J. (2022, July 4). Social Media Marketing Workbook: How to Use Social Media for Business.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

In today’s digital world, social media is critical for marketers. Among these platforms, Instagram stands out for its visual appeal and diverse features, making it perfect for businesses.
Our guide dives into Instagram as a marketing tool, covering strategies from audience demographics to crafting engaging content and using its notable features. Whether you’re new or experienced in social media marketing, this guide aims to give you the insights and tools to succeed in Instagram marketing.
Instagram is a social media platform mainly for sharing photos and videos. Initially released in 2010, Instragram has since been a part of Meta Platforms after Facebook acquired it in 2012 for about $1 billion.
Although you can use Instagram on the web to check your feed and profiles, the best experience is on the mobile app. The application has doubled its daily average usage time from 15 minutes in 2019 to about 33 minutes as of 2024.
Instagram is all about sharing pictures and videos, but it’s grown into much more than that. Here’s what you need to know:
With over 2 billion monthly users, Instagram ranks as the third most popular social media platform globally. Whether you’re a business owner or not, chances are your current and potential customers are active users.
Instagram reports that 90% of its users follow at least one business profile. This information means that reaching a substantial audience organically through your business profile isn’t too grinding
Instagram marketing is great for businesses because it’s all about sharing pictures and videos, making it perfect for showing off products attractively. Research shows that our brains focus more on what we see, with about 90% of the information we take being visual.
Moreover, compared to other social media, people on Instagram are more active, liking, commenting, and sharing content. According to Forrester, top brands get way more engagement on Instagram — 58 times more per follower than on Facebook.
Businesses should prioritize boosting conversions since social media, like Instagram, can attract many potential customers. According to a Meta, 87% of people take action after seeing product info on Instagram, like following a brand or making a purchase.
Although an Instagram profile is limited to clickable links, such as in bios, shoppable feeds, and stories, it still delivers impressive results. This strategy keeps the user experience smooth and saves marketers from paying for unnecessary clicks.
Instagram makes it easy for businesses to sell through the app, improving customers’ shopping experience. With features like shoppable posts and Instagram Shopping, users can buy products without leaving Instagram.
Plus, Checkout on Instagram streamlines the purchasing process, though it’s only available for US businesses. Businesses can use promoted shopping ads and product launch announcements to reach specific groups of people and get them excited about what they’re selling.
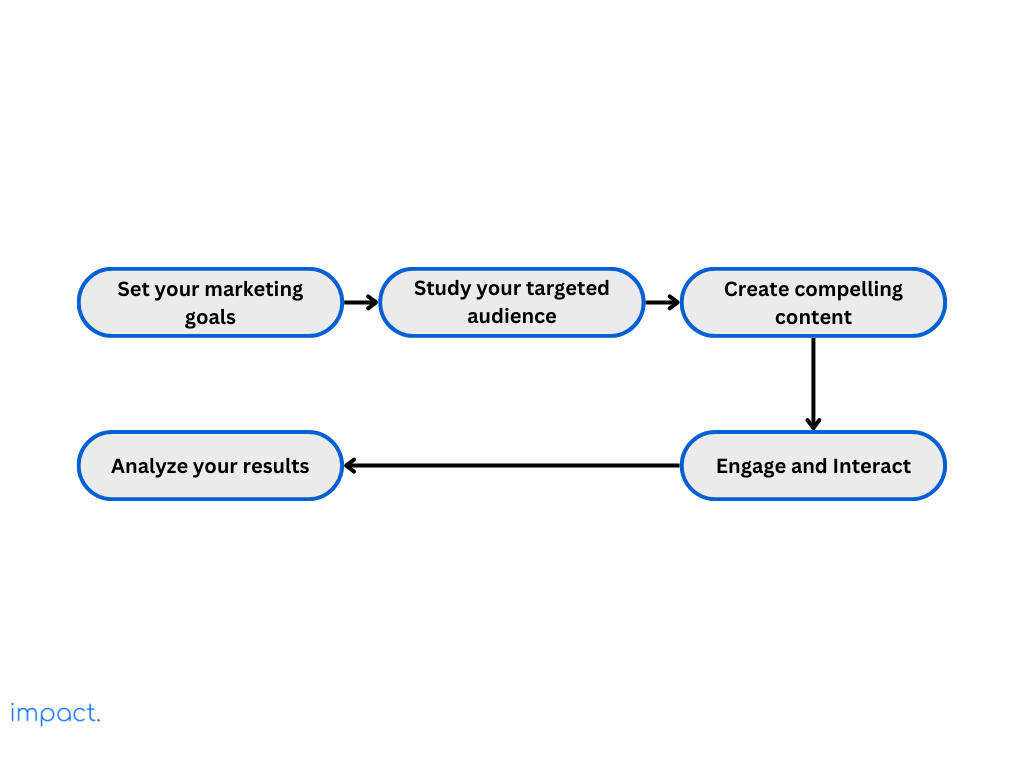
Before diving into Instagram, you and your team must ask yourself why you’re there. To thrive on this platform, you need clear goals and a purpose that aligns with your efforts and resources.
Define what you want to accomplish with your Instagram marketing. Whether getting your brand out there, bringing people to your website, finding leads, or making sales, having specific goals will shape your approach.
To better connect with your audience, research who they are, what they like, and how they behave. Utilize tools like Instagram Insights and surveys to gather valuable data.
For instance, if you’re targeting Gen Z, focus on showcasing product demos, customer reviews, and exclusive launches, as they make up a significant portion of Instagram’s user base for product discovery.
Focus on creating eye-catching content that fits your brand and appeals to your followers. While Instagram started as a photo-sharing platform, it’s evolved into much more.
To make the most of Instagram marketing, use a variety of content types:
To grow a community on Instagram, engage regularly with your followers and fellow users. Respond quickly to comments, messages, and mentions to show that your brand is attentive and caring.
Start conversations by asking questions, running polls, or hosting Q&A sessions. Also, team up with influencers, partners, and user-generated content to grow your presence and credibility.
To boost your Instagram marketing, keep a close eye on critical metrics like engagement, follower growth, reach, and conversions. Instagram Insights offers detailed stats on post-performance, audience demographics, and activity, helping you understand what works best.
Leverage this data to tweak your strategy, spot trends, and enhance your content for optimal outcomes. Test various tactics, learn from them, and consistently adapt your approach to elevate your Instagram game.
Timing is crucial on Instagram. You’ll likely get more likes and comments when you post when your followers are most active.
Research from Sprout Social suggests that Tuesdays and Wednesdays from 10 a.m. to 2 p.m. are prime posting times. However, this can vary depending on your industry, so it’s wise to do some of your research to find the best times for your audience.
Creating a content calendar is essential for social media marketing — it helps you organize your time effectively to produce high-quality content. Planning also allows you to review and edit your content before publishing.
Plan for special events, holidays, or promotions ahead of time to ensure your content stays timely and relevant. Consistent planning helps maintain a strong brand image and keeps your instagram marketing on track.
Establish a clear brand voice and tone for all your Instagram posts. Ensure your captions, visuals, and follower interactions match your brand’s personality and values.
Consistency is critical to building trust and recognition with your audience. Maintaining a uniform voice strengthens your brand identity and establishes a deeper connection with your followers.
One study found that 87% of people buy products because an influencer suggested them. These endorsements on Instagram don’t just get more eyes on your brand; they also build trust with users.
However, when teaming up with influencers, pick ones whose followers match your target audience. Stick to influencers who can reach the people you’re trying to reach.
Hashtags are powerful tools on platforms like Instagram because they make your posts visible to people who search or engage with similar content. Using hashtags strategically increases the chances of a wider audience discovering and seeing your content.
Instead of focusing solely on the most popular hashtags, prioritize those directly related to your product or service. This focused strategy improves the chances of reaching potential customers interested in your offer.
Put your best posts there to ensure more people see them and get more likes and comments. Choose posts that showcase your brand’s strengths, key messages, or important announcements to capture the attention of new visitors.
Regularly update pinned posts to highlight fresh and relevant content, keeping your profile dynamic and engaging.
Instagram isn’t just a photo-sharing platform anymore; it’s a massive social hub with over two billion monthly active users. It might seem daunting if you want your brand to perform well on this platform, but some tools can help.
With the help of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software, you can segment your Instagram followers based on various criteria, such as demographics and engagement level, to tailor your marketing to specific groups for better results. Additionally, CRM enables you to plan, execute, and analyze Instagram marketing campaigns.
McDonald, J. (2022, July 4). Social Media Marketing Workbook: How to Use Social Media for Business.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

In our last piece, we discussed how to market well on Facebook, sharing tips to make the most of its many tools and users. Now, we move on to LinkedIn, another big player in social media marketing.
More professionals and businesses see the benefits of promoting themselves and networking on LinkedIn. To thrive in today’s digital world, you must understand LinkedIn marketing and how to use it effectively.
LinkedIn is a social network made for professionals. Its main aim is to help members connect with people they know and trust in their industry. It’s also helpful in finding job opportunities, learning about companies, and staying updated on industry news.
LinkedIn’s structure includes:
LinkedIn is much more professional than Facebook. It’s where you’ll find business-minded individuals like professionals, decision-makers, and industry leaders.
When you advertise here, you connect with people interested in networking and business. LinkedIn says that showing your brand and messages about getting customers here makes you six times more likely to make sales.
LinkedIn offers a trustworthy and safe environment compared to other social media sites. According to Hootsuite, more than 70% of marketers view LinkedIn as a dependable platform with a promising return on investment.
Because LinkedIn users professionally present themselves, there’s a greater trust in the content and engagements. This environment benefits businesses aiming to foster credibility and confidence among their target audience.
LinkedIn helps businesses stand out by sharing helpful content, participating in discussions, and highlighting their expertise. Businesses can establish themselves as leaders by publishing articles, joining conversations, and sharing insights.
Brands that advertise on LinkedIn are perceived as higher quality (59%), more reputable (92%), more intelligent (74%), and more respectable (59%), resulting in a 10-15% increase in short-term sales performance.
LinkedIn has more than 900 million members worldwide from 200 countries. Out of its total users, about 16.2% of LinkedIn users are active every day, with 48% being active monthly.
Whether you’re targeting a specific group or a broader audience, LinkedIn provides strong targeting options to help your marketing efforts reach the right audience. This broad reach can lead to better brand awareness, engagement, and business growth.
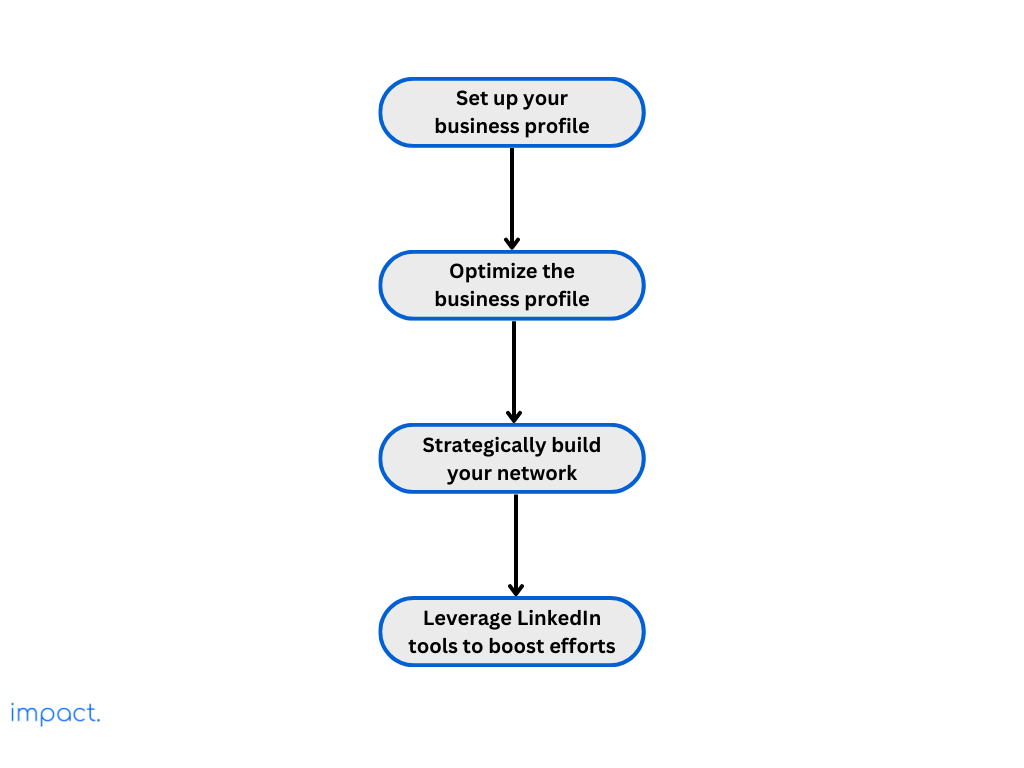
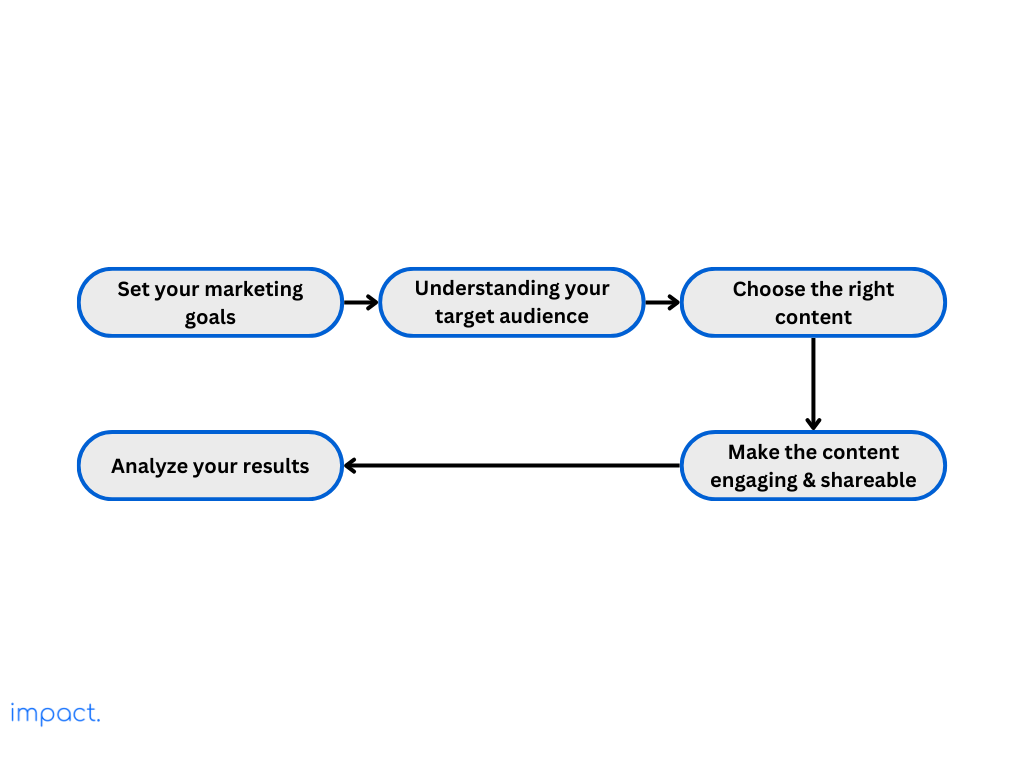
To create an effective LinkedIn content strategy, set clear goals to measure success first. These goals guide your content creation and help you track progress.
The various goals businesses usually aim to achieve using LinkedIn include:
Make sure your LinkedIn content strategy aligns with your business goals. That way, it can actively contribute to achieving those goals.
LinkedIn is great for reaching professionals and businesses. To make the most of it, focus on the ones relevant to your goals.
Defining your target audience helps you customize your company page and connect with the right people. So, decide who you want to reach based on location, company size, and industry.
Choose the content types that match your marketing goals and what you know about your audience for your LinkedIn strategy. The types of content usually on LinkedIn are:
Remember, LinkedIn is for professionals, so ensure your content is top-notch and informative. Consistently post high-quality content if your audience wants to read and interact with it.
Make content that catches people’s eye, makes them curious, and gets them talking. Use catchy pictures, short but powerful writing, and storytelling to make your content stick.
Add industry tips, practical advice, and interesting questions to start good conversations. Also, use LinkedIn tools like hashtags, mentions, and tagging to get seen more and make sharing easy for others.
Keep an eye on how well your LinkedIn posts are doing compared to what you want. Look at how many people engage with your posts, how many clicks on links, how fast your followers are growing, and how many conversions you get.
This analysis allows you to experiment with various post types, timing, and messaging to optimize your LinkedIn page’s performance. Keep refining your strategy to maximize its impact.
LinkedIn Groups are where people who work in similar fields chat and connect. Join groups related to your industry to talk with others, share what you know, and show that you’re an expert.
Groups can also help you see where your customers hang out online. Pay attention to what they talk about. Their discussions and questions help you create content that speaks to them.
Don’t just post on LinkedIn and forget about it. Interact with your followers to make your marketing efforts more effective.
Engage with users who comment on your posts by answering their questions, seeking feedback, and asking thought-provoking questions to encourage discussion. Being active keeps you visible in your network’s feed and helps build relationships with your connections.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) boosts your profile’s visibility in search results on LinkedIn and search engines such as Google. This tactic helps more people discover you, particularly those seeking your skills or services.
Ensure your headline, summary, and experience sections include relevant keywords to enhance your discoverability. However, avoid excessive keyword stuffing, making your profile seem forced and unappealing.
Posting on LinkedIn once a week can lead to up to six times more followers. A consistent presence in your followers’ feeds helps them remember your expertise and services, increasing the chances that they’ll turn to you when they need what you offer.
To stay on track, create a content calendar that helps you stick to a regular posting schedule and ensures your content matches your marketing goals and audience interests. Mix curated content, original thought leadership, and promotions to keep followers engaged.
Social media marketing isn’t just about selling; it’s about genuinely building your brand. LinkedIn can help you find leads, but being too pushy won’t work.
Instead, prioritize delivering value to your audience through informative content, problem-solving, and relationship-building efforts. By establishing trust and credibility, you’ll organically create opportunities for sales over time.
Don’t make the error of sharing identical content on all your social media channels. Since many followers may overlap across platforms, avoid overwhelming them with repeated posts.
Instead, offer exclusive perks like premium resources, special deals, or invites to exclusive events. By providing these benefits, you can enhance your connections on LinkedIn and set your brand apart from competitors.
With its professional focus and robust networking features, LinkedIn is an excellent place for businesses to connect and grow. Using LinkedIn tools well, companies can boost their brand, build essential partnerships, and see results in B2B marketing.
Linking Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems with LinkedIn can significantly improve your sales and marketing. LinkedIn is excellent for networking and finding leads. When it’s connected to your CRM, you can work more efficiently, communicate better, and use data to make smarter decisions.
McDonald, J. (2022, July 4). Social Media Marketing Workbook: How to Use Social Media for Business.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.
