Kanban: Definition, 6 Rules, and its Benefits
Kanban is a crucial part of the Just in Time (JIT) system, which we discussed…
Sean Thobias
May 17, 2025Warehouse costs usually make up 1% to 5% of a company’s total sales, depending on the type of company and the value of the goods stored. Out of the overall logistics costs, about 22% goes towards warehousing, and an additional 23% is for inventory holding costs.
To effectively manage warehouse costs, the warehouse manager must clearly understand the company’s specific expenses. They should also implement the right strategies to significantly reduce warehouse costs and prevent financial strain on the company.
The purpose of this article is to assist managers in gaining a better understanding of warehouse costs. It guides creating budgets, calculating return on investment, and making informed decisions. Additionally, the article compares different financing models for warehouses and practical tips to help reduce warehouse costs.
Read more: Understanding Warehouses: Definition and its Importance
Warehouse fees can change depending on the facilities, storage space, and services you need. The most common costs are handling (receiving and shipping), storage space, operating administration, and general administrative expenses. Now, let’s explore nine types of costs associated with warehouse operations:
There are several types of costs involved in warehouse space. These costs include renting or leasing buildings or land and the decrease in value of the buildings (depending on how they were acquired). Other expenses include insurance, rates, utility bills, wear and tear of fixtures and equipment, wear and tear of shelves, wear and tear of refrigerators, repairs and maintenance costs, cleaning and security costs, depreciation of other building equipment, and waste disposal costs.
The company spends direct labor costs to pay warehouse workers directly involved in running the warehouse. These costs include wages, additional expenses, employee insurance, safety clothing (PPE), taking care of the workers’ well-being, and providing training.
Indirect labor costs (fixed) are the company’s warehouse management expenses, including supervisors and administrators. These costs include wages (with additional fees), insurance, safety clothing (PPE), employee well-being, and training.
Labor costs consist of direct and indirect labor expenses and variable labor costs. Variable labor costs encompass additional fees such as overtime payments and bonuses provided to workers.
The company uses various equipment in the warehouse. Every year, the equipment depreciates. Moreover, the company doesn’t own all the equipment in the warehouse; some of it is leased. As a result, the company incurs fixed costs for the equipment, such as depreciation, borrowing, or rental fees.
Equipment costs in the warehouse vary based on the usage of equipment. These costs cover fuel, tires, lubricants, and packaging materials such as pallets and stretch wrap. The total equipment cost includes some of these expenses.
The overhead costs of management, finance, HR, IT, and other divisions include different expenses. These expenses cover salaries, extra costs, and benefits like cell phones and accommodation. They also encompass expenses for company cars, operations, and the depreciation, rent, or lease of office equipment and furniture. Furthermore, they include costs for information technology hardware and software.
Sales and marketing overhead costs consist of various expenses. These include salaries, surcharges, and in-kind benefits like mobile phones and accommodation. Additionally, company cars and their operational costs are part of these expenses. Moreover, marketing spending, which encompasses advertising, exhibitions, and brochures, is also included.
The warehouse has different costs, including expenses for communication, shipping, banking, interest, funding, insurance, and legal and professional services.
In addition to wages and salaries, the total labor costs include contributions made by the employer for things like national insurance and pensions on behalf of employees. It also covers other expenses like sick leave, maternity, training, recruitment, and other non-monetary benefits.
Most companies don’t know how much they should spend on warehouses. The people in charge of operations know how much money is going toward warehouses. They might realize they need to spend less. Every year, companies worldwide spend about €300 billion on their warehouse operations, and that number keeps increasing.
The reason warehouses cost so much is that most companies don’t have a clear way of figuring out how much they should spend. If a company doesn’t know the right amount to invest in warehouses, any attempts to reduce costs and improve efficiency will likely fail.
Over the past ten years, McKinsey’s research has shown that many companies are spending way more than they should. To deal with this problem, companies need to use the correct method to calculate their warehouse costs.
Two types of costing systems matter for warehouses: traditional costing methods and activity-based costing. Below is an explanation for each way:
Traditional costing systems determine costs for generating profits by allocating indirect production costs. These systems calculate predefined overhead rates and apply them to specific metrics.
In these systems, we estimate overhead rates for specific cost drivers. Let’s consider Customer A as an example. Customer A uses many man-hours and warehouse space but requires low management time. In traditional costing, allocating overhead costs may result in penalties for Customer A.
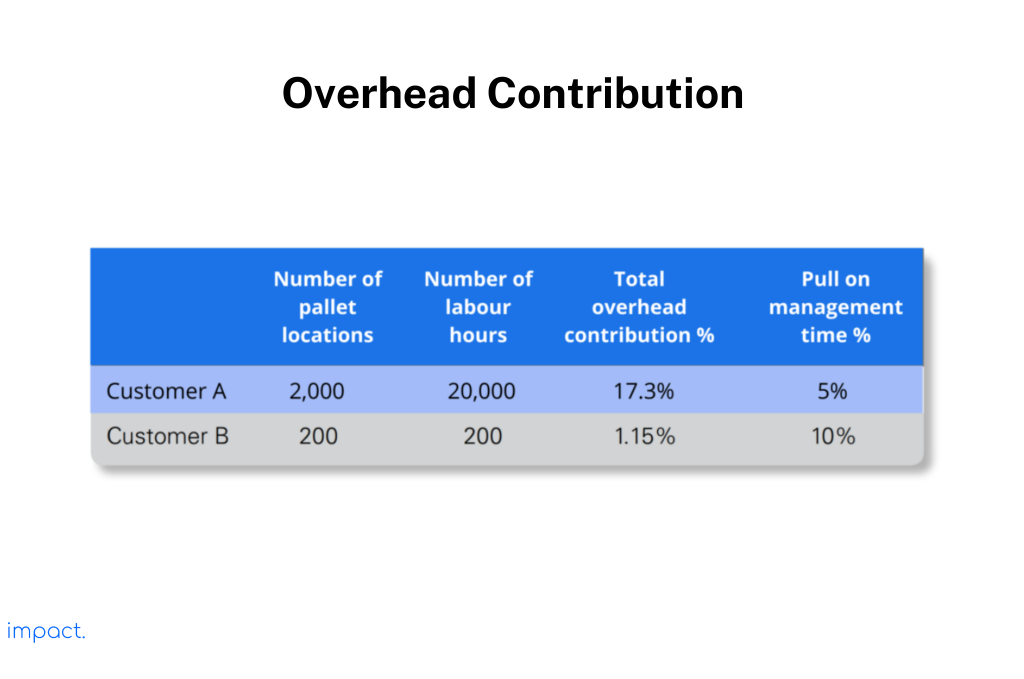
With the rise in products and complicated services, using a single overhead rate is no longer enough. Cutting down on labor or equipment doesn’t bring down overhead costs. So, when the volume decreases, the percentage of overhead expenses concerning direct costs increases.
Predicted volume or utilization forms the basis of overhead rates. When utilization decreases, companies need to increase the percentage of overhead allocation. Consequently, traditional costing methods have a few drawbacks. That’s why many companies are making a switch to alternative costing methods.
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) is a method that helps identify the specific overhead operations associated with manufacturing each product. Instead of applying the exact overhead costs to all products, ABC recognizes that not all products need the same support from overhead costs.
Accountants created the ABC method to solve the inaccuracies arising from traditional costing approaches. Managers need a more accurate cost method to determine which profits are genuinely profitable and which ones are not.
ABC costing increases the number of indirect cost pools companies can assign to specific products, distinguishing it from traditional costing. In the conventional method, total firm overhead costs are universally collected and distributed to all products.
To introduce the ABC model, you must thoroughly understand the company, its operations, and the roles of each staff member. You can achieve this by observing procedures for a time and noting each activity’s duration.
Regarding warehouses, the following table provides an example of the ABC model. Companies can calculate the pallet space occupied and allocate the labor and MHE (Material Handling Equipment) hours to each customer. The company also distributes management time in hours per customer. It assigns other overhead costs, such as postage, legal fees, and insurance, based on a percentage.
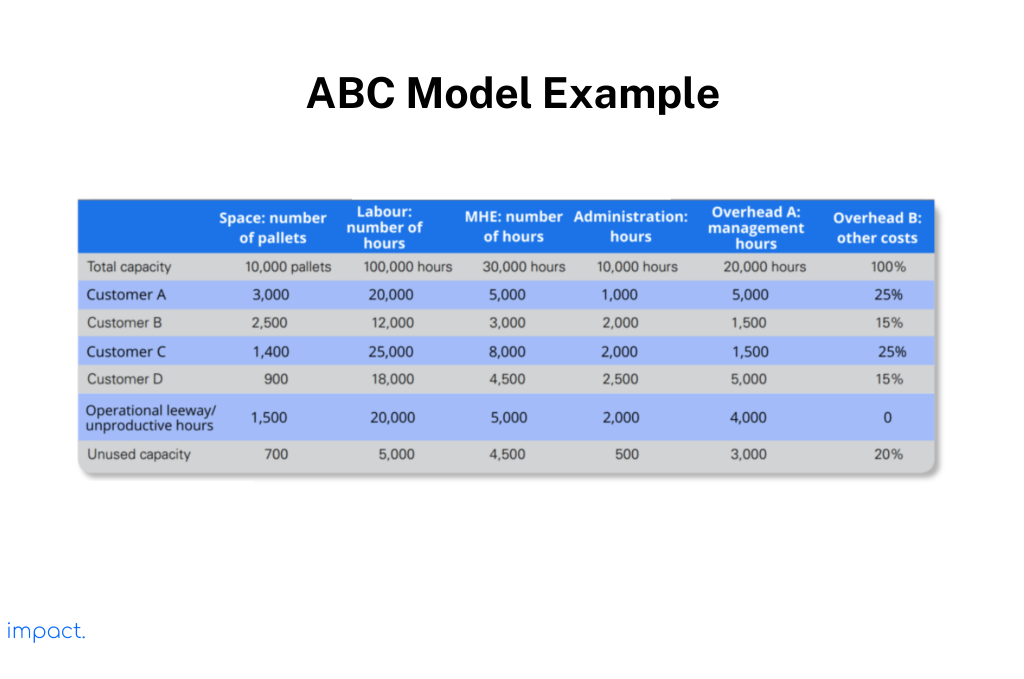
After performing all the calculations, the company can also determine the unused capacity in the warehouse. However, using ABC has its disadvantages. It requires significant work, and collecting accurate data can be challenging. Implementing ABC takes time and necessitates a cost-benefit analysis to assess the time invested and the benefits obtained.
To make it easier to understand the distinctions between traditional and ABC costing systems, take a look at the table below for a straightforward comparison:
| Comparison Aspect | Traditional System | Activity-Based Costing (ABC) |
| Calculation | Uses predetermined rates for costs and applies them evenly to all products. | Allocates costs more accurately among products, including non-manufacturing expenses. |
| Time | Faster, involves fewer variables. | Slower and more complex, requires input from multiple departments. |
| Accuracy | Less accurate, uses limited information. | More accurate, provides detailed information. |
| Cost | Cheaper, the process is simple. | Tends to be more expensive due to specific software requirements. |
Cutting down on warehousing expenses is crucial for businesses to improve their operations. Here are some straightforward tips to help you lower your warehousing costs:
Companies must grasp customer demand accurately and make products based on actual orders rather than relying on estimates. This approach is called a pull system, where the company only produces goods when customers place orders. By following this method, companies can reduce the risk of too much inventory.
To make inventory flow better, giving each item in the warehouse a designated spot is essential. It will make it easier to move stocks around when needed. For example, put the items you ship most often closest to the shipping dock.

To make your warehouse more efficient, check if you need all the items. If there are things you don’t use, take them out to save space. Smaller and more flexible items can also make accessing everything in the warehouse easier. Try using shelves and layouts that fit well and help you maximize the available space.
The warehouse’s operational costs include electricity, fuel, and transportation expenses. To lower these costs, you can take a few steps:
Read more: 7 Warehouse Picking Methods: How to Choose the Right One
Warehouse managers need to understand the costs associated with their warehouse operations entirely. This understanding is essential for the company’s budget and accurately allocating costs to products and charging fees for services provided in third-party relationships.
Consider using an ERP system to simplify and streamline the company’s business processes. Impact ERP includes a warehouse module that can help reduce waste and make the warehouse picking process more efficient. In addition to the warehouse module, it offers other modules such as inventory management, accounting, sales, and human capital management (HCM).
Richard G. 2011. Warehouse Management. Great Britain: Kogan Page Limited.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

In a warehouse, you can handle goods by hand or with machines. When you take goods manually, you use tools and equipment to lift heavy loads to or from the warehouse.
Modern warehouses have Material Handling Equipment (MHE) that includes various types of machinery. MHE helps you carry out tasks safely and efficiently, so you don’t have to rely on manual labor as much.
This article will give you a better understanding of warehouse storage systems and their handling equipment. It will explain MHE, discuss different types, and highlight the advantages and disadvantages.
Material Handling Equipment (MHE) comprises many tools, vehicles, storage units, equipment, and accessories. MHE actively transports, stores, controls, and protects products at every stage of manufacturing, consumption, distribution, or disposal.
There are four main types of MHE. They are storage and handling equipment, engineered systems, industrial trucks, and bulk material handling. However, this article will focus on the first type, storage, and handling equipment.
Read more: Understanding Warehouses: Definition and its Importance
Stockpile systems usually involve grouping non-automated setups with engineered systems. These systems actively use storage equipment to accommodate or support materials during downtime or when the materials are not in transport.
This timeframe can also refer to temporary pauses during long-term transportation or storage, allowing stock to accumulate. The most common storage equipment includes pallets, racks, or shelves where materials can be neatly stacked, ready for transportation or consumption.
Many companies have explored ways to improve storage efficiency by designing packaging that enables materials or products of a specific type to occupy less space while in stock.
In warehouses, there are different tools for storage. Each device has its advantages and roles. Companies must consider trade-offs between speed, cost, and capacity for storage systems.
The more storage an operation needs, the denser pallet storage is required. The choice of storage also depends on the building layout, the type of material handling equipment (MHE) in use, and the budget available.
Two popular storage tools in warehouses are pallet racks and stacking. Now, let’s take a closer look at warehouse storage systems.
In situations where warehouse heights are low, budgets are tight, and products and packaging are robust, block stacking is the most common method for storing large quantities of single SKU products.
Block-stacking is a method where we put each item on the floor and stack them up to a safe height based on how heavy and stable the stack is. It works well for products you can’t store on pallet racks and are difficult to stack.
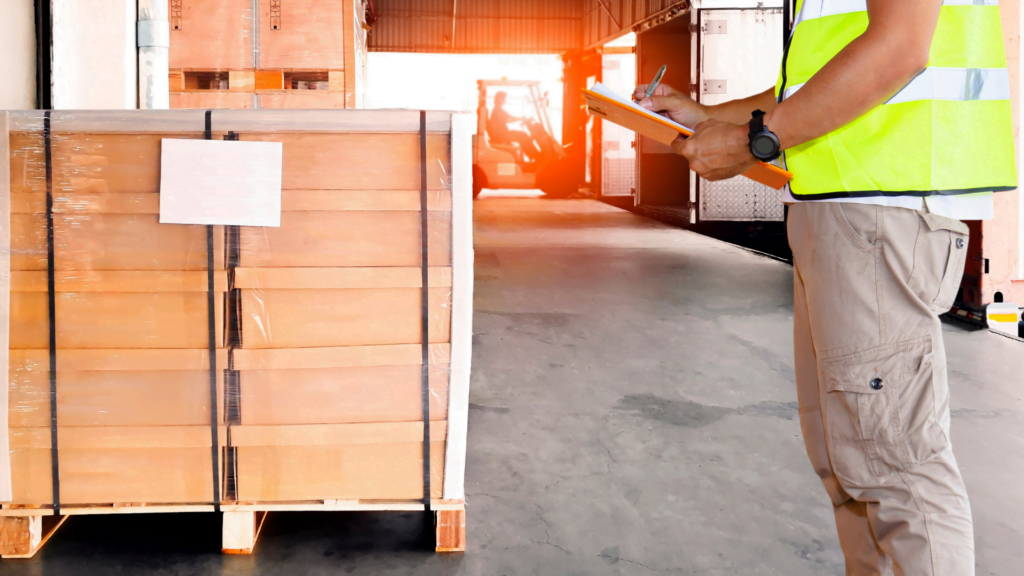

This method allows us to store products such as washing machines, refrigerators, cans, and bottles. It provides a cost-effective solution for robust products that have a high number of units per SKU. Additionally, we can utilize tools like pallet collars and converters to minimize the potential damage to the bottom pallet.
However, block-stacking also has its downsides. It can be tough to reach the goods, and there’s a greater chance of damage. Managing inventory without following the last in, first out (LIFO) method can be tricky, especially when optimizing limited space.
People often use shelving systems to store fragile, high-maintenance items requiring extra attention. This system is pricier than stacking, but it offers improved accessibility.
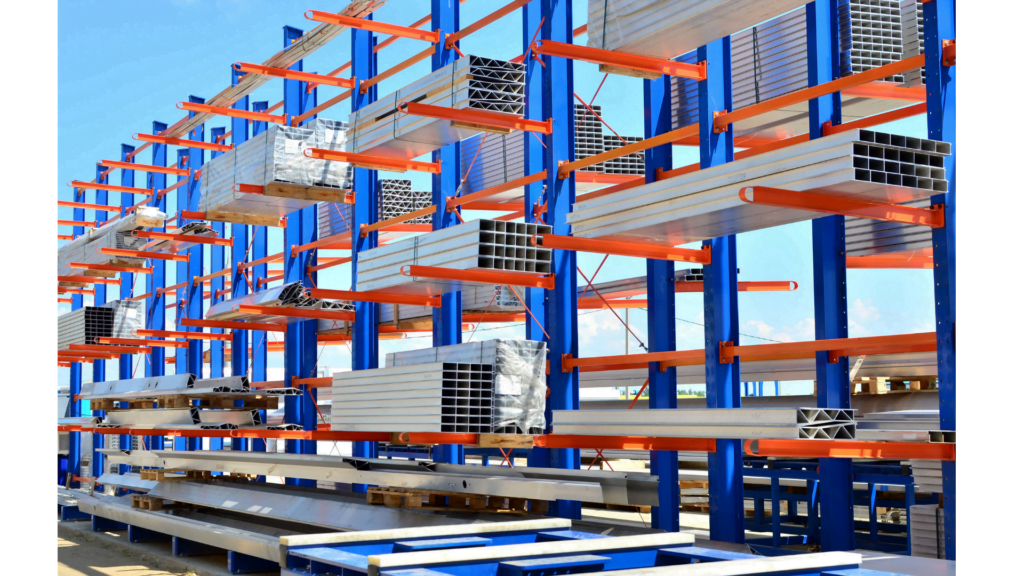
The terms adjustable pallet rack and wide aisle rack are interchangeable. Moreover, there are various shelving systems, each with pros and cons. Here are eight common types of racked storage found in warehouses:
Warehouses around the world commonly use this type of rack. It is highly versatile and doesn’t require any special equipment for handling. You can easily adjust the beam height to meet your needs.
With this rack, you can quickly and easily access each pallet. It is simple to install and move. However, there is a downside to consider. The forklift truck needs a broader aisle to turn around quickly.
Double pallet racking allows for storing pallets at two different depths. This system requires special equipment, like extendable forks and wider aisles. However, it’s important to note that this configuration slows down the access speed.
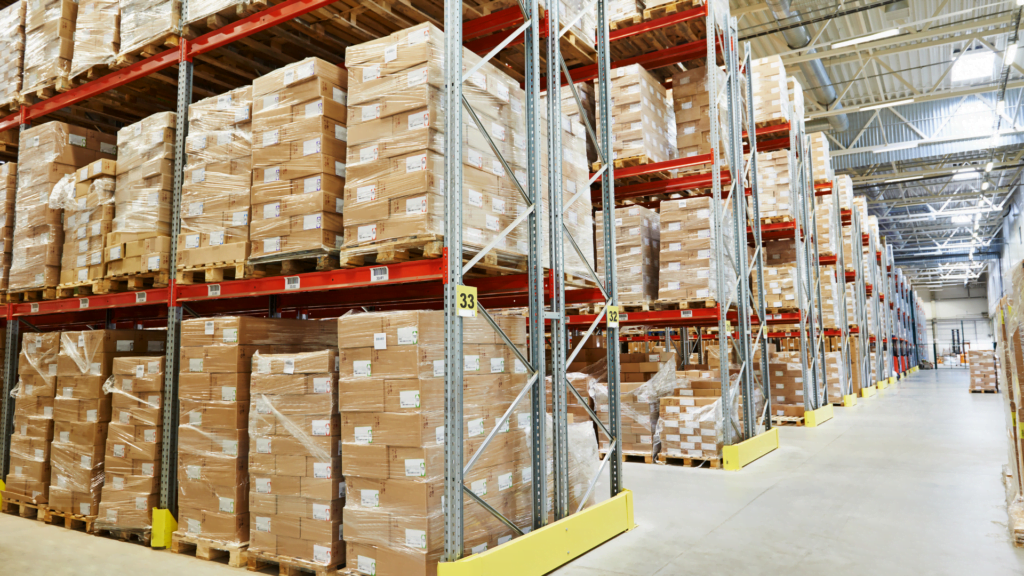

On the other hand, the double-deep configuration, which reduces the number of access aisles, offers a highly efficient storage system by utilizing the saved space to accommodate additional shelving.
This rack uses APR and can store more pallets by narrowing the aisle width to around 1.6 meters. You need narrow aisles or tower trucks to store and access pallets in this rack.
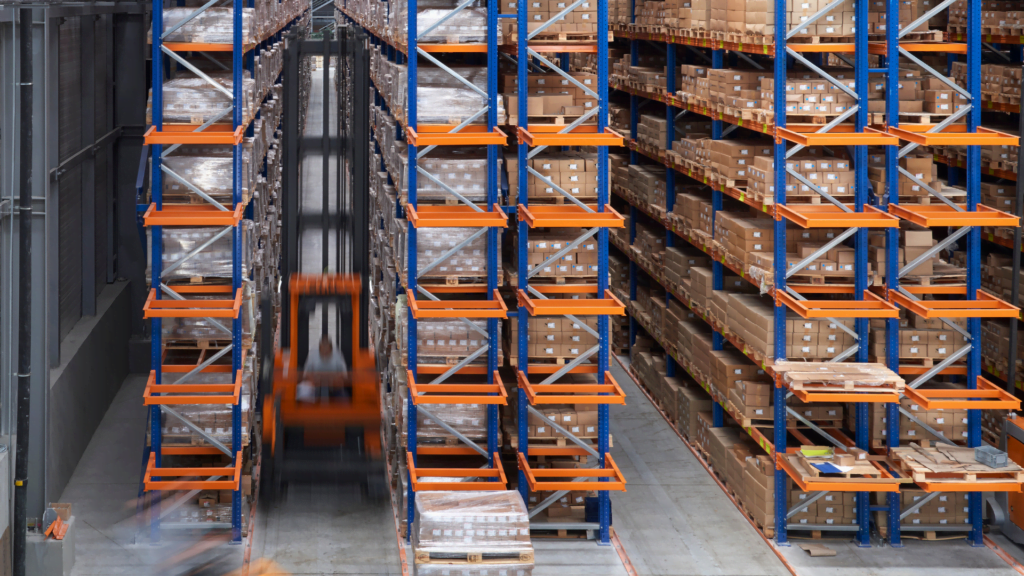

When setting up narrow aisle racking, it is crucial to ensure a flat floor, particularly for heights exceeding 10 meters. During construction, we use lasers to guarantee a perfectly level floor.
Drive-in and drive-through racking systems improve safety and efficiency by preventing the stacking of fragile or unstable loads. The L-shaped rail in each upright drive-through rack accommodates pallet placement and allows forklift trucks to maneuver easily.
Drive-in racking eliminates the need for aisles, allowing for maximum utilization of floor space. The amount of space used depends on the lifting capacity of the forklift truck.
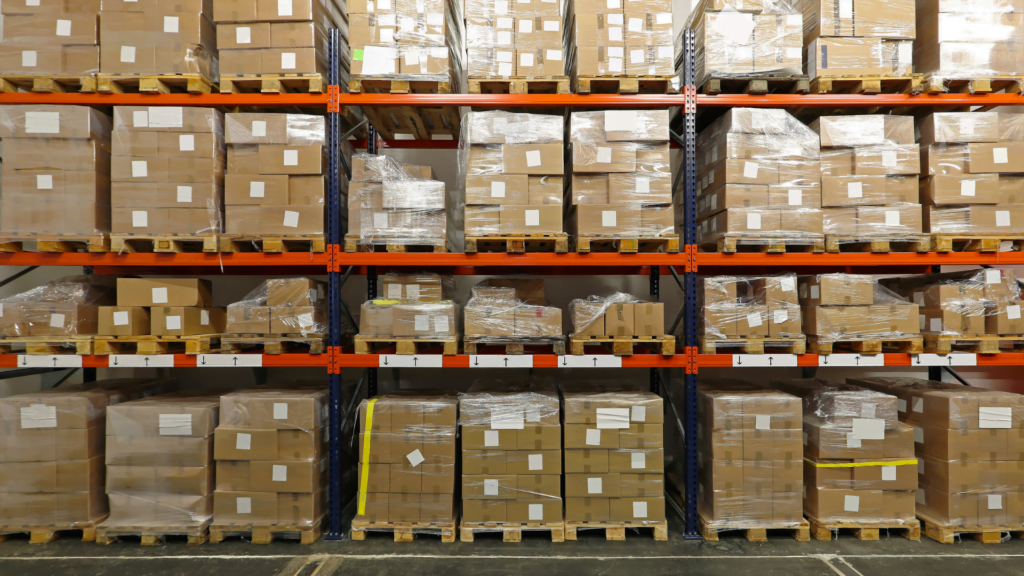

It’s important to note that drive-in racking does not support First In, First Out (FIFO) systems. These racks are ideal for storing large quantities of single SKUs in a high-density manner.
However, there are some disadvantages to consider. This storage method has a higher risk of damaging both the products and the shelves. In addition, the loading and unloading rates are relatively low. Since there is no room for picking individual cartons from the ground floor, this storage relies mainly on handling full pallets in the central area.
Gravity drives the operation of pallet-flow racking. It is suitable for rapidly moving products that require rotation in the order of their arrival. Here’s how it works: You load the pallets at the top of the slanted track and automatically move down using skate wheels when you remove them from the picking area.
With a single block roller conveyor rack, you only need two aisles for loading and picking. This setup allows for quick processing times. Plus, you can best use your warehouse space by storing the pallets in a sequence with fewer aisles.
However, there are a couple of downsides to consider. First, you may be unable to utilize the available space efficiently in terms of volume. Second, different products require different angles of inclination based on their weight.
The push-back system actively positions pallet loads on carts that move forward along sturdy steel rails due to gravity. When an operator loads a pallet from the front, it pushes it behind its back in one position. During unloading, the system releases the front pallet, and the rear pallet automatically moves to the front picking position. This active process facilitates easy inventory management in a last-in, first-out (LIFO) manner.
Operators can store products from two to five pallets deep using the push-back system. They can load pallets from the front using just one aisle. This system offers flexible storage because each lane works independently. Additionally, the vertical storage operates separately from the routes below, allowing for efficient use of space.

In compact warehouses with limited floor space, shelving units can be mounted on rollers to enable easy movement. Only one access passage is needed, and the operator can create an entry by moving the unit. However, this approach slows down the process of picking up goods to save floor space.
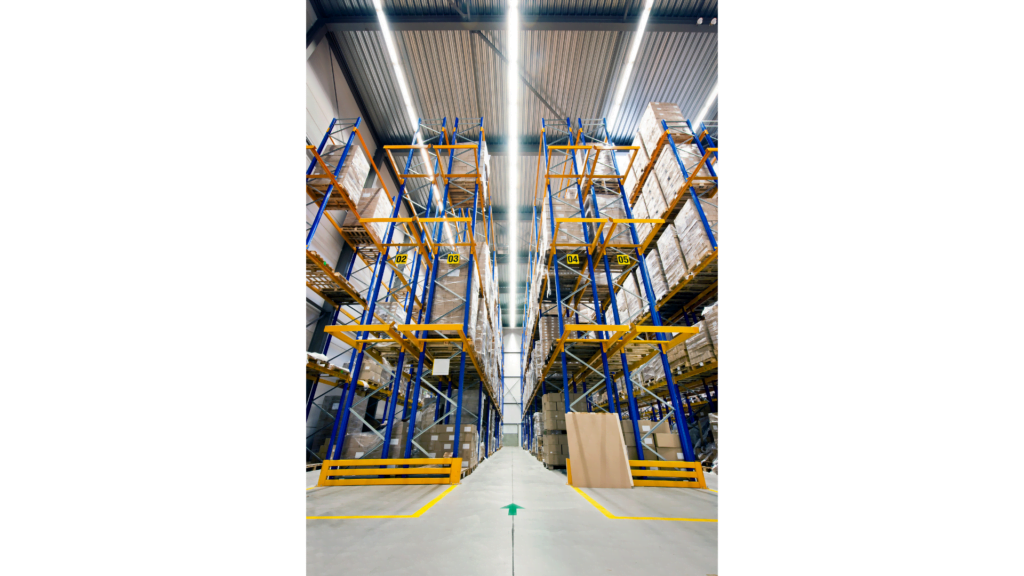

Satellite systems work like drive-in racking, but they use shuttles placed at the front of the rack. The remote control system operates the shuttles utilizing a radio frequency (RF) battery-operated control system and dedicated channels.
This storage system can handle pallets in racks up to 40 meters long. The shuttles have sensors built-in to detect where the pallet was before. Then, they place the new load at a set distance and return to the starting point.
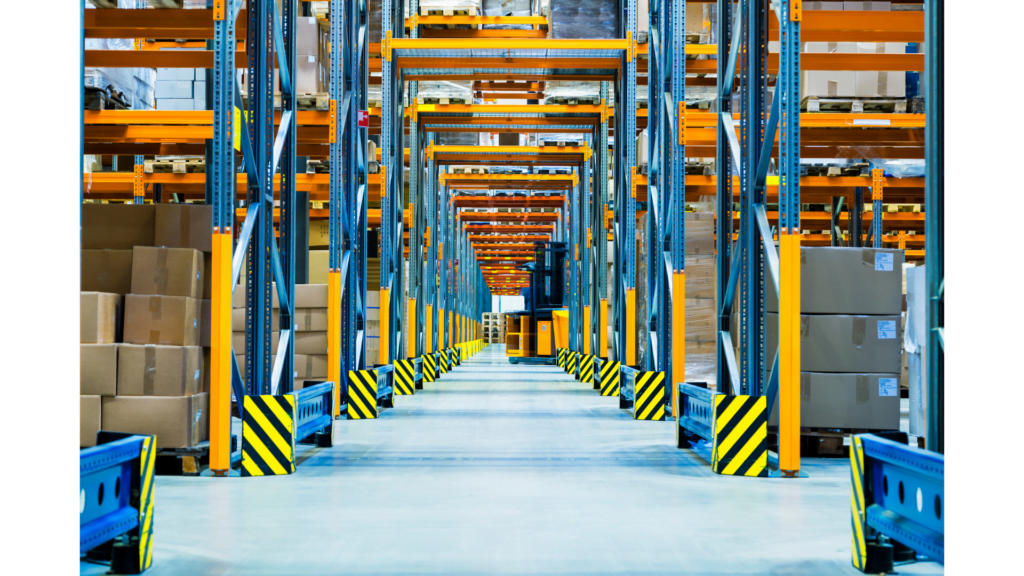

Forklift trucks can quickly move shuttles between lanes. One forklift truck can control several shuttles. By not needing to drive into the rack, the system reduces the risk of damage.
The system automates the placement of pallets on the storage lines, making the loading and unloading times faster. Satellite racks also make good use of the space above the building.

Read more: 7 Tips for Selecting the Ideal WMS
Manufacturers encounter various challenges due to a culture of round-the-clock operations and an aging workforce. These challenges demand higher accuracy, shorter lead times, and lower costs. As a response, manufacturers have developed handling systems that require minimal manual input and increased throughput.
To overcome these challenges, companies can achieve the following advantages by selecting the right equipment:
In a warehouse, different actions happen when storing, picking, or moving goods. Each activity needs a specific tool to handle it. Here are some simple steps in the warehouse and the tools used for them.
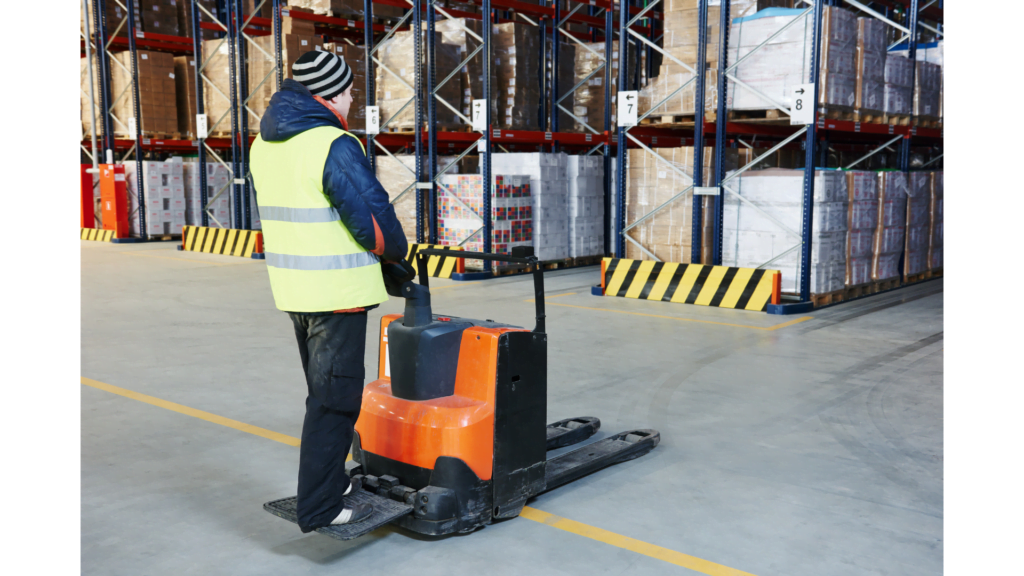
Here are some examples of equipment that can handle horizontal movements in warehouses:

You need to lift pallets, or unit loads into position to make the most of a building’s space. Here are six common types of forklift trucks that can help:

In an automated storage and retrieval system (AS/RS), a fixed-track crane actively collects pallets from the front of the racking system and transports them to an empty location in the rack. This method boosts productivity by storing full pallets at the front of the aisle before retrieving another pallet.
The crane moves horizontally and vertically simultaneously, reducing the time it takes to lift and place the pallets. Usually, the crane remains in one aisle. However, haul trucks can actively move the cranes from one aisle to another if there is a high need for storage and low throughput.
Specific warehouse units require special handling equipment since they cannot be moved or lifted using standard pallets. Here are some examples of additional equipment used in these operations and for such products:
To select the right equipment and storage, focus on the characteristics of your products, warehouse size, environment, product speed, and budget. There are different storage types like collections and racks and handling equipment such as forklift trucks.
Using storage and handling tools helps companies improve productivity and efficiency in warehouse activities.
You can also automate all company processes by using an ERP system. ERP Impact includes a WMS module that reduces waste and streamlines the picking process. It also has modules like inventory, accounting, sales, and HCM.
Richard G. 2011. Warehouse Management. Great Britain: Kogan Page Limited.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

The company’s warehouse plays a vital role in storing its products—essential tasks like picking and receiving occur there.
Companies need to reduce travel time and unnecessary steps to make warehouses more efficient. The proper warehouse layout can help achieve this. Designing the best layout requires paying close attention to details and analyzing data.
Consultants and companies specializing in handling materials and setting up racks can assist in determining the most suitable warehouse layout based on the available space. In this chapter, we will explore the concept of warehouse layouts, essential factors to consider when designing them, and the benefits they offer.
A warehouse is an integral part of manufacturing and the supply chain. It’s where all the materials, from raw to finished goods, are stored. Companies need to organize the layout properly to make things run smoothly in the warehouse.
Warehouse layout involves planning how to arrange things in the warehouse for efficient operations. A well-designed design improves production and distribution processes.
Because there are many tasks in the warehouse, like receiving goods, shipping them out, and storing inventory, companies need to figure out the best way to set up the warehouse. Organizing the layout well allows companies to make the most of the space and keep costs low.
Managing warehouse activities is complicated, so companies often use Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) to automate things in the warehouse.
Read more: Understanding Warehouses: Definition and its Importance
You need to consider three important things to create an efficient warehouse layout. Let’s take a look at each of these aspects:
According to a survey conducted by Cranfield University in 2008 (Baker and Perotti), allocation in the warehouse floor area is as follows: 52% for storage, 17% for pick/pack operations, 16% for receiving and shipping, 7% for value-adding services, and an additional 7% for storage areas like battery charging, empty pallet storage, and other uses.
Different operations determine the distribution of these areas. To ensure the warehouse is efficient, the company must collect data on the other sites it needs for its operations.
A company warehouse requires various areas for smooth operations. These areas include:
For accurate analysis, it is crucial to consider current and past data and future volumes and changes in product or area characteristics. This comprehensive approach allows for a more reliable understanding of the data.
Different companies have varying needs, which affect the calculation of required space. Below, you’ll find several commonly used formulas for space calculation.
To calculate the space needed for arranging vehicles at a vehicle manufacturing company, you can use this simple formula:
| Space = hours to (unload cargo) / Shift time x (number of pallets × space per pallet) |
For example, let’s say the company receives 20 vehicles each day. Each load has 26 pallets, each measuring 1.2 meters by 1.0 meters. It takes 45 minutes to unload a load and 30 minutes to inspect it. The company operates for eight hours.
Using the formula, we can calculate the space requirement like this:
| Space = {rounded((20 × 1.25) ÷ 8) × (26 × (1.2 × 1))} = 4 × 31.2 = 124.8 square meters |
In addition to this space, we also need to consider the work and travel space around the pallets. The amount of this space depends on the type of forklift or pallet truck used for unloading and loading the vehicles. It might be necessary to double the shipping area’s space to provide enough room to access the pallets.
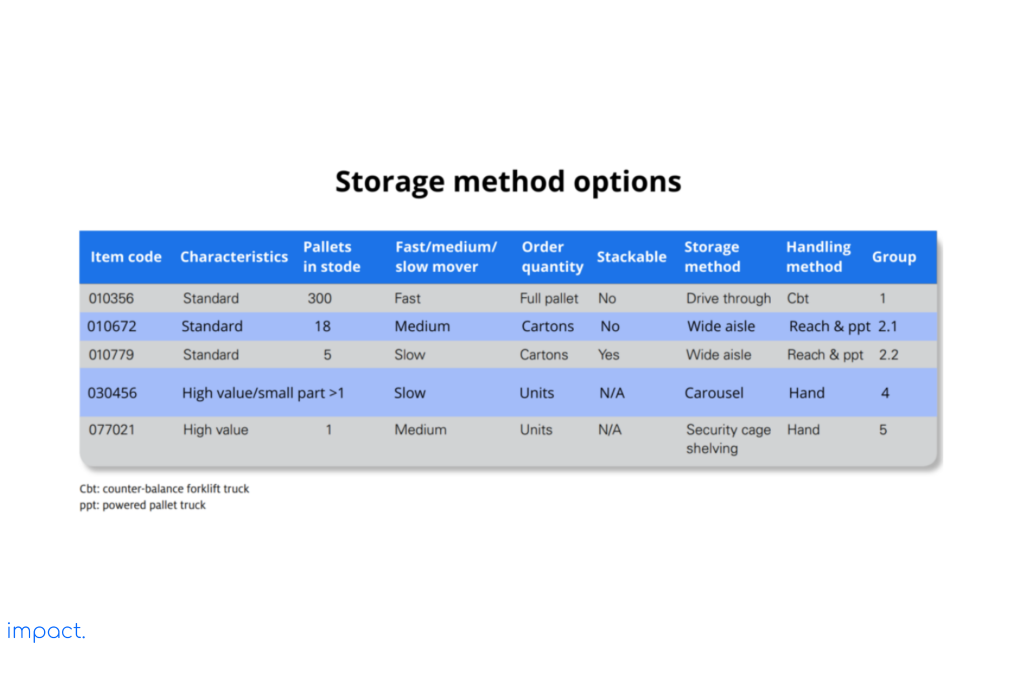
First, you need to evaluate and record the properties of each item and the attributes of the potential storage options. Calculate how many goods can be stored per product line and convert that into the number of pallets required. It will help you determine the pallets needed for each product line.
Next, create a chart that details the number of pallet locations needed and their height requirements. Remember that the height of the pallets may vary depending on the products.
Look at the table below, which shows the characteristics of each item and the different storage options we considered. The table also includes as much information as possible about storing and ordering the products. This information will guide you in choosing the most suitable storage and handling options for your needs.
One important thing to consider when planning a warehouse layout is the width of the aisles. The aisle width is simply the distance between racks next to each other. To ensure everyone stays safe, companies must figure out how much space is needed between pallets once they are on the shelves. The aisle width depends on how much the forklift truck can turn and the size of the pallets it carries.
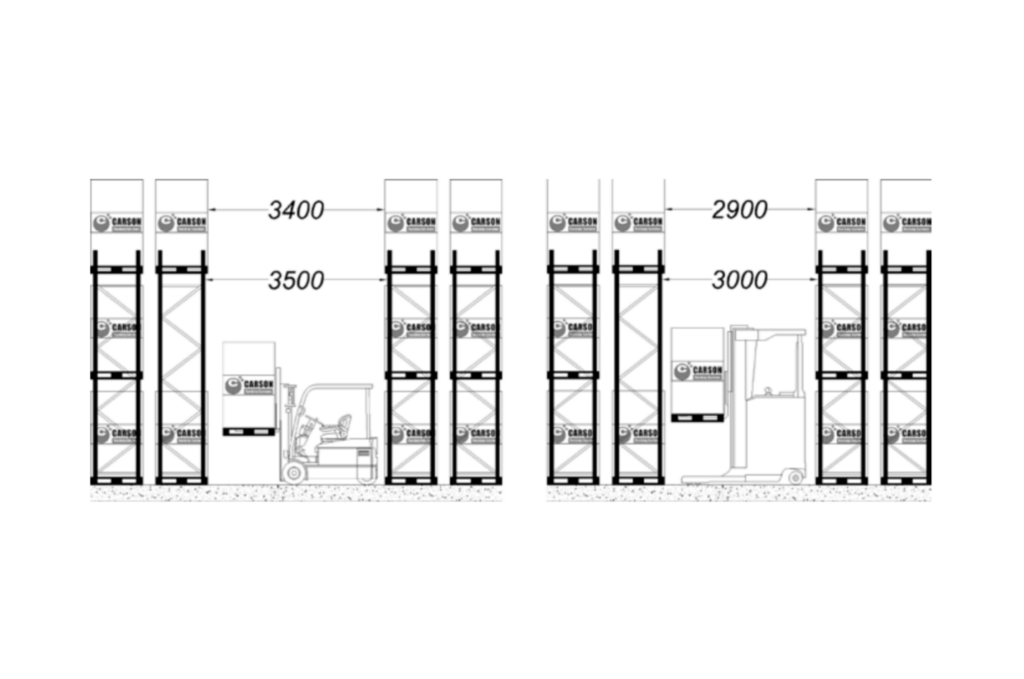
Source: Richard G. 2011. Warehouse Management. Aisle widths (courtesy of Carson Racking Systems Limited)
To keep things safe and efficient, it’s a good idea to add about 100 mm of space on each side of a typical pallet, making a total of 200 mm. This extra space helps with quickly storing and getting pallets when needed. Another thing to consider is the overall width of the forklift truck as it moves along the stacking aisle.
When choosing the aisle width, it’s crucial to find the best balance between productivity, making the most of the available space, flexibility, safety, and the cost of the equipment needed for the specific job.
In addition to the aisles, the warehouse reserves specific areas for tasks such as packing, enhancing product value, and managing returns. The size of these areas depends on factors such as the level and type of work, the number of people involved, and the equipment used.
When planning warehouse space, people sometimes forget to consider specific areas. These areas include the storage, recharging, and replacement spots for forklift batteries or gas cylinders, as well as parking spaces for equipment when it’s not in use. Remembering these things is crucial for using the warehouse space efficiently.
To determine the suitable warehouse layout for your needs, analyze your gathered information and goals. The flow of your warehouse relies heavily on the available space and how things will move in the entire operation.
Companies employ three warehouse layouts to organize their operations effectively: U-shaped, I-shaped, and L-shaped.
Companies commonly utilize the U-shaped warehouse flow because it effectively serves beginners. This layout arranges all the parts semi-circle, with the sending and receiving areas on opposite sides. In contrast, the storage area occupies the middle.
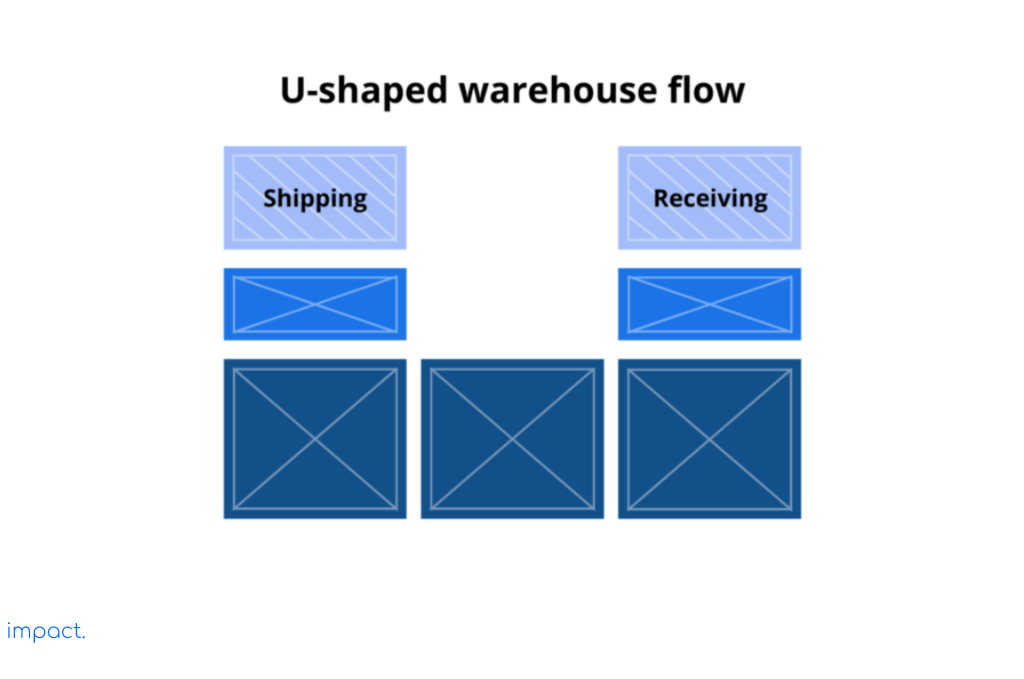
The U shape helps to keep the main traffic flows in the warehouse separate and efficient. By having the material come in and go out on different sides, we avoid jams and keep things running smoothly. This flow of goods also helps to save space.
The entrances and exits on the same side of the building reduce the need for ample package space. It enables our employees to swiftly transfer products between the reception and delivery areas. However, one drawback of the U-shaped flow is that it can create issues when the sending and receiving sites are nearby and share similar functions. These circumstances can result in production bottlenecks.
Big companies with large storage spaces prefer this type of warehouse flow. They like it because these companies usually have many things to make and need a straightforward way to bring something in and take them out.
The shape of this kind of warehouse goes straight from where things come into, where they go out, and the other way around. This type is the best way to make the most of the whole length of the warehouse.
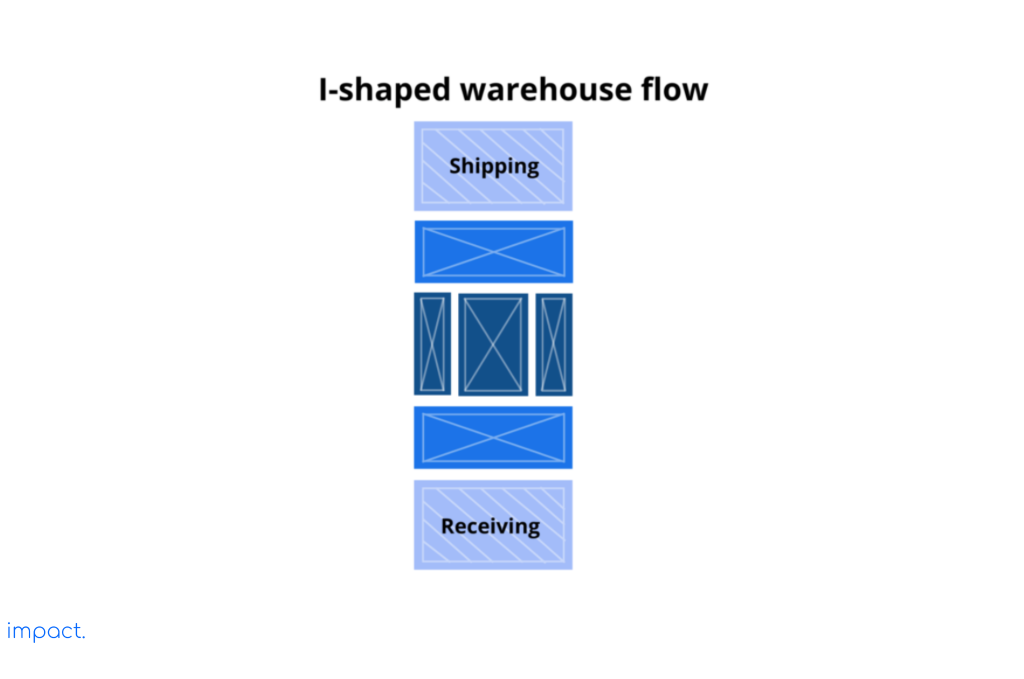
It also keeps similar things apart, like on an assembly line, so working with them is more manageable. This way, there are fewer places where things can get stuck or delayed because they have to go back and forth.
But there’s a downside to this type of warehouse. The company needs enough space on both sides of the building for loading and unloading. It can cost more money to buy equipment for bringing things in and taking them out. Also, things often have to travel through the whole warehouse to get where they need to go.
The least common flow type is this one, used for buildings with an L shape. The L shape consists of a shipping area on one side and a receiving site on the adjacent side, forming a 90-degree angle. L-shaped flow and I-shaped flow share similar advantages.
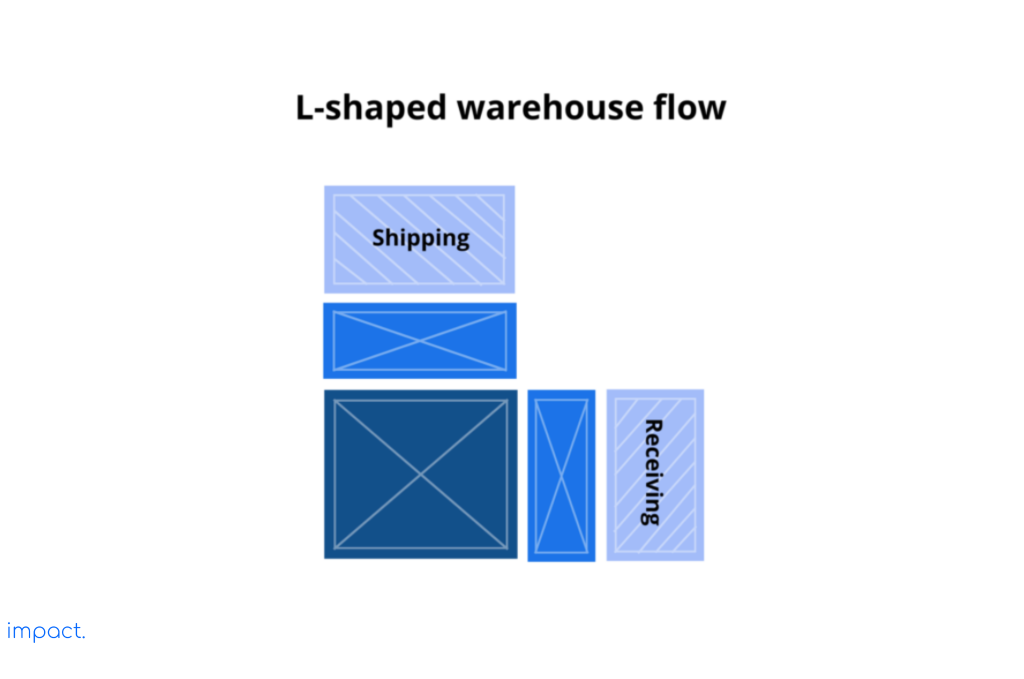
The L shape helps prevent congestion by avoiding back-and-forth movement. It effectively separates products by placing inbound and outbound docks on opposite sides. However, the main downside of the L-shaped warehouse design is that it needs much space to work well.
Read more: 7 Tips for Selecting the Ideal WMS
Designing a warehouse involves considering all the crucial areas a company requires and using the available space best. Here are the steps to develop a warehouse:
Before you decide, take some time to create a visual tool that will help you estimate the available space. It involves marking areas where you can place shipping docks and accommodate recipients. Blueprints will assist you in seeing the warehouse as a blank canvas.
Begin by planning how to prepare the different components of the warehouse. This process involves considering offices, employee living areas, and shipping and receiving docks. Consider all the main areas, such as assembly lines, manufacturing materials, workstations, conveyor belts, and other equipment needing space.
Once you have carefully examined the room, you can determine which designs will naturally meet your needs. If you want to keep the shipping and receiving areas close together, you can opt for a U-shaped warehouse flow.
Suppose your priority is to maintain a smooth workflow with minimal space usage. In that case, you may prefer an I-shaped warehouse flow. If you have a warehouse with a unique shape, an L-shaped warehouse flow would be suitable.
Once you’ve decided on the ideal flow for your requirements, it’s time to buy and assemble all the equipment needed to optimize movement within the warehouse. This equipment comprises forklifts, racks, bins, pallet racks, rolling ladders, picking and packing stations, processing technology, and other machinery essential for efficient warehouse operations.
When you’re unsure, test your proposed plan. Track the most profitable traffic flows before installing equipment into the warehouse layout. Consider the opinions and concerns of the warehouse staff and other participating employees actively involved in the workflow.
Here are some of the benefits of implementing warehouse layouts in companies:
The main aim of designing a warehouse layout is to optimize warehouse space utilization. By effectively using the available space, companies can reduce the time required for product manufacturing and streamline processes at every stage.
It is essential to make the most of every inch of the warehouse. The size and area of the warehouse play a significant role as they directly impact the overall efficiency and productivity of the space.
The main objective of creating a practical warehouse layout is to optimize operations, enhance productivity, and minimize the chances of congestion or errors. Surveys have shown that 67% of customers take their business elsewhere when they receive notification that an item they ordered is out of stock.
The warehouse management team actively collaborates with the operations management team to ensure a seamless production process from start to finish and efficient and accurate order fulfillment.
Some warehouse layouts can be more expensive to construct and maintain, depending on the available floor space. Understanding the materials on hand and determining the appropriate staff positioning are essential factors in finding a suitable design.
By implementing a suitable warehouse layout, companies can allocate resources more efficiently. It includes using the budget for warehouse maintenance and hiring the correct number of employees to carry out the operations in the warehouse environment.
Maintaining tidiness and avoiding significant problems in the warehouse is possible by implementing an efficient warehouse layout. An appropriate floor plan for the warehouse reduces the risk of goods being misplaced or mishandled, ensuring that everything has its designated place in the flow of the operations.
Efficiency is critical to organizing all warehouse operations. The design of a warehouse plays a vital role in effective warehouse management. It actively creates an environment where it effectively manages inventory, swiftly replenishes stock, treats staff fairly, and efficiently fulfills orders.
When you face a space shortage in a warehouse, you have several options. You can expand the warehouse, rent additional space, or make more room in the existing building.
Another way to increase available space is by reducing inventory levels. However, the warehouse manager may not have the authority to do this. Nevertheless, the warehouse manager can identify slow or stagnant stock and collaborate with the sales and finance departments to dispose of it as agreed.
Here are some options you might have missed:
Read more: 7 Warehouse Picking Methods: How to Choose the Right One
To create an efficient warehouse layout, we need to minimize the number of travel and labor touchpoints. It will help us avoid congestion and traffic jams as much as possible, ensuring that movement occurs logically.
There are three types of flow warehouses that companies can use. The most common one is the U-shaped flow, which makes it easier for warehouse traffic to move smoothly.
Furthermore, we can automate all of our company’s business processes by using an ERP system. Impact ERP also includes a WMS module that reduces waste and streamlines the picking process. In addition to the WMS module, ERP has various other modules, such as inventory, accounting, sales, and HCM.
Richard G. 2011. Warehouse Management. Great Britain: Kogan Page Limited.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

Welcome to the next chapter of our SEO guide! In the previous chapter, we learned about technical SEO, which is all about making your website better for search engines. Now, we will talk about another important part of SEO: off-page optimization.
When we say “off-page optimization,” we mean things you do outside your website to make search engines see you as trustworthy and reliable online.
In this article, we’ll explain why off-page SEO is important and share five effective strategies that can help. Our main focus will be on link-related off-site SEO. We’ll teach you about creating a good link profile and show you what to avoid when building links. These strategies will help you build authority and improve your website’s rankings in search engine results.
Off-page SEO, or off-site SEO, means optimizing your website beyond its pages to boost its rankings and visibility in search engines. You achieve this by getting other respected websites, pages, and people to link to or promote your website, which acts as an endorsement for the quality of your content.
Off-site SEO is different from on-site SEO. On-site SEO is all about optimizing the content on your website. You can observe the variations in focus through the image provided below.
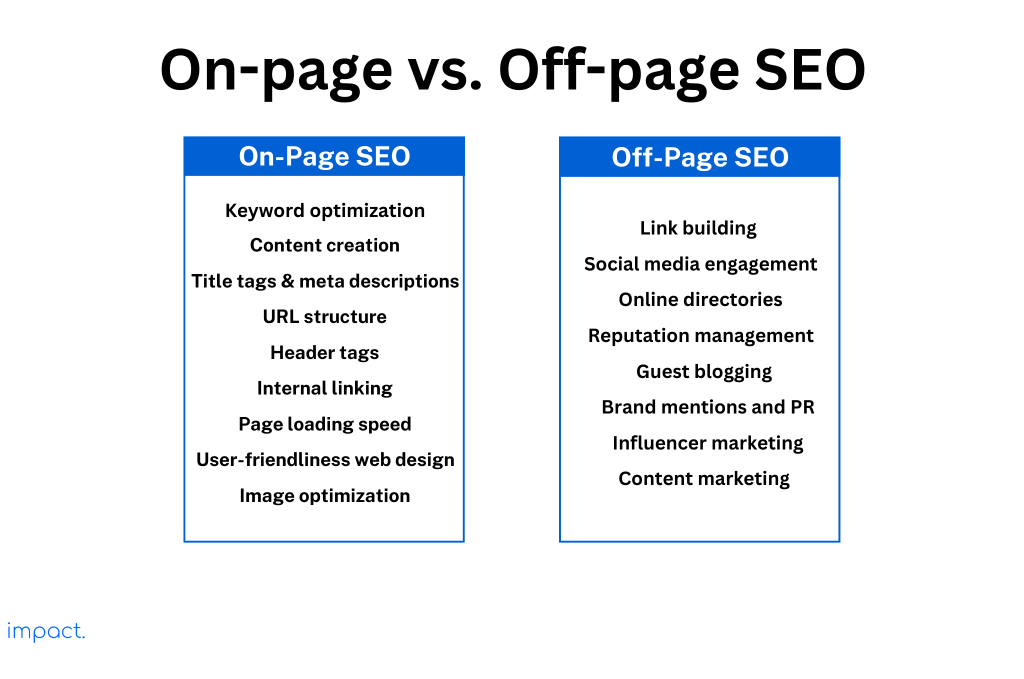
Read more: On-Page SEO: Key Components and 4 Mistakes to Avoid
By doing off-page SEO activities, you can make your website more popular and reach more people. It helps your website rank higher in search engines and makes it more visible online. Here are some reasons why off-site optimization is important:
Earlier, we explained off-page SEO as things done outside a website to boost its search engine rankings and make it more visible online. Now, let’s look at some popular off-page SEO strategies you can use.
Link building is important to improving your website’s visibility and credibility. It means getting other websites to link to your site, called a backlink. According to search engines like Google, these backlinks are like votes of confidence or endorsements for your content.
When reputable and relevant websites link to your site, it tells search engines that your content is valuable and trustworthy. However, not all backlinks are the same. Quality matters here. Backlinks from authoritative websites have a stronger impact on how search engines rank your site.
It’s essential to focus on acquiring high-quality backlinks to truly enhance your website’s SEO performance. This can be achieved through various link-building strategies, each tailored to create a diverse and robust backlink profile. Some effective link-building efforts include:
Content marketing is all about creating and sharing great content that is useful, interesting, and engaging for your specific audience. The idea is to consistently produce informative and engaging material that can bring organic visitors to your website, increase your visibility on social media, and earn natural backlinks from other sites.
There are many different types of content you can use for content marketing, such as blog posts, articles, videos, infographics, ebooks, and podcasts. The main objective is to offer valuable information that caters to the needs and interests of your audience, establishing your website as a trusted source in your industry.
Read more: Content Marketing: 7 Steps to Strategize for Success
Guest blogging or posting is a strategy where you write for other websites in your industry or niche. It’s a way to promote your content and establish yourself as an expert. When you contribute a guest post, the website editor often highlights you as a guest author. This strategy helps you reach a new audience and build relationships with other website owners.
When you write a guest post, you include a brief author bio that links to your website. It brings traffic to your site and improves its authority and visibility in search engines. Guest blogging is a content marketing tactic that can benefit your online presence and increase your website’s credibility.
Social media marketing uses platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, and others to promote your content, interact with your audience, and raise brand awareness. Google confirms that social signals don’t affect rankings, but they can help expand the reach of your content.
Think of social media as discovery platforms that expose you to potential customers. Sharing and engaging with your content on social media can drive traffic to your website, boost brand visibility, and potentially lead to conversions.
Read more: Social Media Marketing: A Guide & 3 Strategies for Success
Brand mentions, and PR activities are important for your website’s online visibility and reputation. When your brand is mentioned or discussed on different online platforms, it can create awareness, increase website traffic, and get backlinks.
PR efforts like press releases, reaching out to the media, and collaborating with influencers or industry experts can boost your brand’s message, grab media attention, and earn valuable backlinks from credible sources. These activities increase your website’s authority, build a positive brand image, and attract organic traffic.
Local SEO is a vital off-page SEO strategy to boost local traffic, visibility, and brand recognition. While Local SEO constitutes a distinct SEO domain, some of its elements align with off-page tactics, such as Google Business Profile (formerly known as Google My Business) and NAP citations.
Google Business Profile is a no-cost business listing tool that enables you to shape your Google presence. As this occurs beyond your website, optimizing your profile becomes a pivotal off-page SEO approach.
It’s crucial for local SEO rankings, enhancing your website’s prominence on Google’s search results pages. Consider, for instance, a search like “plant store near me,” where optimizing your Google Business Profile could secure a prime spot in the map pack.
Link building is the main strategy that we will use in our off-site optimization efforts. To start, you must understand what a link is.
An inbound, backlink, or external link is a clickable connection between two websites. It’s equivalent to a virtual reputation currency that holds great online significance.
Similarly, internal links are connections between different pages within the same website. They work equally for your site. If you have many internal links pointing to a specific page, it signals to Google that the page is important. However, it’s important to ensure that these links are created naturally and not in a spammy manner.
A ‘good’ link is one that follows Google’s rules and helps improve how a website appears in search engine results. It makes the site more trustworthy, easier to find, and boosts its overall SEO performance. Here are the factors that determine a good link:
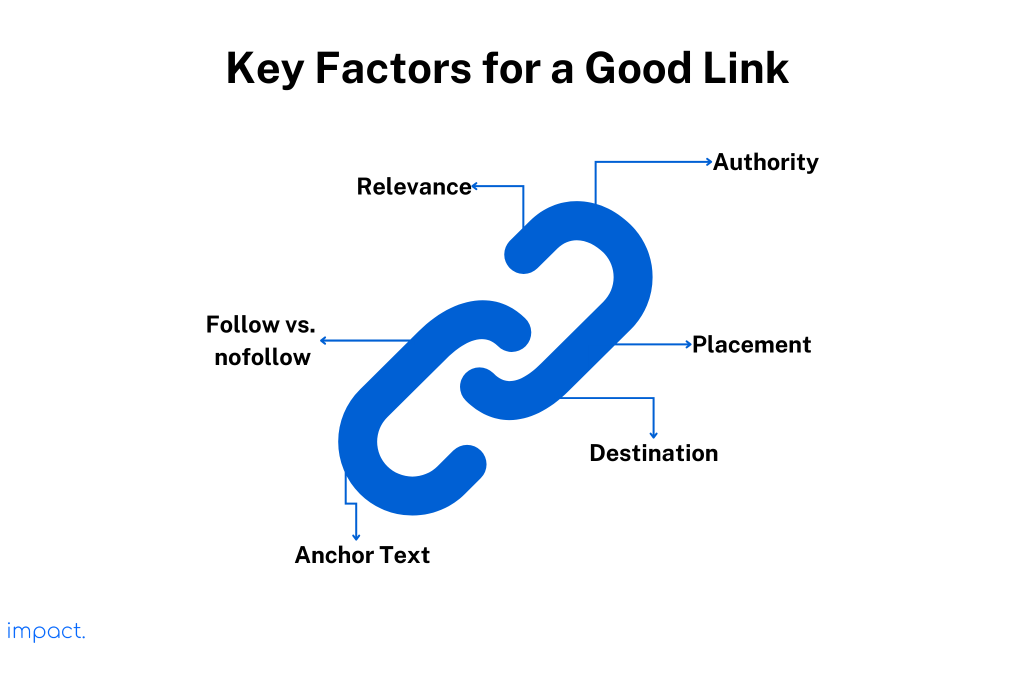
The authority of the website that links to your page is paramount. A good link comes from a website that is trustworthy, popular, and has a strong reputation. Regarding search engine rankings, links from high-authority domains have a greater impact. Let’s take an example to illustrate this point.
A link from a reputable source like Harvard Business Review can significantly boost your website’s search engine ranking. On the other hand, links from less credible sources, like your friend’s blog, may not have the same impact.
Search engines like Google view links as “votes” influencing a page’s ranking. A page with strong votes from high-authority domains will have a stronger influence than a page with no or weak votes. So, it’s important to aim for quality links from reputable sources to boost your website’s visibility and improve its search engine rankings.
A good link matches the content of the website it connects to. It should come from a source that relates to the topic or industry of the linked website. Search engines view links as more important and valuable when links are relevant.
For example, let’s say you have a business website that provides tips for entrepreneurs. Getting a link from a trusted business publication or industry blog is valuable for your content. On the other hand, a link from an unrelated website, such as a cooking blog, would have less impact because it doesn’t align with your business-focused content.
The text you click on to go to another page is called anchor text, and it affects the value of a link. Good anchor text should accurately describe what the linked page is about. It’s important to avoid using overly optimized or spammy anchor text because it can harm your search rankings. Instead, aim for a natural and varied distribution of anchor text to impact your website’s visibility positively.
Regarding links, there are two types: “follow” and “no follow.” A good link is a “follow” link. It’s like a thumbs-up from search engines, telling them to pay attention to this link when ranking websites in search results.
On the other hand, we have “no follow” links. These links don’t have the same impact on search engine rankings. They can still bring traffic to a website, but they don’t directly affect how search engines rank it.
Generally, going for “follow” links is better because they have more weight and make a stronger impact. These are the links that can boost your rankings.
However, it’s still worth considering if you find a relevant and trustworthy page that offers a “no follow” link. Even though it won’t directly affect your rankings, it can still be beneficial in driving traffic to your website. So, don’t overlook the opportunity if it fits your website well.
Where you put a link on a page can make a difference. It’s important to consider the placement of the link because it can affect the number of people who click on it, known as the Click-Through Rate (CTR).
When it comes to placing links, there are some best practices to keep in mind:
On the other hand, there are places where it’s generally not recommended to put links:
When you add a link to your website, the link’s destination must be useful and related to what you’re talking about. There are three main places where you can direct your links:
Avoid broken or low-quality links as they harm the user experience and SEO performance. Good links direct users to high-quality content.
Regarding off-page SEO techniques, it’s crucial to avoid common mistakes that can negatively impact your website’s ranking and reputation. Here are four key points to keep in mind:
Avoid buying links or joining schemes that promise quick results. Search engines, like Google, don’t like these practices and can penalize your website. Instead, focus on building good links naturally by forming genuine relationships, creating valuable content, and reaching out to others.
Be careful not to overdo it with your anchor text. Anchor text is the clickable text in a hyperlink. When you use the same keyword or phrase over and over again as your anchor text, it can make search engines suspicious, and they might penalize your website. Instead, try to use a variety of anchor texts that describe the content of the linked page in a natural way.
When it comes to link building, not all links are the same. Getting links from low-quality or unrelated websites can harm your off-page optimization strategy. Concentrating on getting links from trustworthy sites related to your industry or topic is important. Quality is more important than quantity when it comes to building links.
We use redirects to guide individuals from one web address to another. Misleading redirects are when you trick people or search engines by sending them to a different page than they expected. This method can make people unhappy and harm your website’s reputation. Ensure your redirects are clear, relevant, and done correctly to avoid this.
Off-page optimization is an important part of SEO that goes beyond your website. Boost your website’s authority and search engine rankings with off-page SEO. Try these five strategies: link building, content marketing, guest blogging, social media marketing, and brand mentions. See the impact on your online presence.
One important thing to remember is the value of having good links to your website. When other relevant and trustworthy websites link to your content, it shows reliability.
To build a good link profile, think about the words used in the link (anchor text), whether the link is a regular one or a special kind (follow vs. nofollow), where the link goes, and its placement.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

The warehouse is significant in manufacturing and supply chains because it stores everything from raw materials to finished products. You must have up-to-date information about the warehouse’s conditions to manage it well.
Today, companies need ways to exchange data quickly and safely for their warehousing needs because customers want modern solutions. That’s where a Warehouse Management System (WMS) can help. It automates warehouse tasks and makes them easier to see.
Now, let’s talk about a Warehouse Management System, its advantages, and how to pick the right one for your business.
The Warehouse Management System (WMS) is software that helps organizations control and manage their warehouses. It takes care of tasks like receiving goods and sending them out. WMS improves visibility and assists with managing the supply chain from distribution centers to stores.
The main goal of the WMS is to make sure that goods and materials move through the warehouse efficiently and at a low cost. It handles different jobs like keeping track of inventory, picking items, receiving goods, and storing them.
WMS can be used independently or as part of an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system. It supports the latest warehouse technologies like automation, RFID, and voice recognition.
Currently, companies can rent the WMS monthly using Software as a Service (SaaS) and Cloud computing. This system makes it more affordable because you pay for what you use, share resources, and use only the features you need.
Read more: Understanding Warehouses: Definition and its Importance
Incorporating a Warehouse Management System (WMS) into your operations brings many advantages. It not only makes your business more competitive but also helps you meet the increasing demands of customers. A good WMS must work in real-time, manage all warehouse processes, and communicate with other company systems.
A reliable WMS should process data quickly and coordinate movements within the warehouse. It helps companies generate reports and handle large amounts of transactions, like those found in e-commerce.
Here are some of the potential benefits of using a WMS for your company:
Trade isn’t just about goods; it’s about information. Goods stay in warehouses until information tells us what to do with them. So, having good knowledge of the warehouse is crucial.
The diagram below, known as the Tompkins diagram, shows how having good information can help increase sales and lower costs.
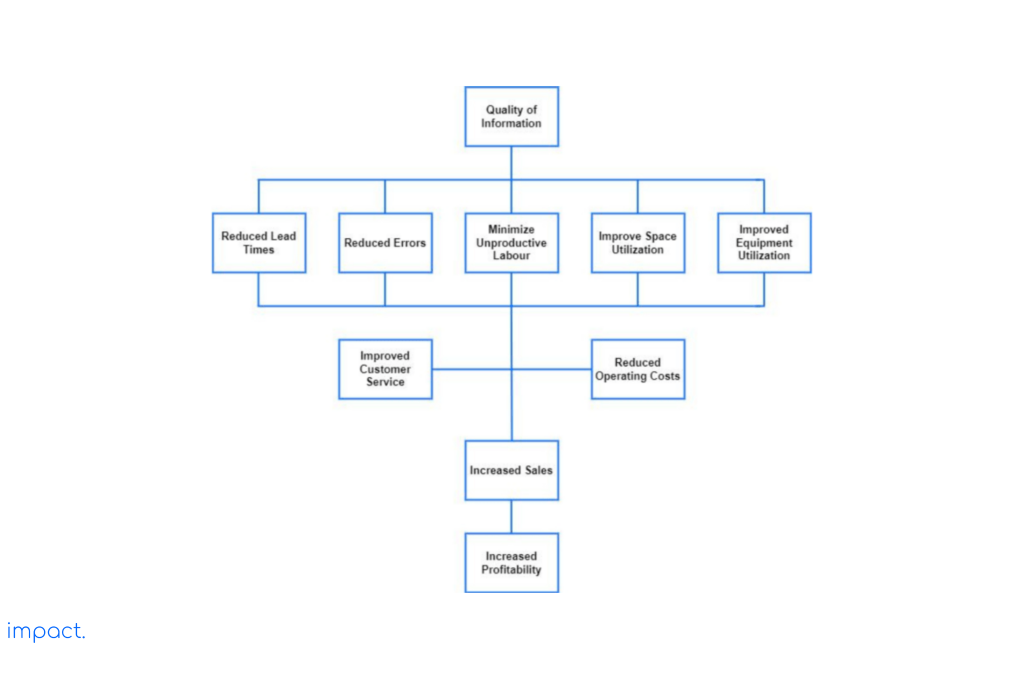
When picking the right WMS for your company, first understand your company’s needs and main business requirements for the future.
Know your company’s strategy and ensure the chosen solution aligns with your business goals. Calculate the Return on Investment (ROI) for the WMS purchase.
To make sure you choose the right system, follow some helpful guidelines from the Business Application Software Developers Association (BASDA) (2009) and Sage Accpac (2005).
Here are seven steps that you must fulfill to get the most suitable WMS for you:
Gather a group of people who are good at logical thinking. This team will figure out what the company needs from a Warehouse Management System (WMS) and what features it should have. The unit can include people from finance, sales, production (if there are any), IT, and warehouse departments.
Once you form the team, choose a leader for the project and decide on the roles, responsibilities, and how much each person will be involved in making decisions and setting the timeline for this process.
The next step is to gather and compile as much information as possible about the company’s current processes and procedures. After completing that task, the team must actively review each method and determine its necessity.
Don’t automate processes that don’t work well. Involve the project team and warehouse staff to determine which methods they find frustrating, wasteful, or inefficient.
You should understand which processes to improve with a Warehouse Management System (WMS). Understand how warehouse staff communicates internally with other departments and externally with customers, suppliers, and transportation companies.
The project team must individually identify and prioritize the essential functions needed for the system. All team members must collaborate and create a list of basic requirements that we agree upon. We will include these requirements in a Request For Information (RFI).
This list should include a crucial function considered a ‘must-have.’ It will help swiftly eliminate systems that fail to meet the fundamental requirements.
To make informed decisions about your WMS, you must think about what might happen in the future. It’s not easy to predict the future, but there are some things you should consider.
For example, do you plan to have more SKUs in the next few years? Will your upcoming surgeries involve “kitting” procedures? Which systems will you need to work together with? These things will help you decide what’s best for your WMS.
Having the right Warehouse Management System (WMS) can help you make the most of your workforce, space, and equipment while improving accuracy. It is crucial to compute and incorporate these advantages in the ROI report to show the worth of your investment.
In Indonesia, many companies provide WMS (Warehouse Management System) services. Each company has its own differences and unique features. One of these companies is Impact, which also offers consultants and comparative data for different WMS options.
Before starting a bidding process, talking to several vendors and visiting their operational locations is a good idea. Direct discussions with users will give you a better understanding of the system’s abilities. They might even change your thoughts about it.
Before you decide on an offer, involve your financial partner in calculating the potential return on investment. The ROI calculation will help determine how much money you can make from the opportunity.
Also, consider the following things, as suggested by Stephen Cross (2010) from ATMS:
You can divide WMS costs into the following different parts:
Kindly request suppliers to indicate whether their prices are fixed or can vary. Be careful about additional costs that might not be obvious, such as travel expenses, time spent on travel, and project management time. Make a spreadsheet to summarize all the costs, starting with the initial payments and including fees for each year from year 1 to year 5, along with the total accumulated amount.
Remember that specific systems seem attractive at first glance. Still, calculating the costs over a more extended period could be significantly more expensive.
To achieve effectiveness, a Warehouse Management System (WMS) must include the following components, as stated by Ruriani in 2003:
The system must work well with accounting software, ERP and MRP systems, and transportation management systems. It should also be able to connect with tasks in the back office, such as order entry, inventory control, purchase orders, and invoicing.
Additionally, the system must be compatible with automation systems, conveyors, material handling equipment (MHE), and modern picking technologies like voice commands, wearable scanners, RFID, and pick-and-put-to-light systems. We should make sure that these connections won’t cost too much.
A modular system is an excellent choice because you only pay for the needed features. It also means you can get up and running faster with training and implementation. Plus, you have the option to add more features later.
On the other hand, buying a system with more features than you need will only cost you more for training. It will waste your time and, as a result, give you less value for your investment. So, avoiding unnecessary features and focusing on your needs is best.
Given the current staff mobility, the system must enable remote access through the web and ensure secure password protection. The system should prioritize critical functionalities such as generating performance reports, modeling service costs, and conducting standard inventory queries.
Opt for a WMS (Warehouse Management System) that is easy to use. Look for a system with a simple point-and-click interface that is easy to understand. Your staff can work more efficiently and accept the system more readily. Ensure the technology operates in real-time and provides instant updates on inventory.
If you’re involved in storing customs and excise goods, ensure that the relevant authorities approve or can approve the system you use. Additionally, ensure the system can perform essential tasks for your business, such as tracking lot and serial numbers (if needed), managing expiration dates, identifying dangerous goods, and calculating royalties.
According to BASDA, to achieve the best practices in warehousing, the system should be capable of optimizing movement within the warehouse. It involves effectively combining pallet placement and picking, known as task interleaving.
Ideally, the system should track the speed of goods in the warehouse and arrange them accordingly (slotting). It should also provide data in a format that transfers easily to a program with a slotting function.
Ensure the system has a complete set of reports and can report any failures.
The success of your project, like many other extensive service offerings such as outsourcing, depends on how well you get along with the people at the software company.
That’s why it’s essential to meet the salespeople and others who handle the day-to-day operations and support. When you’re choosing a partner or vendor, here are some critical things to look for:
Before you make a final decision, ask the WMS provider to share a detailed plan for putting the system in place. This plan should include a timeline for installation and the resources needed.
Here are some important rules to follow when implementing a new system:
Having real-time data is crucial for effective warehouse management. It helps increase speed, productivity, and accuracy. You can use a Warehouse Management System (WMS) to achieve this.
Before implementing a WMS, there are a few steps you need to consider. First, form a project team and choose a vendor. Then, select the features that best suit your needs. Choosing the right WMS can improve your company’s efficiency and productivity.
Another way to streamline your company’s processes is using an ERP system. ERP Impact offers a WMS module that reduces waste and simplifies picking. In addition to the WMS module, ERP includes other helpful modules like inventory, accounting, sales, and HCM.
Richard G. 2011. Warehouse Management. Great Britain: Kogan Page Limited.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.
