Kanban: Definition, 6 Rules, and its Benefits
Kanban is a crucial part of the Just in Time (JIT) system, which we discussed…
Sean Thobias
May 17, 2025Dan Ramsey’s book “The Everything Guide to Starting and Running a Retail Store” defines retail as selling small quantities of products directly to customers. It comes from the French term “retailler,” meaning the literal division of goods.
This article is the introductory chapter for a broader comprehensive guide for anyone interested in the retail industry. This chapter covers the essential retail principles, different retail types, and opportunities and challenges for aspiring entrepreneurs.
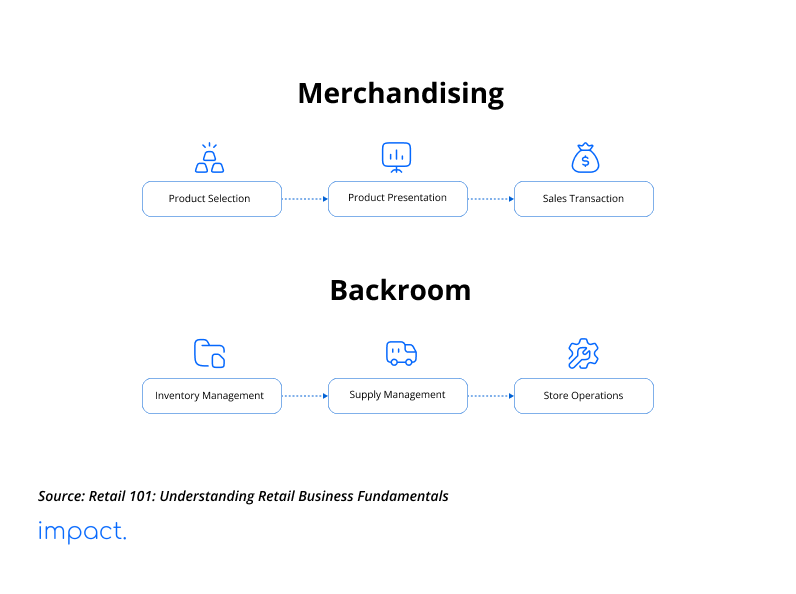
Retailing consists of two main components that ensure the business runs smoothly:
Grocery stores and supermarkets offer a variety of food products, including fresh and packaged foods, as well as essential household items.
Pros:
Cons:
Convenience stores are small, open 24/7, and conveniently located for quick trips. They usually have simple foods, drinks, and everyday items; some are connected to gas stations.
Pros:
Cons:
Specialty stores focus on a specific product type, like different brands or styles in a particular category. You can usually find these stores on local main streets or in malls, and they aim to offer a unique and diverse range within their specialized niche.
Pros:
Cons:
A department store, usually found in malls, offers a wide variety of things like clothes and electronics all in one place. They’re known for having fancy brands, even though the prices are slightly higher.
Pros:
Cons:
An outlet store sells discounted products, often from a particular brand or maker. These stores offer lower prices because they have extra stock, end-of-season items, factory seconds, discontinued products, or items with minor defects.
Pros:
Cons:
Warehouse stores provide a wide range of products at prices lower than the market average. They’re famous for cost-effective options on essentials, and buying in bulk helps customers save more.
Pros:
Cons:
The key opportunity in retail today lies not in the product itself but in enhancing the sales process through retail technology. Implement modern point-of-sale (POS) systems at checkout for automated and efficient transactions, improving the overall customer experience.
Retailers can boost efficiency and cut costs by using advanced inventory management software. Products often have a Universal Product Code (UPC) to simplify inventory management.
More than 2.14 billion people shop online, a big jump from a few years ago. This statistic accounts for 27% of the world’s 7.9 billion population, showing a significant presence of digital buyers globally.
Retailers should make it simple for customers to connect with their brand in-store and online. To encourage repeat business, they should create loyalty programs that work smoothly regardless of whether customers shop online or in a physical store.
Data is helpful to stay ahead of competitors and offer customers products they like. Using data helps make targeted marketing campaigns, which are promotions designed for specific groups of customers, making them more relevant and likely to grab attention.
Most customers, around 71%, expect personalization when they shop. According to McKinsey, businesses that do well in personalization can boost their revenue by 10% to 15%.
E-commerce has changed how regular stores work. Online shops are popular because they are convenient, reasonably priced, and offer various products.
Traditional stores must invest heavily and adjust to new technology like POS systems, inventory tools, and online selling platforms to keep up. If not, then they will be further left behind by their competitors.
The Covid-19 pandemic created global supply chain issues, impacting retail operations. In 2021, 98% of retail executives experienced problems, with 59% anticipating higher prices or shipping costs for consumers.
Disruptions like shortages, delays, and higher costs have impacted retailers. Retailers must have a strong and flexible supply chain to tackle these challenges.
Rising operational costs, driven by higher minimum wages and increased real estate expenses, pose challenges for retailers. Small and independent retailers struggle to balance these costs while keeping prices competitive.
Starting a retail business comes with challenges and opportunities. Small retailers often face difficulties, as outlined by Dan Ramsey in his list of primary reasons for failure:
However, these reasons shouldn’t deter you from starting your retail store. Our guides will ensure you have the knowledge, information, market understanding, a good location, a solid plan, and enough funding to succeed.
In the next chapter, we will look at the planning stage of your retail business, which includes analyzing your assets, looking at franchises as an alternative, and writing your business plan.
Ramsey, D., & Ramsey, J. (2010). The Everything Guide to starting and running a retail store: All you need to get started and succeed in your own retail adventure. Adams Media.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

In our previous chapter, we delved into the intricacies of retail branding, exploring its crucial role in shaping a retail business’s identity and perception. We learned how effective branding can set your store apart from the competition and create a distinct, memorable presence in the minds of consumers.
Building on that foundation, we now focus on another cornerstone of business – retail marketing. If you’re looking to boost your sales, marketing is the key to achieving that objective.
Marketing helps you tell people about your products and why they should buy them. They help address customers’ lingering doubts about your products or services and minimize the dreaded “buyer’s remorse” that affects 77% of shoppers after making a purchase.
In this chapter, we’ll dive into retail marketing and how to use different strategies to boost your sales. From online ads to in-store deals, we’ll cover the tips and tricks to make your business shine and keep customers happy. Whether you run a physical store, an online shop, or both, these marketing ideas can help you stand out in the crowded retail world.
Retail marketing is a part of marketing about selling products to customers through retail channels like stores or online shops. It involves advertising, pricing, and connecting with customers to get them interested in buying.
Marketing and branding are often confused, but they’re not the same. Marketing focuses on making people aware of your products and teaching them about what you offer. On the other hand, branding is about shaping your brand’s identity, like its values, personality, and visual elements.
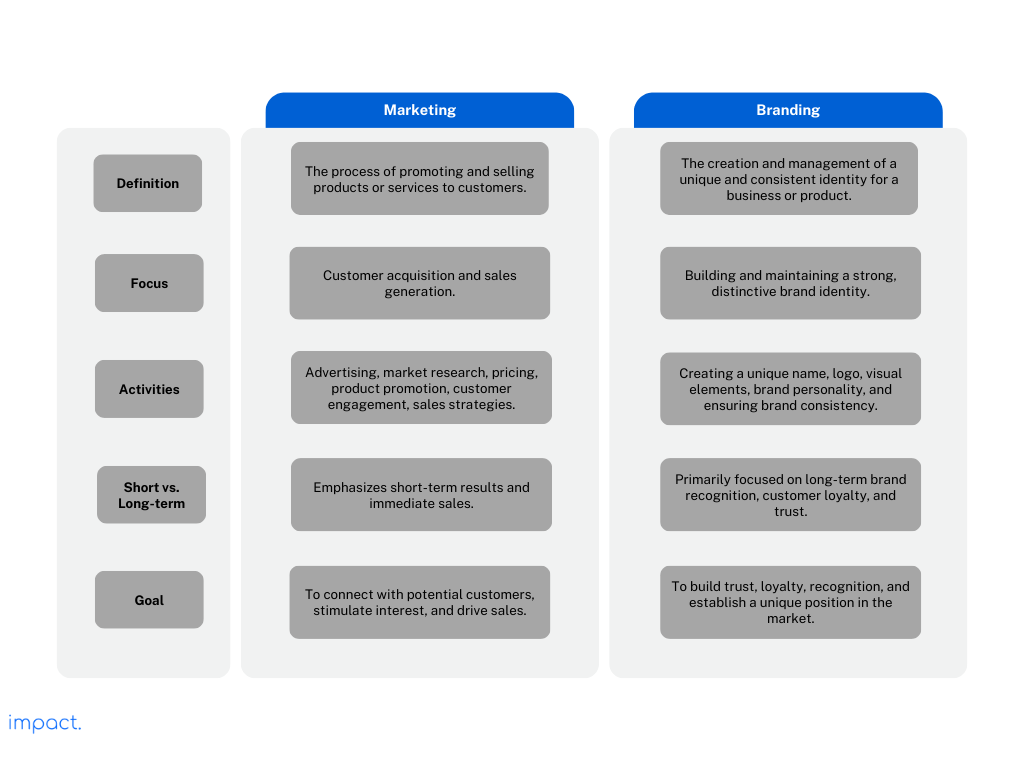
Marketing and branding, while distinct, share a close relationship and collaborate to achieve specific objectives. Think of them as two integral parts of the same puzzle, working hand in hand to create a harmonious synergy.
Read more: Elevate Your Retail Branding for Sales Success
We usually discuss the “4Ps” when discussing traditional marketing mix: Price, Promotion, Place, and Product. But in retail, we add two more essential elements to the mix, making it the “6Ps.” These extra two Ps are Presentation and Personnel.
Your retail marketing campaign should focus on all these factors to ensure you’re on the right track. Let’s break them down:
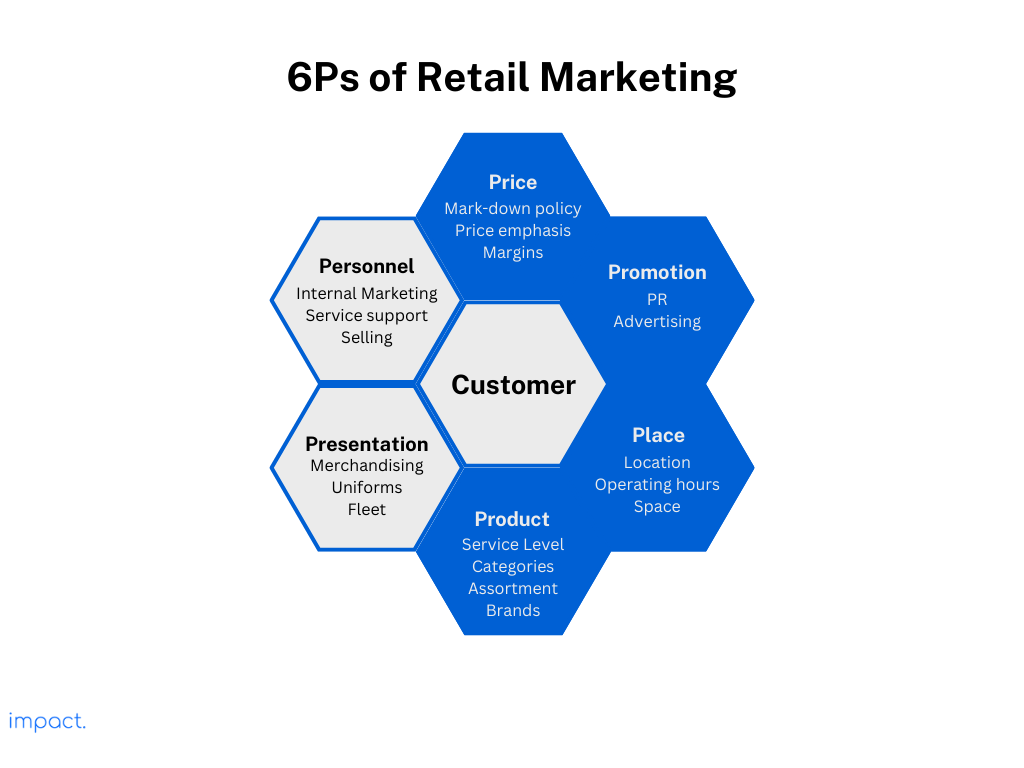
Product:
This component of a marketing strategy is what you’re selling. Ensure you have the right products that meet your customers’ needs.
Price:
The price is how much you charge for your product. It depends on how much it costs you to make the product, your marketing promotions, and how long you plan to sell it. Your pricing plan should match what your customers are willing to pay and what your competitors charge.
Place:
“Place” means the location of your store, whether it’s a physical shop or an online store. Choose the right spots for your business, whether a physical store or a website. Being at the top of Google search results is as essential as having a good location for a physical store.
Promotion:
This element of marketing is about how to reach people about your product. Retail promotion means getting in touch with customers and making them know your brand. If people don’t know you, they won’t buy from you.
Personnel:
Your employees play a significant role in how your business is perceived. They create the first impression that either brings in customers or pushes them away. Everyone involved, whether directly or indirectly, can affect sales and how happy your customers are. So, make sure to train your staff well and make sure they give outstanding service.
Presentation:
The final “P” in marketing is how your product appears to your customers. It includes your packaging, messaging, and communication to customers. The presentation needs to be eye-catching and well-arranged to attract customers.
Read more: Choosing the Right Retail Location in 5 Steps
To grasp the importance of retail marketing for your business, let’s dig into how it can boost your growth and success in today’s competitive market.
Retail marketing aims to bring new customers to your business and keep them returning. Retail marketing uses strategies like promotions, advertising, and making your store look appealing to attract customers to your physical store or online shop.
This extra attention and traffic can boost your sales, making your business more money and growing. Whether you use social media, search engine optimization (SEO), partnerships, or paid ads, they are all ways to make more money for your business.
In retail marketing, how you set up your store and make your products look matters. It can make a big difference in how much you sell. Using strategies like making your products look good and putting them in the right places can attract more customers and make them more likely to buy.
These strategies include arranging products nicely, using eye-catching displays, and making the store feel inviting for customers. It’s all about making the shopping experience enjoyable, which, in turn, can lead to more sales. So, by investing in these strategies, you can boost your sales and have a more successful business.
Retail marketing is like having a treasure trove of information about your customers. This data helps you understand your customers better and customize your marketing to suit their needs.
When you use customer data, you can create personalized customer experiences and build long-lasting relationships. More than 70% of customers are more likely to shop with you again if you give them offers that match what they like or want. So, gathering and using customer data is smart for your business.
Retail marketing channels, like social media and email, offer direct customer communication. This two-way interaction builds trust and lets you quickly address customer concerns and feedback.
Effective retail marketing promotes this back-and-forth between businesses and consumers. This open line of communication builds trust and loyalty, which can lead to repeat business and positive word-of-mouth marketing.
Retail marketing involves various methods to attract people to buy products and services. Here are the three main types of retail marketing:
In-store marketing aims to enhance the shopping experience within physical retail spaces. It employs strategies to captivate, engage, and sway shoppers while they’re in the store. This marketing approach is especially vital for brick-and-mortar retailers.
Examples of in-store marketing include:
Traditional marketing uses offline channels to connect with potential customers. Despite the growth of online marketing, these offline methods remain valuable for certain retail businesses and customer demographics.
Examples of traditional marketing include:
Digital marketing involves promoting your store or products online, including organic and paid efforts. A comprehensive digital marketing strategy should incorporate multiple online platforms.
Examples of digital marketing include:
Read more: Unlocking Growth: 19 Traction Channels for Business Success
Retail marketing is dynamic, and combining strategies can be highly effective. Here are nine retail marketing strategies to consider:
Collaborate with brands that go well with your products. This strategy helps both companies reach more people and grow their customer groups. When you team up with respected companies, it can build trust in your brand. Joint promotions or events can also get your brand in front of more people. It’s a win-win situation for both parties involved.
To better plan your retail marketing strategy, gather customer feedback through surveys. You can include surveys on your company website, product purchase emails, and in-store receipts. This feedback helps you understand what your customers like and want. It lets you see trends in sales and consumer habits, helping you make your products and customer experience better.
When you give discounts, have sales, or run promotions, it grabs the attention of shoppers looking for good deals. They might end up buying more on the spot. Consider having sales during different seasons or clearance events to get even more people interested.
Give back to your regular customers with discounts or special access. This program makes them want to come back to your store. Plus, when you have a customer loyalty program, you can create profiles of your shoppers. These profiles help you know what products they like and make your marketing more personal.
Remarketing means tailoring your marketing to people based on their past purchases. It includes sending emails with discounts or promotions for new products or getting people to subscribe for regular purchases. You can also use remarketing to reach people who’ve shown interest in your products but didn’t buy them.
Selling in multiple places is essential for your business. To increase your sales, ensure a seamless shopping experience across all your sales channels. You must link your social media accounts and website to help customers find all your channels. This way, you can increase the chances of consumers to view your products. Remember to keep things consistent in your physical stores, websites, mobile apps, and social media.
Improve your online presence for better search engine visibility. This approach is essential for attracting online customers, especially those searching for products in your area. By optimizing for local searches, you can increase the likelihood of your company appearing on the first page of results when customers look for nearby products.
Host in-store or online events to bring people to your store. These events also give you a reason to send out marketing materials. You can launch new products, hold workshops, or celebrate seasons. You can even offer special deals for the first visitors or buyers during these events. Use them to show off your products and get more people to notice your store.
In your retail marketing strategy, partner with influencers who match your brand and can promote your products or services to their followers. Influencers can help you expand your reach. You don’t have to go for the most prominent names; smaller influencers with a few thousand followers can also be influential. Look for local bloggers or content creators who can promote your store and products to your target audience.
In this chapter, we’ve discussed the importance of retail marketing in growing your business. Marketing is the key to boosting sales and building trust with customers. It helps you tell people why they should buy your products and reduces the chances of customers regretting their purchases.
It’s crucial to grasp that branding and marketing are not separate; they can collaborate effectively. Flourishing businesses begin by understanding their brand identity and their target audience. Then, they employ marketing to convey that brand to the market. This alignment ensures that marketing activities harmonize with the brand’s fundamental values and message.
Our next chapter will discuss inventory management, another crucial part of running a successful retail business. We’ll explore the strategies to manage your stock effectively, reduce waste, and always have the right products to meet customer demand.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

In the last chapter, we discussed the importance of improving the customer experience and training your staff for better service. In this chapter of our retail guide, we’ll dive into retail branding for your business.
For businesses, branding is a big deal. According to a 2021 report by Lucidpress, consistent branding can boost your revenue by up to 20%. If your brand doesn’t have a consistent look and feel, it might hold you back from connecting with customers and making sales. People tend to buy from brands they connect with and ones that seem genuine. It’s tough to communicate with a brand that keeps changing its appearance.
In this guide, we’ll explain why branding is so important and how to figure out your branding. We’ll also show you some great examples from well-known companies.
Let’s begin by defining what a brand is. A brand represents people’s mental image when they think about a company’s products or services. It encompasses not only practical aspects like the qualities of a product but also the emotions it stirs.
For instance, think about Apple. When you see their sleek, modern designs, it’s not just about user-friendly gadgets. Apple products also evoke feelings of sophistication and innovation.
You can’t copy a brand, unlike a product. Consider McDonald’s and Burger King. Both offer fast food products, yet some people strongly prefer McDonald’s, while others lean towards Burger King. There’s a unique charm to each brand that makes them stand out.
A brand is what people think about when they hear a company’s name or see its products. Branding is the strategy that shapes how people see your store, products, and services.
The goal is to make your company, products, or services stand out in people’s minds. When you do that, it’s easier for people to know your brand and choose your products over others because they remember what’s unique about your brand. Branding helps you build a strong group of loyal customers and others who trust that your products always do what your brand says they will.
In essence, branding goes way beyond the business itself. It has a significant impact on many different groups:
In today’s fast-paced and competitive business world, using branding strategies isn’t just a choice; it’s essential. These strategies form the core of your business’s success. They help you:
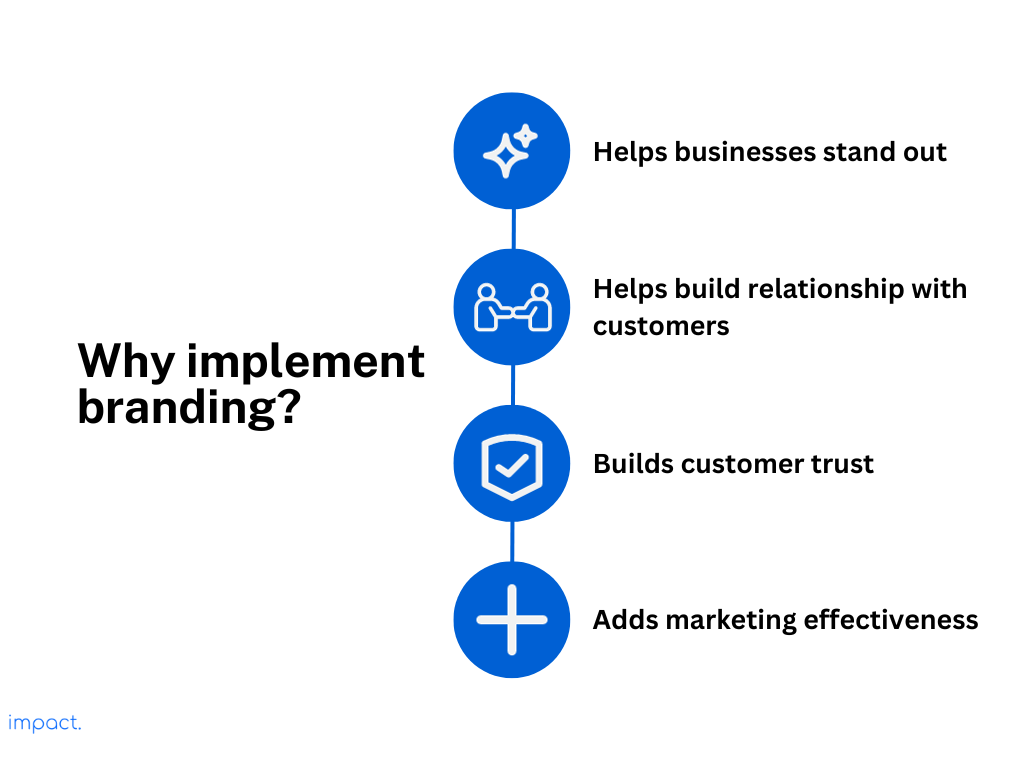
People always discover new brands in today’s fast-paced social media and online shopping world. It benefits consumers greatly, as they have lots of choices and can find the best ones. However, it’s becoming challenging for businesses.
If a business lacks strong branding, it can be challenging to stand out. Without a unique and memorable identity, people may not notice or remember the business, leading to missed opportunities for growth and customers.
In today’s changing consumer landscape, merely grabbing attention isn’t enough. Businesses can’t afford to be just transactional anymore. To truly excel, brands must forge strong, lasting customer bonds. When a brand connects with customers emotionally and truly understands their needs, it can offer remarkable experiences beyond price and convenience.
According to a Motista report, 71% of customers recommend a brand because they share an emotional connection with it. What’s more, emotionally connected customers tend to spend twice as much on their favorite brands. By nurturing these connections, brands cultivate loyal customers and a dedicated community. This community becomes their most valuable asset, driving repeat purchases, positive word-of-mouth, and long-term success.
Trust is crucial in business. A strong brand with a good reputation shows that your business is reliable and consistent, and this builds trust with your customers. People are likelier to choose a brand they know and trust, even if it costs more. However, earning trust isn’t always easy.
Branding helps you show potential customers you’re a well-established, trustworthy business. It’s like a promise to your customers about what they can expect from your business. Investing in creating a solid brand means, “We’ve put in the effort to improve our business, and we want you to know what we’re all about.” Customers notice details that build trust and attract business.
Lastly, your business needs branding and marketing to succeed. These two are like partners. To have effective marketing, you must start by building a solid brand.
When you have a strong brand, it makes your marketing easier. You don’t have to keep telling people about your company or products. A recognizable brand makes your marketing work better because customers already know what you offer.
Read more: Content Marketing: 7 Steps to Strategize for Success
Embarking on your branding journey is an exciting endeavor that can set the stage for your business’s success. To guide you on this path, let’s explore the five essential steps to kickstart your branding process.
To begin your branding journey, you must understand your business identity clearly. This step is like laying the foundation for your brand, and it’s crucial to get it right.
Once you’ve figured out what your business stands for, it’s time to focus on your customers. To create a strong brand, you need to understand them well.
Start by doing some research on the market. It means getting to know your industry, what your customers like, and how they shop. You should also check out what people say about your brand and your competition. Start your research on social media, review sites, and forums to find where your competition finds customers, what customers like about them, and what they’re not so good at.
To simplify things, you can categorize your customers based on their behavior and characteristics. Create what are known as “buyer personas.” These are similar to profiles of the people you want to sell to. These profiles should include fundamental details such as their age, location, and income.
It’s not enough to understand your customers’ demographics. You should also take the time to explore their interests, how they utilize your product, and which other brands they prefer. As you continue to run your business and make sales, you’ll gain a more profound comprehension of your customers.
Read more: Retail Marketing Success: 9 Key Strategies for Your Business
In this part of your branding journey, you must choose the right words to discuss your business. The aim is to make a message that tells people what your brand is about and speaks to your audience.
Start by creating a unique personality for your brand, which we call your “brand voice.” Your brand voice guides what you say and how you say it. It should be unique and reflect your company’s values. Keeping your brand voice consistent across all communication channels is essential because 90% of customers prefer a consistent brand voice.
To connect with your audience better, try using storytelling in your messages. Stories help people relate on a personal level. Storytelling can complement your values by explaining your brand’s existence and what it believes in.
Lastly, make sure your message is clear and straightforward. Avoid using confusing jargon or complicated words that might puzzle your audience. The best messages are easy to understand. Use words and phrases that your audience knows well.
The next thing to do is work on your brand visuals. Visuals are essential for your brand because they are the first thing people see to connect with your business. When people think about your company, they think about these visuals first.
Once you’ve figured out your brand – the look, the message, and who you are, it’s time to weave it into everything you do. This final step means making your brand a part of your products, how you talk to customers, your ads, and even your online material.
To keep it all consistent, make a style guide. It’s like a rulebook that says how your brand should talk, look, and feel. Your brand’s personality should shine through in everything you post on social media, every ad you run, and the design of your website.
If your brand isn’t achieving the desired results, consider making changes. In such cases, a “rebrand” can be a good approach, giving your brand a new appearance and feel. However, it is essential to tread carefully and test it before implementing it.
You can ask your current customers for feedback before making any changes. They are the ones who matter the most. You can also take the opinion of people similar to the new customers you want but don’t forget about your existing customers. They are your most important group.
Zara and IKEA are two globally recognized companies with notable branding. Here’s an overview of their approaches:
Zara, a fashion brand from Spain, started in 1975. It’s one of the most successful fashion brands globally, known for pioneering fast fashion. Zara wants to get people excited about fashion and reach people from various cultures and age groups.

Fast Fashion Pioneers:
Zara’s key to success is its agility in keeping up with ever-changing fashion trends. It’s the place where quality meets affordability. Zara closely monitors global fashion shifts and swiftly transforms them into fresh collections, often in just a week or two, setting it apart from competitors who take months.
Customer-Centric Approach:
Zara’s obsession with customers fuels its culture. It co-creates products by valuing customer input and encourages its store staff to be highly attuned to customer needs.
Empowering Young Talent:
Embracing an entrepreneurial spirit, Zara fosters young talent, promotes from within, and values risk-taking and fast implementation.
Minimal Advertising, Maximum Visibility:
Zara’s marketing stands out because of its great store locations, drawing in many shoppers instead of using traditional ads. Their eye-catching window displays, created by a skilled team, are critical to their communication. These displays are regularly changed to match the fast fashion idea. Zara employees wear Zara clothing while working, but the outfits differ in stores to match the local vibe.
IKEA is a global retail brand for well-designed, functional, affordable home furnishings that started in 1943. Its flat-packed furniture concept is all about saving money while providing quality furniture. Since 2008, IKEA has been the world’s largest furniture retailer.

Swedish Identity:
IKEA proudly carries its Swedish heritage, from design elements to product names like “Billy” and “Lack.” This Swedish connection symbolizes simplicity, affordability, and practical design. You also can’t miss IKEA with its blue and yellow colors.
Unique Shopping Experience:
IKEA stores are like a journey through a home. You can see how furniture fits into different living spaces. It helps you visualize how your home could be. Plus, you can bring the whole family and enjoy “happy home” activities like trying out furniture.
Quality at Affordable Prices:
IKEA is known for quality products at prices everyone can afford. This strategy creates trust and loyalty among customers.
Sustainability:
IKEA cares about the planet. They use renewable and recycled materials, and they’re working to be more eco-friendly. This approach matches what more and more customers want – products and practices that are good for the environment.
We’ve explored the pivotal role of retail branding in your business. We’ve highlighted the significance of consistent branding in boosting revenue and establishing meaningful connections with customers. Remember, a well-defined brand creates a lasting impression that helps you stand out in a crowded market, fostering loyalty and trust among your customer base.
As we move forward in our guide, our next chapter will explore retail marketing. It’s important to note that branding and marketing are intricately connected. The synergy between the two often propels successful businesses to new heights.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

In the previous chapter, we discussed the “Customer Development Manifesto.” It contains 14 critical ideas that startups use in the Customer Development Process. These ideas have been beneficial to many entrepreneurs in building successful businesses. Now, let’s shift our focus to another crucial aspect of entrepreneurship: creating a successful web startup.
In today’s digital world, web startups are becoming increasingly important. But what exactly is a web startup, and how can you start one successfully?
This article isn’t just about explaining a web startup; it’s a practical guide to help you turn your ideas into a real business. We’ve taken many insights from “The Startup Owner’s Manual” by Steve Blank and Bob Dorf to provide you with tailored advice on how to take concrete steps toward making your dreams a reality.
Keep reading this article to learn the ten essential steps to guide you through this exciting business journey. Whether you’re an experienced entrepreneur or just starting your first startup adventure, this chapter will help you understand and master the art of building a web startup.
In our first chapter, we looked at Steve Blank’s definition of a startup. He describes a startup as a temporary organization trying to find a business idea with a repeatable and scalable business model.
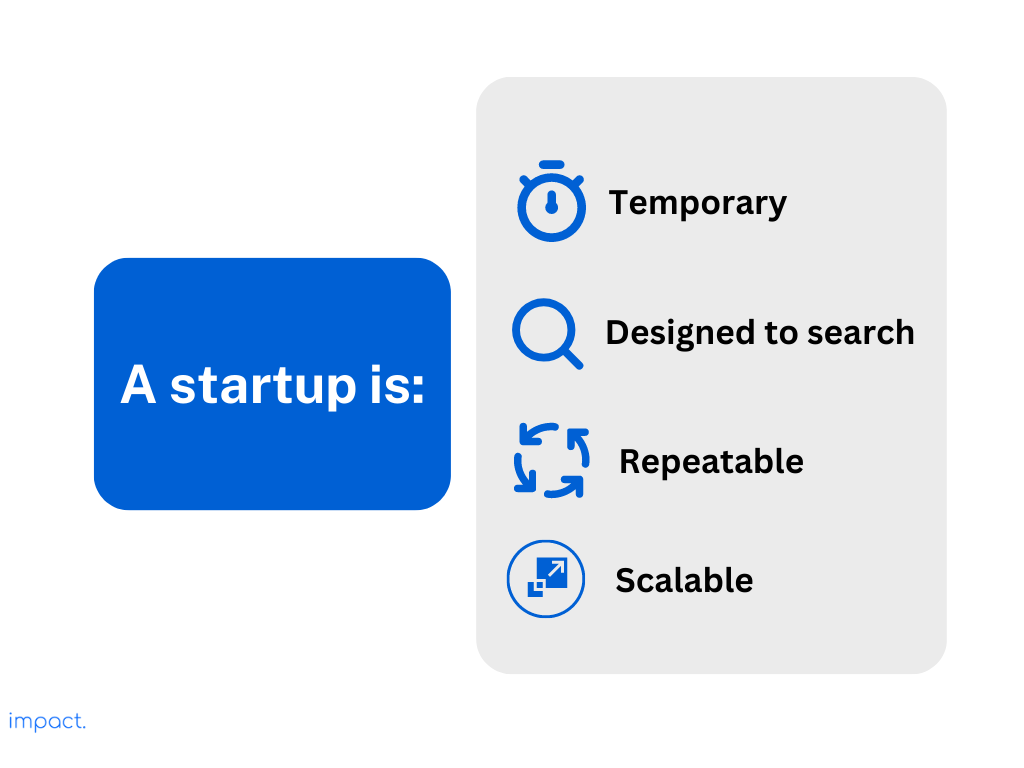
Now, let’s focus on web startups. These are a special kind of startup that mainly works online. They’re different from regular startups that might sell physical products. Web startups offer digital services or products. They use the internet to connect with customers, provide services, and generate revenue.
Here’s how web startups differ from regular startups:
Read more: Startup Essentials: Key Definition and 9 Mistakes to Avoid
Many companies are moving their operations online, and some are even starting their businesses online. This shift isn’t always a choice; often, it’s a necessity.
As we all know, the Covid-19 pandemic in 2020 significantly changed how we conduct business. Many companies were caught off guard by the new restrictions and shutdowns. However, many businesses could adjust and persevere — by going online.
Financial experts at Gartner, Inc. found that Chinese companies that did best during the pandemic were those that teamed up with trusted online service partners and used automation in their business plans.
In addition to changing habits, customers are also the driving force of this shift. Today, more people than ever are turning to the internet for their shopping needs.
By 2025, e-commerce businesses will generate a staggering $7.4 trillion in sales. Even though you might think big online stores rule everything, there’s still room for online shops focusing on unique interests and making customers happy.
Starting a web startup can be an exciting but challenging journey. To guide you through this process, we’ll follow the proven steps outlined by Steve Blank. These ten steps will help you set up your web startup from scratch and increase your chances of success.
First, ensure your team is ready, and you’re on the right track with your startup. Start by understanding the Customer Development Model, which helps you know your customers better.
Create a WordPress Blog to document everything you learn about your customers. This blog will be like your startup’s diary, helping your team stay on the same page and keep track of your progress.
To chat with your team, use Skype and Zoom. They’re great for team talks and meetings, especially if your team members are in different places. Good communication is critical to making your startup work, and these tools will help you chat, share ideas, and make decisions together.
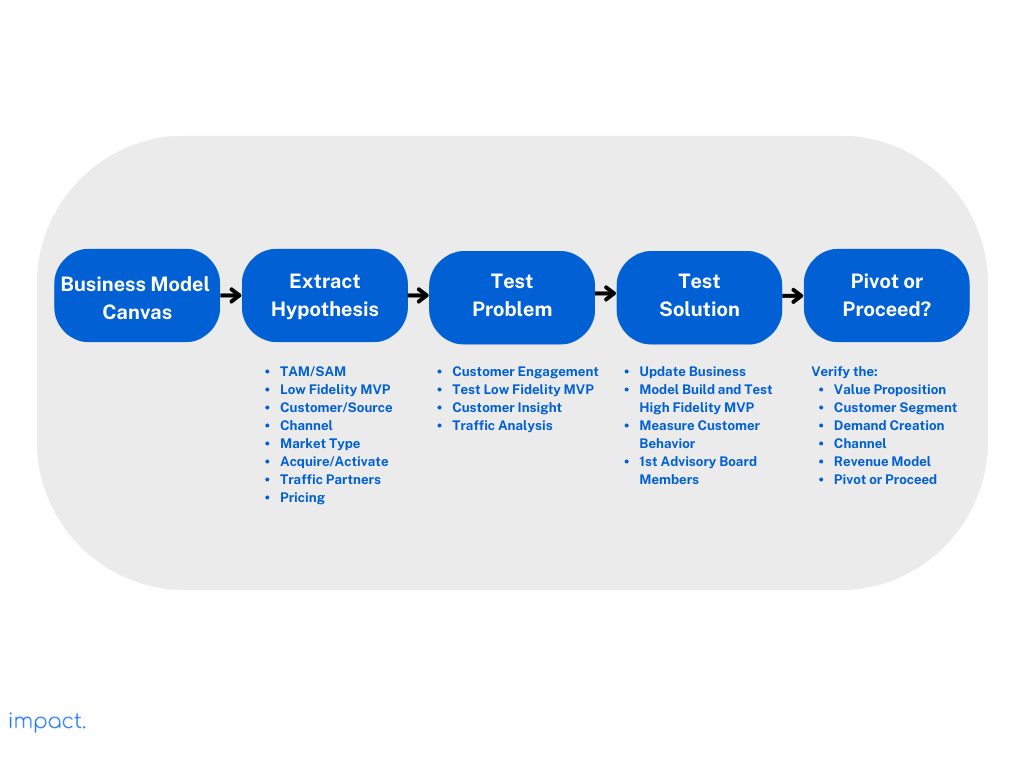
The next step in creating a web-based startup is to craft your company hypothesis. This step involves laying the foundation for your business by defining your strategy, understanding your market, and outlining your initial product offerings. Here are key points to consider during this phase:
Start by creating a comprehensive Business Model Canvas that outlines your business’s core components. This model should include hypotheses about your value proposition, customer segments, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, essential resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure. These ideas will be like the building blocks for your startup’s strategy and help you choose what to do next.
Identify the key features that are essential for your MVP. Focus on the minimum set of functionalities that will allow you to test your hypotheses and gather valuable user feedback. These features should address your target audience’s most pressing needs and pain points while keeping development costs and timeframes in check.
Use tools like Google Trends, Google Insights, and Facebook ads to see if enough people are interested in your business idea. Look for signs that the market is growing. Also, look at what other companies are doing in the same space.
Use Crunchbase and other relevant tools to research your competitors. Understand their strengths, weaknesses, market positioning, and customer base. This analysis will help you identify gaps in the market that your startup can exploit and determine how your product or service can stand out.
Calculate the Total Available Market by estimating the total number of potential customers in your chosen market segment. Consider age, location, and other factors that define your target customers. Also, consider how much each customer might be worth to your business over time.
Determine the market type your startup is entering, which could be one of the following:
Selecting the right market type is crucial as it influences your go-to-market strategy, competitive positioning, and marketing approach.
Read also: Customer Development Process: 4-Step Framework for Startups
Next, it’s time to formulate a concise and easy-to-understand description of your company. This statement should explain why your business exists in an easy-to-understand way. You can use a format like “We help X do Y by doing Z” to make it straightforward.
After you’ve written this statement, ask a few people (even if they’re not your exact customers) if they understand your business. If they’re confused, explain your startup in more detail and ask them for feedback.
Others can give you helpful ideas and suggestions to improve your value proposition, making it more understandable and appealing. Their fresh perspective can help you create a statement that connects with your target audience, sparks their interest, and makes them want to learn more about your web startup. Remember that a well-defined value proposition is the cornerstone of a successful business.
The next step for your web startup is setting up the website logistics, which is crucial for your online presence. Here’s what you need to do:
However, you can set up a web host if you know how to code.
Setting up the logistics of your website is just the beginning. Creating a simple website is part of the next step. This website should tell people what your product or service is and what they can benefit from. It should encourage them to take action, like learning more, filling out a survey, or pre-ordering.
For non-tech experts:
For coders:
After creating the website for your startup, your task is to get people to visit your website. After all, your brilliant idea and well-designed Minimal Viable Product (MVP) won’t mean much if no one knows or uses it. You need to employ a multifaceted approach to draw potential users to your site and begin validating your customer segment and value proposition.
In short, to get customers to your web startup, you need a mix of paid ads, SEO, networking, email marketing, and surveys. These methods will bring visitors to your site, and their feedback will help you improve your product and attract more customers.
Read more: Social Media Marketing: A Guide & 3 Strategies for Success
The next step for your web startup is to connect your user interface (UI) to a web application framework. First, pick the proper framework based on your needs and your team’s skills. Some popular options include Node.js, Ruby on Rails, and Django.
After selecting a framework, it’s time to integrate it with your user interface (UI) by transforming your design into functional code. This connection is crucial for making your startup operational. Begin building the essential components of your startup, such as user registration, backend logic, and databases. It’s vital to ensure that your application functions well and can accommodate a large user base.
Don’t forget to test and fix any problems you find. User feedback helps make your app better. Also, use analytics to understand how people use your app. This information enables you to make more improvements.
The next stage of creating a web-based business is to test the identified “problem” with the data you get from customers. This phase is about deeply understanding your target audience, their needs, and how your product or service can address those needs effectively. Here are some key points to consider during this step:
To understand how people use your website, you need web analytics tools. Google Analytics is a good start. It tells you how many people visit your site, how long they stay, and where they come from. This info helps you know if people like your site and which marketing works best. Later, when your startup grows, you can check out more advanced analytics tools for better insights and options.
Set up accounts on user feedback websites. These sites let users share their thoughts, problems, and ideas directly. This approach shows them you care about making their experience better.
When you ask users specific questions, you get better feedback. For example, ask, “Is there something stopping you from signing up?” or “What more info would make you like this solution?” These questions make users share their issues and hopes so you can make your product even better.
Ask users for their email addresses; it lets you communicate with them personally. You can check back with users who shared feedback to learn more, have chats with them, or even give them early access to new stuff to say thanks. Having their email helps you stay in touch and understand them better.
It’s time to test your startup idea by creating a polished website. Here’s what you need to do:
The last step in launching your online startup is receiving payment. Here’s how you can do it:
Picking the right billing provider is crucial. Ensure they fit your business model, have reasonable pricing, and offer good customer support. Also, set up your billing processes properly, like deciding on prices, managing discounts, and handling any issues that might come up during transactions.
We’ve covered some important information about web startups in this article. These startups differ from regular ones because they offer digital products or services and use the internet to connect with customers exclusively. They can reach people worldwide, cost less, and scale faster.
We have provided you with a ten-step roadmap based on Steve Blank’s advice to help you launch your web startup. These steps will guide you in setting up your business from scratch and seeking funding at the right time.
The upcoming chapter will delve into the business model canvas – a crucial tool for developing your startup. We will examine all of its nine components.
Blank, Steve, and Bob Dorf. The Startup Owner’s Manual: The Step-By-Step Guide for Building a Great Company. 2020.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

A wholesaler is a person or company that purchases bulk products and resells them at a lower price. They take an essential role in the supply chain in fulfilling consumer demands.
The parties involved in this process include manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, and others that can distribute goods directly to consumers.
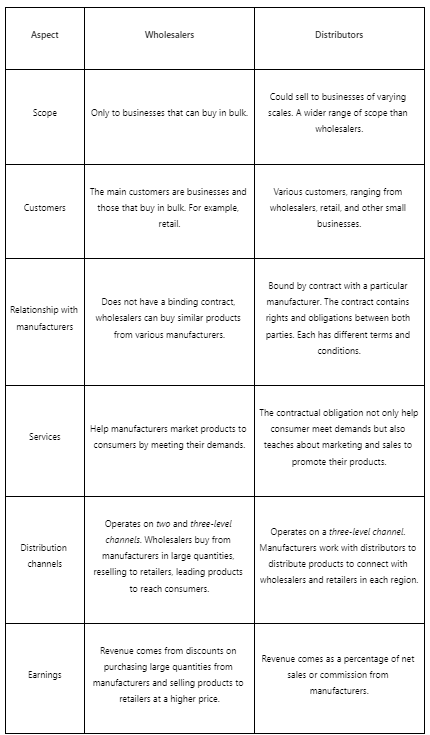
Wholesalers differ from distributors. They do not have a binding relationship with manufacturers, which means they can sell similar products from different brands. Through this process, all parties can experience benefits from various aspects.
Besides being beneficial to those parties, the wholesale industry is vital to Indonesia’s economy.
According to a 2022 report Central Bureau of Statistics (BPS), the retail industry, particularly food and beverage (F&B), has become one of the most significant contributors to Indonesia’s GDP — 34.44% or Rp302.28 trillion.
The report also shows a 5.44% (YOY) growth in retail business in September. The statistic indicates wholesalers are vital to the nation’s economy when they supply retailers.
Are you interested in learning more about wholesalers? Read through the article below for a more comprehensive look.
Wholesale is the process of buying large amounts of goods from manufacturers, then selling them back in small quantities at a higher price to consumers. The consumers here may refer to retailers, commercial businesses, institutions, and other wholesalers. Sales proceeds and manufacturer discounts are the sources of a wholesaler’s revenue.
A wholesaler acts as a go-between for manufacturers and consumers to distribute products. Manufacturers need wholesalers to market their products, and consumers need wholesalers to obtain the products they want. Therefore, wholesalers play an essential role in the supply chain.
Wholesalers are responsible for acquiring, managing, and preparing small amounts of products for retailers. They can run well if business owners understand customer needs, market trends, and product prices to build strong relationships with business partners. Wholesalers must build a solid upstream relationship with manufacturers and be trusted by downstream consumers, such as retailers and other businesses.
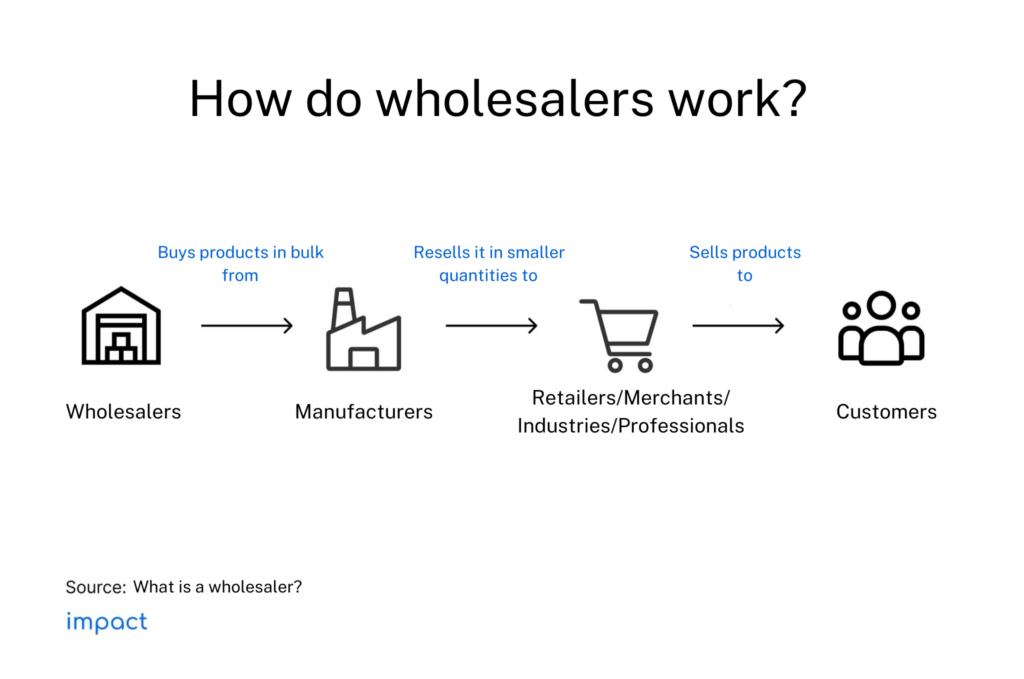
Simply put, wholesalers deal with two important parties — manufacturers as product owners and retailers as customers that buy the product. It is important for wholesalers to find the right products, according to consumer demand, at a lower price that is high in quality.
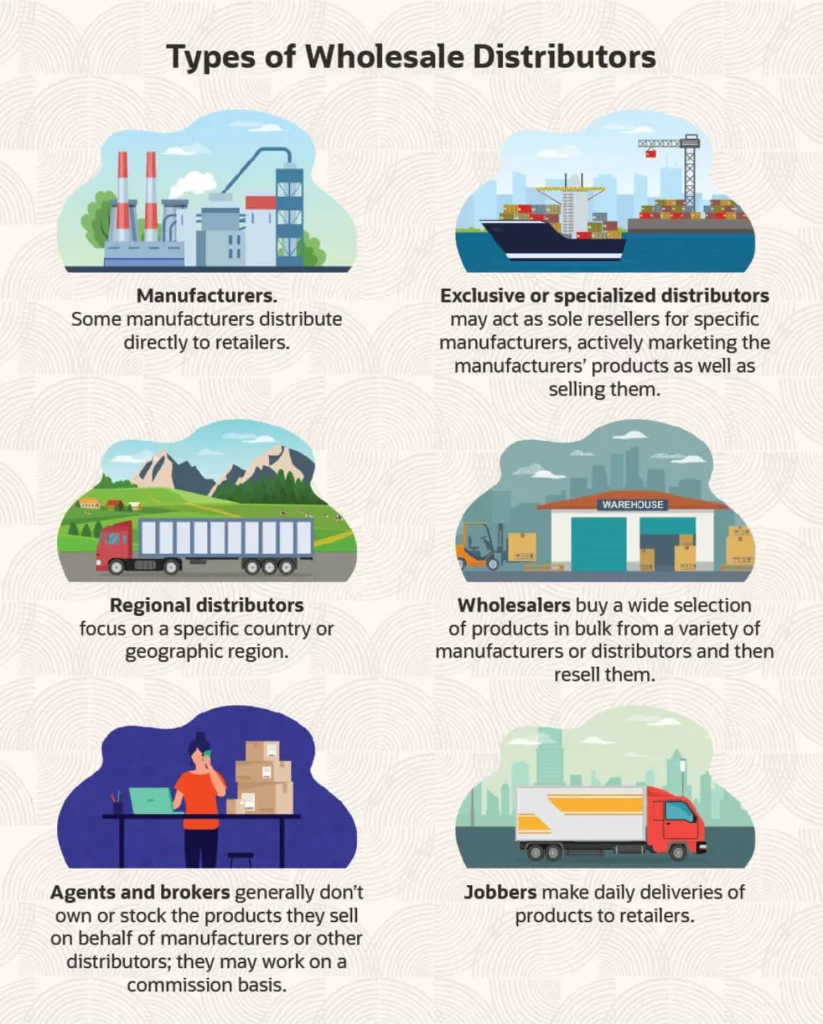
Source image: Netsuite; What is Wholesale Distribution? Benefits, Examples & Tips
Companies from a specific market or industry can be involved in wholesale. Each business that is engaged has different business models. This difference makes wholesalers vary. Here are some of them:
Few manufacturers not only sell their products to wholesalers but also directly to retailers. In this case, the manufacturer will wholesale without a middleman. An example of this is boutique manufacturers that sell straight to customers.
Prices received by retailers can be cheaper because there are no go-betweens. However, manufacturers will face competition from traditional distributors already active in the market.
Some distributors are sole sellers for certain manufacturers. In addition to making sales, they will conduct analyses related to the market, marketing, and product sales.
When manufacturers aim to sell their products, they first analyze the different regions to identify product opportunities. This involves studying the customers, languages, trends, regulations, and import procedures of specific countries or regions.
Based on the results, the manufacturers work with regional distributors to sell their products. The analysis helps them understand which products will likely sell well in a particular region and how best to reach the customers in that region.
Several industry sectors distinguish wholesalers and distributors. In wholesale, they buy products in large quantities from various manufacturers and distributors and sell them in smaller amounts. Besides selling, a wholesaler has to set prices, provide storage, and compete for retail needs with their competitors.
Agents and brokers are people who help wholesalers to find official manufacturers with the best quality and price. They do not own or sell their products directly but will focus on finding customers and selling products on behalf of the manufacturer. Unlike drop shipping, agents and brokers can manage products prepared by manufacturers.
Agents and brokers are people who help wholesalers to find official manufacturers with the best quality and price. They do not own or sell their products directly but will focus on finding customers and selling products on behalf of the manufacturer. Unlike drop shipping, agents and brokers can manage products prepared by manufacturers.
Businesses involved in the supply chain can reap the many advantages wholesalers provide. The benefits include:
Manufacturers will spend less investment on expanding their market. By utilizing wholesalers, products can reach consumers without employing extra energy that is more costly. Wholesalers are responsible for distributing products to retailers that are difficult to get.
Wholesaling can simplify business operations for distributors, wholesalers, retailers, and consumers. Manufacturers can work with fewer wholesalers to fill large orders. As for retailers, they can get supplies from a variety of different wholesalers as opposed to just one manufacturer.
Simplifying business operations can reduce the costs incurred by manufacturers and wholesalers. Retailers will find products cheaper if they buy from wholesalers, as there is no need to purchase large quantities of multiple products.
Wholesalers usually own large warehouses to accommodate products and inventory items. The ability to store items can free manufacturers and retailers from the cost of maintaining large stocks of products.
Through inventory maintenance, wholesalers help maintain a stable supply of products. Wholesalers also reduce the risk of shortages for businesses involved in the supply chain.
Many wholesalers operate across various industries in Indonesia, resulting in intense market competition. As a result, these wholesalers are facing several challenges, including:
Wholesalers must be ready to compete with online businesses, as many retailers are shifting to B2B online sales. This means that customers can enjoy the convenience of shopping for lower-priced products with transparent pricing and faster delivery. Additionally, online platforms enable suppliers to sell their products internationally, creating even more competition.
Technological advancement forced us to adapt to the changing times. You can digitally transform to reach a broader range of customers. This digitalization process can start with social media and online marketing. This method helps customers choose and view products that are being sold. You can improve digital marketing by harnessing Google’s algorithms, such as SEO, SEM, etc.
Read more: 8 Best Wholesale Distribution Software Recommendations 2023
A competitive market has resulted in many manufacturers selling directly to consumers. Wholesalers will face challenges as this undermines market prices since manufacturers sell at a much lower price.
Checking how well the manufacturer performs first is a good idea to ensure you get good quality products. This way, you can also make sure they’re not selling directly to consumers or in the same area as you.
The expectations of consumers have risen due to the emergence of online entities, such as fast delivery, real-time visibility of orders, and 24/7 customer service. As such, wholesalers must work extra hard to meet consumer expectations. A solution would be providing other services that online entities do not have, like being able to choose and try products at will.
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) can help manage relationships with consumers. Impact CRM lets you quickly know customer data from the most bought, satisfaction levels, and contact details. With Impact, you can improve customer retention and service, indirectly increasing sales.
In the era of globalization, the downward pressure on prices — especially for commodities — is enormous. Shrinking margins will force wholesalers to increase their efficiency, leading to other forms of stress. There is competition for prices between wholesalers, so it is not uncommon for them to lower costs, resulting in reduced profits.
In cases like this, you could keep a list of prices that vary based on the number of items sold, the location, and the type of customer. You will know what’s the lowest profit you can accept. You can also use volume pricing to encourage customers to purchase more products.
Wholesalers often work in a particular industry that sells certain products. This lets distributors focus on meeting specific product demands and facing regulation within the sector. Here are the four most significant sectors in the wholesale industry:
In Indonesia, the F&B industry is still in high demand by businesses because of the potential of its continuous growth. Despite F&B’s decline during the Covid-19 pandemic, the growth rate has continued to increase. According to BPS, the F&B’s growth rate fell to 1.58% in 2020 but rose in 2021 to 2.549%, and in the second quarter of 2022, it increased further to 3.68%.
This positive trend shows that the F&B industry has prospects that will continue to proliferate. This sector’s growth has impacted retail and wholesale growth, which is increasing to meet customer demands. This industry requires wholesalers to provide raw materials that meet proper hygiene, freshness, storage, and distribution standards.
The healthcare sector has contributed significantly to national economic growth following the Covid-19 pandemic. Despite not having a significant share in the national economy, healthcare continued its surge to reach 10.46% in 2021. This figure is much larger than other sectors dominating Indonesia’s GDP.
The ongoing expansion of healthcare impacts retail and wholesale businesses that supply raw materials and equipment. Wholesale distributors are critical in providing medicines, medical equipment, and other supplies to state-run hospitals and clinics. As a result, it is essential to understand the regulations and procedures involved in handling medical goods for distribution.
Another sector that improved during the pandemic was the information and communication sector. When the economic growth rate declined, this sector increased to 10.61% in 2020. This number even reached 7.14% in the first quarter of 2022. A significant factor of this growth is the emergence of new habits such as working and studying from home.
The need for technology products is growing in Indonesia, affecting the number of wholesalers. Wholesalers not only need to supply everyday technology, but they also have to fulfill orders for advanced electronic products. Keeping up with technology trends and retail meeting demand will be challenging for wholesalers.
A wholesaler is a supplier that deals with many products for B2B businesses and retail customers. They buy products in bulk from manufacturers and sell them in smaller quantities to businesses for resale.
The industrial sector still holds the position of being the most significant contributor to Indonesia’s GDP. However, to get their products to the consumers, the industry requires a middleman to distribute them from the manufacturer to end-users. This is where wholesalers come in.
Wholesalers purchase products from producers in large quantities and then resell them in smaller amounts to retailers at a higher price. The process of wholesaling can benefit producers, retailers, and consumers. To market their products efficiently, many industrial sectors rely on the presence of wholesalers.
Wholesaling involves various parties, and operational activities must be carried out effectively. Data integration and business process automation can help wholesale companies to generate more revenue as the company’s productivity increases.
Impact wholesale distribution can help you automate business processes such as sales, inventory, accounting, and others. It is time to undergo digital transformation. So, take the first step by starting a free demo with Impact.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.
