Kanban: Definition, 6 Rules, and its Benefits
Kanban is a crucial part of the Just in Time (JIT) system, which we discussed…
Sean Thobias
May 17, 2025After picking, the warehouse performs other tasks. These tasks include replenishing inventory, providing value-added services, and delivering products. Additionally, this article will discuss how the stock is managed and calculated and the importance of keeping the warehouse clean and organized.
Read more: Understanding Warehouses: Definition and its Importance
To ensure a smooth and efficient picking process, it is essential to always maintain sufficient product availability at the picking locations. Replenishment is crucial in restocking those locations, benefiting the pickers by saving time and reducing costs.
Right now, a system called WMS gives real-time information about when and where replenishment is needed. It can also tell how many orders there are, so the restocking can be done before the next batch of orders arrives.
Replenishment is crucial because late replenishment can lead to space shortage and non-compliance with the “first in, first out” (FIFO) rule. Moving products directly from the picking area to the restocking area is preferable to ensure enough space, but planning is necessary.
If there’s no system like WMS, the warehouse manager needs to make sure they have planned how much of each product to have available based on how much they expect to sell and how much space they have. They must also train the staff to recognize when restocking is needed and tell their supervisors or forklift truck drivers.
There are different ways to make this process faster, like combining multiple places where the same product is picked, using unique shelves where restocking is done from other aisles, or scheduling different tasks for different times of the day. For example, they can refill in the morning and pick up in the afternoon.
Read more: 9 Vital Warehouse Processes You Need to Know
Let’s examine the crucial factors of stock replenishment. Here are five factors you must consider:
Several warehouses currently offer value-adding services in dedicated or co-owned warehouses. Third-party logistics companies provide these services to their customers. The value-adding services include:
In addition to the mentioned services, more advanced tasks involve production processes. For instance, after a customer orders, these services include adding components such as a graphics card and installing software on personal computers and laptops. Value-adding services also encompass handling returns and providing repair services.
To efficiently perform these activities, having enough space near the dispatch bay is essential to minimize unnecessary movement. The ideal location is a warehouse with a height that allows placement above the dispatch bay, typically on the mezzanine floor.
Support activities in a warehouse are essential for making processes more efficient. These activities, carried out by supervisors, specialized teams, and housekeeping teams, include:
You can group these activities into three sections:
The warehouse manager guides inventory staff in determining the appropriate safety stock level and handling procedures for goods. Managers also actively identify items that suppliers can ship directly without requiring storage. Here is the classification table:
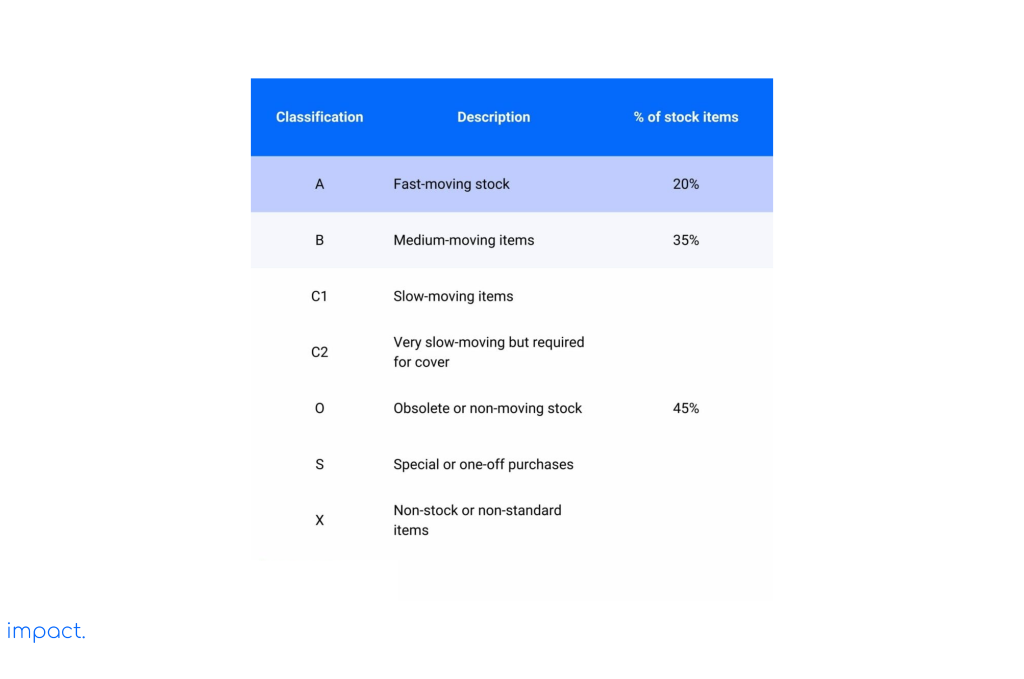
Read more: Warehouse Manager: Roles and 10 Challenges to Overcome
To quickly and efficiently handle slow-moving excess stock in a warehouse, follow the formula below:
| Stock turn = cost of goods sold ÷ average cost of goods stored |
Or
| Stock return = Annual throughput in units ÷ average number of units held in stock |
Suppose a company sells 1,200,000 units annually and keeps an average of 100,000 units in stock. In that case, they replace its stock 12 times yearly or once a month. This calculation means the inventory stays in the warehouse for too long, and the company has set too high safety stock levels.
Here are some examples of stock turnover rates in different industries:
This example shows that higher numbers mean better company performance. The maintenance shop always keeps low stock because it needs to have some on hand if something breaks down.
Doing a complete stock count requires closing the warehouse for a certain period. During this time, the warehouse stops receiving or sending out any items. Companies perform this task annually, usually at the end of the year. However, some companies do it more frequently, either every three months or once a year, depending on the auditor’s instructions.
The auditor will agree to conduct a yearly stock count and audit based on the company’s requirements, provided that the company can prove the reliability of its ongoing calculations. When the estimates are accurate, the Warehouse Management System (WMS) will give the final stock numbers for the year.
When performing cycle calculations, it’s better to use ABC analysis to ensure you count fast-moving, high-value items more often than slow-moving, low-cost items. Here’s a recommendation: measure fast-moving, high-value items every month and slow-moving goods once or twice a year.
To ensure comprehensive calculations, you can use the following percentages as examples:
Increasing the frequency of daily counting will give you more accurate calculations. However, it depends on the available resources and their costs. You need to consider the trade-off between the cost of potential errors and the cost of identifying those errors in the first place.
Warehouse managers have a crucial responsibility to ensure the safety and security of products, regardless of ownership. They accomplish this by taking good care of the products, implementing security measures, and promoting a vigilant staff. Effective security management prevents inventory loss, reduces insurance costs, and minimizes personnel turnover.
Securing the loading dock and platform areas is paramount as they are vulnerable spots for outsiders to steal items. While traditional security systems focus on external threats, it is now essential to address internal theft within the organization.
Installing closed-circuit television (CCTV) at strategic locations in the warehouse is highly beneficial to maintain security. Conducting routine inspections and patrols proves cost-effective and practical. Boosting protection in loading bays can be achieved by separating them from employee parking areas, making it harder to remove goods. Implementing thorough checks of incoming and outgoing goods through staff or a system effectively prevents losses.
Protecting crucial warehouse management system (WMS) data requires specific measures. Using strong passwords and external firewalls to control access and enhance security is vital. Regularly backing up the data and storing backup files in a separate location is critical.
Secure equipment like servers, computers, and laptops for theft prevention and data security. Lock these devices with keys or access codes and regularly update passwords on personal computers. Here are essential security measures for warehouses:
The return or reverse logistics process includes different steps, such as managing product returns, handling transit packaging, and dealing with excess goods. Take a look at the image below to see the other steps involved:
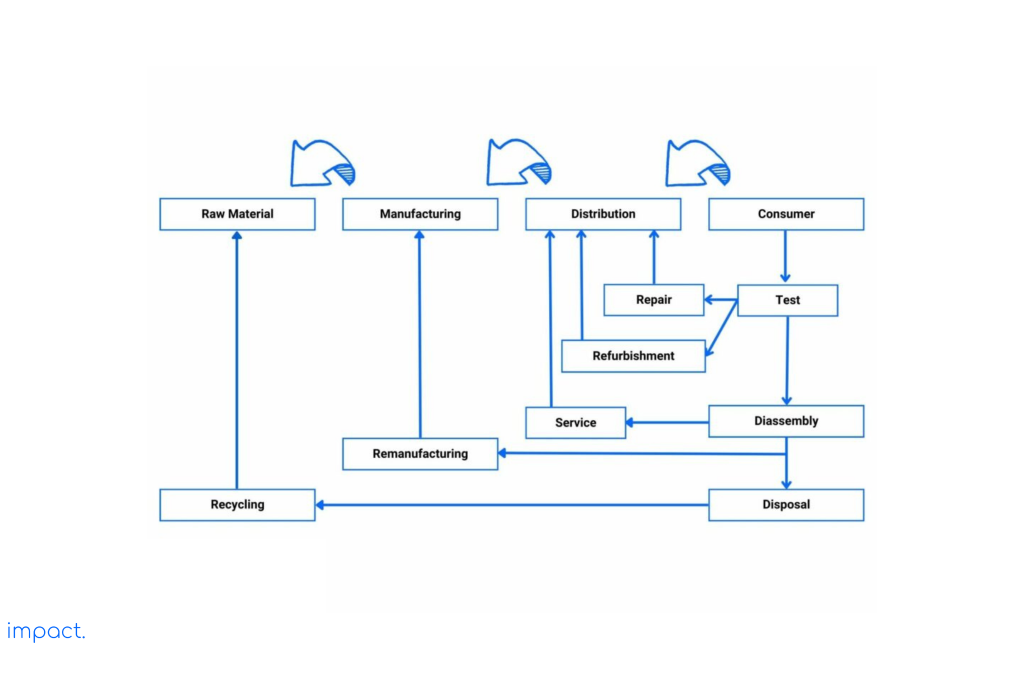
Companies must prioritize handling returned goods to avoid unnecessary costs. Leaving these items in the warehouse leads to problems: they take up space, complicate stocktaking, and make valuation difficult. Companies can resell the products and restock them at a cost to deal with this.
The increase in e-retail has also led to more returns. The most commonly returned items are textiles and clothing. Customers with a 14-day return option frequently return high-quality items that we can quickly put back into stock.
Companies should handle product recalls with care. They must quarantine the products to ensure public safety, avoid mixing them with good products, and mistakenly send them out. The latest laws impose expensive landfill fees, prompting many warehouses to implement reverse logistics programs and establish special warehouses to manage returns.
Companies establish special warehouses dedicated to sorting, inspecting, repairing, and disposing of returned goods. The objective is to swiftly reintegrate stock into the supply chain, whether as finished goods or spare parts or dispose of them effectively. When conducting the return process in an existing warehouse, it is crucial to handle it with caution to prevent any mixing with other goods.
Before deciding on a reverse logistics operation, you need to calculate several things, such as:
Once you have these calculations, you can choose between handling the reverse logistics internally or subcontracting to a third party. The decision depends on the following factors:
Regarding disposal, companies must obtain certification to prove proper disposal of non-recyclable products and packaging.
Read more: 7 Warehouse Picking Methods: How to Choose the Right One
Effectively managing and coordinating the shipping process with other warehouse activities is essential. When the receiving and shipping operations utilize the same door, it is crucial to establish a daily schedule that optimizes labor and equipment utilization. It is necessary to adjust the workload according to the number of available doors To avoid congestion.
Loading bays in warehouses need enough space for cargo and various inspections. Coordinating well ensures that there is a correct delivery sequence for orders. As a result, the final delivery loaded onto the vehicle is given priority during the unloading process.
Many companies use a marked grid on the warehouse floor in the shipping area to determine the maximum vehicle area that can fit. For example, a warehouse that handles industrial pallets may have a grid equivalent to 26 pallets. A warehouse with euro pallets may extend it to 36 pallets. This process helps separate and quickly identify orders when a vehicle carries multiple shipments.
Ready-to-ship full pallets are picked up from the rack area and loaded onto vehicles. Just like during the receiving process, checking the driver’s documents to ensure they are transporting the correct cargo is essential. Additionally, trailers undergo inspections to ensure they are clean, watertight, and free from odors that could contaminate the product, have the right temperature, and their floors are undamaged.
Some companies want drivers to help load and check the cargo. In contrast, others worry about safety when having external workers in the loading area. If it’s the latter case, the driver should go somewhere else.
Furthermore, let’s address what the driver should do after loading the cargo. If the driver personally witnesses the loading process and the vehicle is sealed before leaving the loading area, they can sign the document. If the truck is sealed, write down the seal number on the shipping document and provide the driver with additional paperwork, such as a hazard datasheet.
Receiving and picking are important tasks in a warehouse, but replenishment and dispatch are equally essential. Timely replenishment ensures efficient picking, while accurate, timely delivery satisfies customer expectations.
The warehouse’s ability to provide added-value services allows manufacturers to postpone certain activities until orders arrive. This postponement reduces the number of stock codes. It enables retailers to return actions to the warehouse, saving travel time. Maintaining accurate stock count, ensuring security is crucial for product integrity, and maintaining trust in internal and outsourced warehouse operations.
Richard G. 2011. Warehouse Management. Great Britain: Kogan Page Limited.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

Barcodes, voice technology, and pick-by-light systems have made picking goods in warehouses faster and more efficient. These advancements are also considered valuable investments.
Today, warehouses use various methods to pick up goods. This article will discuss the most popular picking methods currently in use. We will build upon the information from the previous article, which covered the equipment used in the picking process.
Read more: Understanding Warehouses: Definition and its Importance
When it comes to selecting items from a warehouse, there are several picking methods that companies employ. These methods vary in efficiency, complexity, and suitability for different types of operations. Let’s explore seven typical ways for warehouse picking:
If there is a mistake, write it on the selection list immediately. The supervisor will check it and find another place to get the item if insufficient. Ensure that you write neatly and correctly because you must enter the choice details by hand into the system.
Put the fast-moving things close to where they will be delivered to save time. To do this, people must help and change how things are collected. The people organizing the items will use carts, cages, and machines like forklifts to help them.
The paper with the list of things to collect usually have the order number, code, description, and how many items are needed. The system will show the details of each item in order so that the collection process will be fast and smooth.
We use a list of labels printed on sheets in the pick-by-label method. We organize the tags in the order of item selection. The picker attaches a label to each item and returns any
unused labels. If there are any mistakes, we promptly check them and print more labels if stock is available elsewhere.
People play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy of the recorded information in this method. As a result, we increasingly utilize technology to enhance warehouse management.
Read more: 9 Vital Warehouse Processes You Need to Know
Warehouse management widely uses the pick-by-voice method, particularly during the picking process. Here’s how it works: the operator wears a headset, microphone, and a small computer attached to their belt. The computer receives messages from the warehouse management system (WMS) through radio frequency (RF) transmission.
Here are the benefits of using sound technology:
In a survey conducted in 2007 by the ARC Advisory Group and Modern Materials Handling magazine, almost 60% of the people who participated said that using sound technology helped them increase productivity in the picking process by more than 8%.
Additionally, over 83% of the companies that tried this technology reported that it met their goals. The image below shows other advantages of using sound technology when picking up goods.
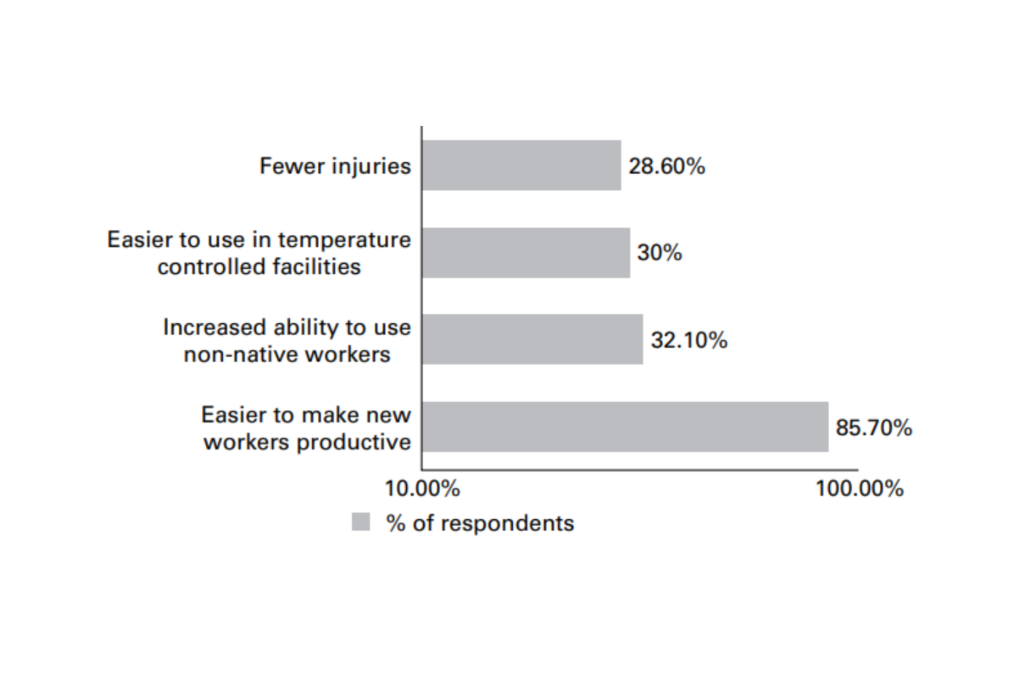
Source: Warehouse Management; Benefits of voice picking
Pick by voice is now commonly used in the food industry, especially in cold and frozen environments. It offers advantages over paper lists, labels, and barcode scanning because it allows for a hands-free approach. This method of picking goods also improves accuracy for companies.
Improving accuracy can significantly impact your returns. Let’s consider a warehouse that handles half a million cases per week. It has an accuracy rate of 99.8% (resulting in 52,000 errors per year, or 2 per 1000). However, by increasing the accuracy to 99.96% (reducing the errors to 41,600 per year, or 0.4 per 1000), the total savings would amount to £624,000, assuming each error costs around £15.
Companies that have invested in voice systems have seen accuracy rates improve by over 99%. Additionally, they have reduced staff turnover and training time. The image below demonstrates how sound technology can simplify picking, increasing productivity and accuracy.
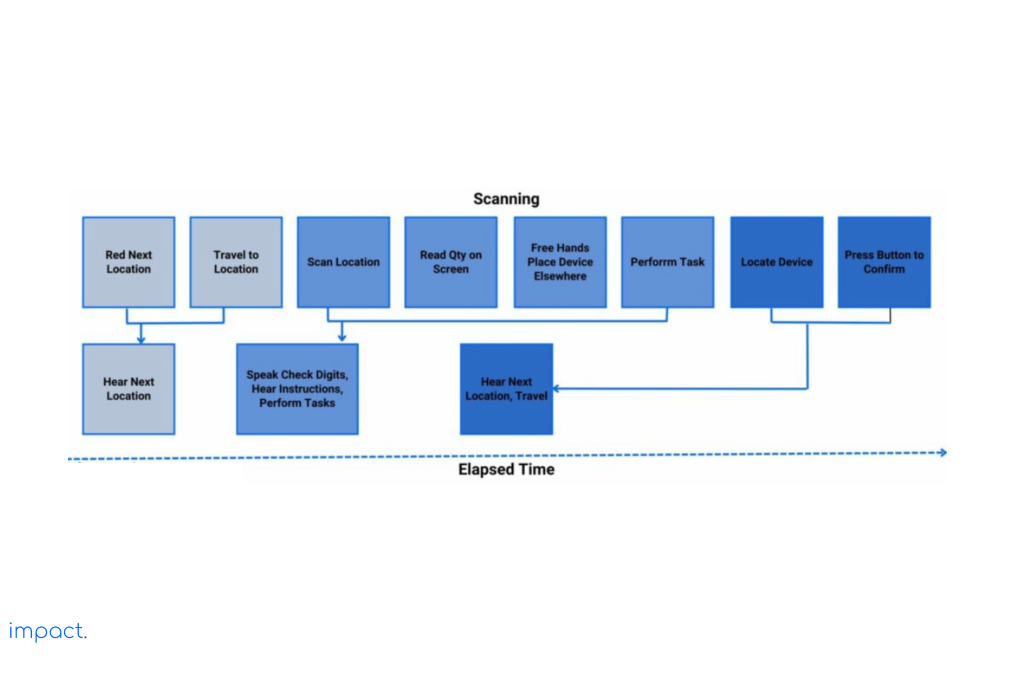
Barcodes comprise different vertical bars in different sizes for letters, numbers, and other symbols. They are commonly used to identify products, mark warehouse locations, label containers (like totes, cartons, and pallets), track serial numbers and organize batches. Two two-dimensional barcodes, like the one shown below, can store more information in a smaller space.

Barcode scanners come in different types: handheld, static, or wearable. Handheld scanners have screens and triggers that decode barcodes, store the data, and send it to the computer. They can read different types of barcodes, and some PDAs and cell phones now also have barcode scanners.
To access the scanner’s data, you can connect it to a computer using a USB cable. Alternatively, you can transfer data in real-time using RF technology. Using handheld scanners helps warehouses collect data faster and more accurately, which boosts productivity.
However, handheld scanners have some drawbacks. Operators must set up the scanner, and placing the scanner on a surface often leads to errors. This movement can cause mistakes in item counting or misplaced items. Companies use stationary scanners that read barcodes as they pass through a conveyor to address this issue.
Advancements in technology allow operators to use both hands by holding a barcode scanner, paper, or roll labels simultaneously. Wireless-enabled computers help operators receive instructions in real-time. These computers, with screens and tiny keyboards, are usually worn on the wrist.
Companies favor wearable equipment that workers can easily adjust and install. The wearable devices are lightweight, ensuring they do not cause discomfort. Utilizing wearable devices speeds up the picking process, reduces errors, and enables significant cost savings.
Let’s say there’s a warehouse with 20 pickers who handle 100 cases per hour (based on eight hours/day, 253 days per year). With an accuracy rate of 99.5%, would be 20,240 errors in a year. However, if the accuracy improves to 99.8%, the number of errors decreases to 8,096. Assuming each mistake costs £15, that adds up to annual savings of £182,160.
Computers can also have user-friendly touch screens and dual imaging. Some can even be voice-activated, which improves picking accuracy. Barcode scanning offers other benefits, too, such as better customer service, shorter training time, fewer accidents and damages, increased employee satisfaction, and more. However, it’s important to note that barcodes can be damaged easily, which makes scanning difficult and may lead to inaccurate information.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a way to identify items using radio waves. It involves exchanging data between tags and readers using specific frequencies. Library books, toll tickets, and identity cards commonly use RFID.
There are two types of RFID tags: passive and active. Passive tags don’t need their power source, can store limited data, and can only be read. They also have a limited range. On the other hand, active tags have their power source, can store more data, can be read and written to, and have a more extended range.
Passive tags store basic information and rely on a database for more detailed data. For example, in a sorting system, they can identify items and get instructions from a database about where to send them. Active tags have more capacity and can update an item’s status after completing a task. Still, they have a shorter range for writing data.
Regarding cost-effectiveness, it’s better to use RFID for identifying groups of items rather than individual items. Tracking things like roll cages, pallets, and reusable packaging (totes, barrels, and trays) becomes more accessible and affordable with RFID.
One challenge with RFID is that barcodes are cheaper to produce, so they’re still widely used for item identification. Additionally, the cost of running an RFID system depends on factors like the specific application, size of the installation, frequency used, and the number of tags needed.
To implement the RFID application, you will need the following items:
However, there are some drawbacks to using RFID:
Pick to light, also called pick by light, uses light indicators attached to racks, flow racks, pallet racks, or other storage locations. The process starts by scanning a barcode on the tote or shipping carton to indicate the order number. Then, the system sends a message to the operator’s zone, and the pickup location lights up according to the instructions.
Implementing pick-to-light boosts productivity and requires simple training, making it easy to adopt. Many companies already use portable pick-by-light methods to move goods efficiently in the warehouse. Regarding system integration, pick-to-light is uncomplicated; you must download a file with the order number, product code, location, and quantity.
However, this type of goods picking has some downsides. A potential issue is that the scanner needs to be positioned accurately by the operator, as scanning surfaces that are not even can lead to errors.
This drawback can result in the picker going to the wrong location or miscounting items. To address this issue, we now use stationary scanners to read barcodes as they pass through the conveyor, which reduces these challenges.
The Warehouse Management System (WMS) gathers all store orders based on location or delivery time from the distribution center (DC). The goal is to ensure that each store group receives equal products. The staff can adjust the number of locations they handle based on the daily volume.
The required product lines are gathered in large quantities to fulfill store orders and given to operators. Operators use baskets, pallet trucks, or conveyors to move the items. They know where to place items with the aid of a flashing light.
The system immediately sends the confirmed ‘put’ results, updating the information in the WMS in real-time. When using pick-to-light or put-to-light methods, setting up a central processing area to create new layout designs and introducing additional equipment if needed is essential.
To utilize put-to-light technology, you must combine orders and select products in batches. If you don’t receive complete cases of products, you must return pallets or casings to stock. The pack or put-to-light approach can effectively integrate with cross-dock operations, where you receive, place, pick up, and ship goods on the same day if needed.
The table below shows different picking methods in warehouse management. In Part One, there is a single-picking process where the picker collects all the items for an order and then moves them to ship. The picker can choose items from a lower shelf or, if there are many different items, from a higher shelf.
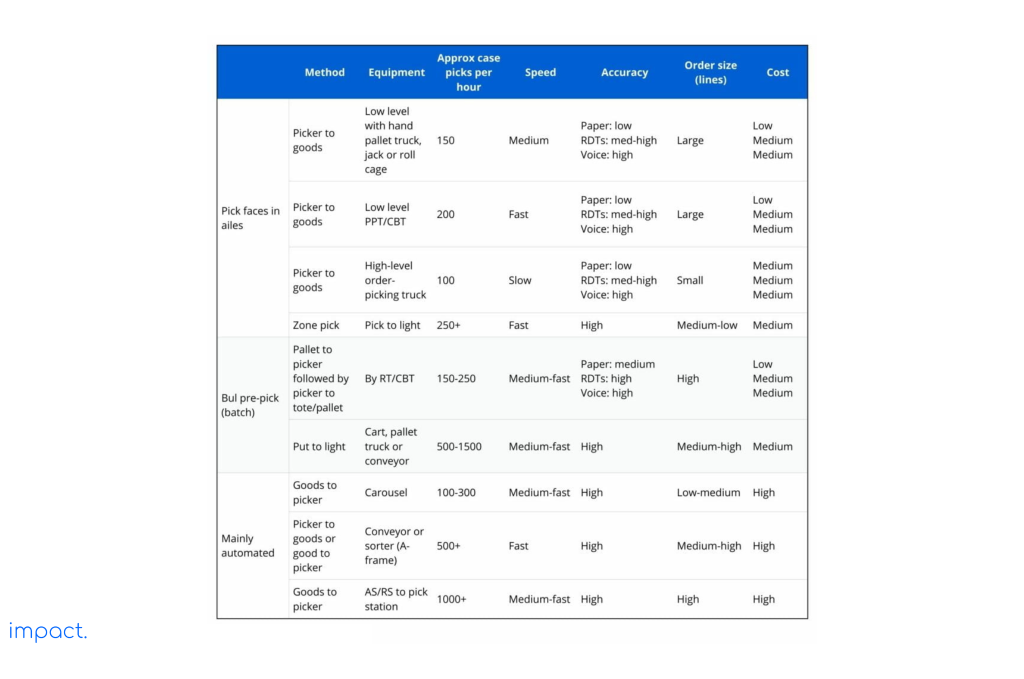
In Part Two, there are two main steps. First, we gather a large number of products, like a batch. Then, we sort them into individual orders. Even though it’s a two-step process, we have a high success rate in finding the right items. We also double-check to make sure everything is accurate. To speed things up, we use put-to-light picking to collect all the items needed for a specific order at once.
We use tools like carousels, conveyors, flow racks, and the AS/RS system in Part Three. These tools help us improve accuracy and handle many different products.
Managers have to think about labor, productivity, accuracy, and service level when deciding how to pick items. Here are the things to think about when choosing which picking methods to employ in the warehouse:
A significant amount of money invested will impact the decision between choosing automation or a more hands-on approach. It’s reasonable to expect a three-year payback period when investing in warehouse operations.
Ergonomic problems are also significant when deciding which goods to choose. We need to consider worries about energy use and the potential for taxing equipment that is not environmentally friendly.
The company’s long-term plan will affect the investment in new equipment. Suppose there’s a possibility of moving the business, changing the products, or altering the distribution channels. In that case, we need to think carefully about investing in automation. The cost of taking apart and putting back together the equipment will be prohibitive because it’s a significant amount.
The period before Christmas is not the right time to automate everything. iForce, a fulfillment center in the UK, has decided not to invest significantly in automation. The company’s Managing Director, Mark Hewitt, believes that the large quantity of a few items during the busiest times can make the technology less useful.
A large and stable workforce of skilled and unskilled operators, who receive reasonable wages, plays a crucial role in determining how much automation we can implement. This available workforce helps us gain benefits like increased operations flexibility, lower investment costs, and improved cash flow.
Simulation software enables the comparison of picking solutions like pick-to-light and pick-by-voice. It assesses essential performance indicators such as how quickly operators can pick items and the overall efficiency of order processing. The software recommends the most cost-effective picking method by analyzing the obtained results.
Read more: Warehouse Manager: Roles and 10 Challenges to Overcome
Every company has different warehouse management needs, so they use other methods to carry out operations. To ensure everything runs smoothly, warehouses need the right picking method. There are seven methods to do this:
Barcode scanning is the most commonly used of these options because it’s easy and affordable. Different types of barcode tools can be used depending on the product.
In the following article, we will discuss replenishing stock for shipping.
Richard G. 2011. Warehouse Management. Great Britain: Kogan Page Limited.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

A wide range of machinery is employed when handling and picking warehouse items. Warehousing equipment can be as primary as affordable trolleys or as large as conveyors for taking sizable orders. In the picker-to-goods system, warehouse operators commonly use pallet trucks, lift trucks, and racks.
Our previous articles discussed different strategies and methods for picking items in warehouses. Now, let’s focus on the equipment used during the picking process. This valuable information will help you choose the equipment that best fits your needs.
Read more: Understanding Warehouses: Definition and its Importance
To effectively manage warehouse operations, it’s crucial to have these six essential warehousing equipment pieces in place.
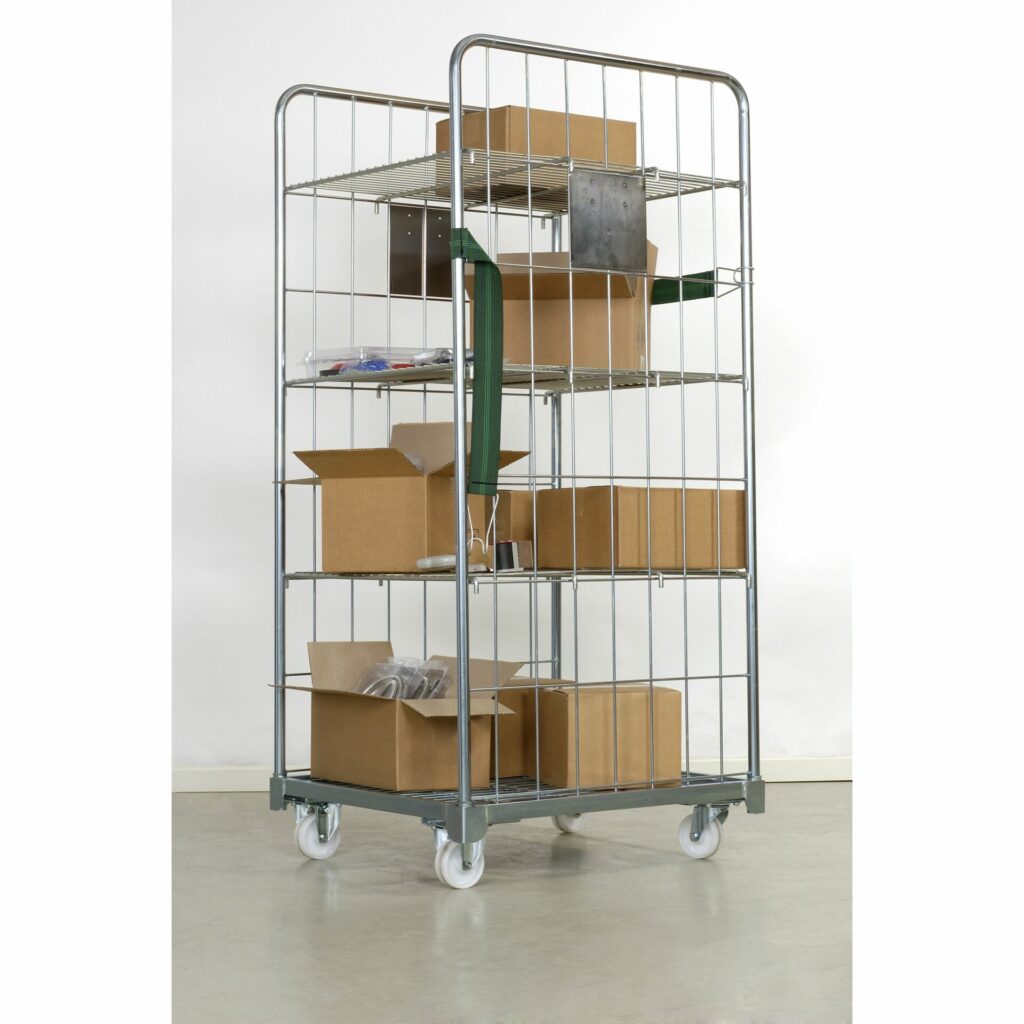

The first piece of equipment in a warehouse is the trolley/cage. The picker uses it to store items. They push the trolley along the aisles and use it as a shelf. Warehouse staff can also use the roll cage for transportation to avoid handling goods twice.

A pallet is a sturdy board that supports goods and keeps them stable while being lifted or moved with a forklift or similar tool. This warehousing equipment helps pickers handle goods more efficiently. There are three types of pallets:
To choose the right truck, consider the number of pallets you need to move per hour and the distance they have to travel in the warehouse.
Read more: Warehouse Manager: Roles and 10 Challenges to Overcome
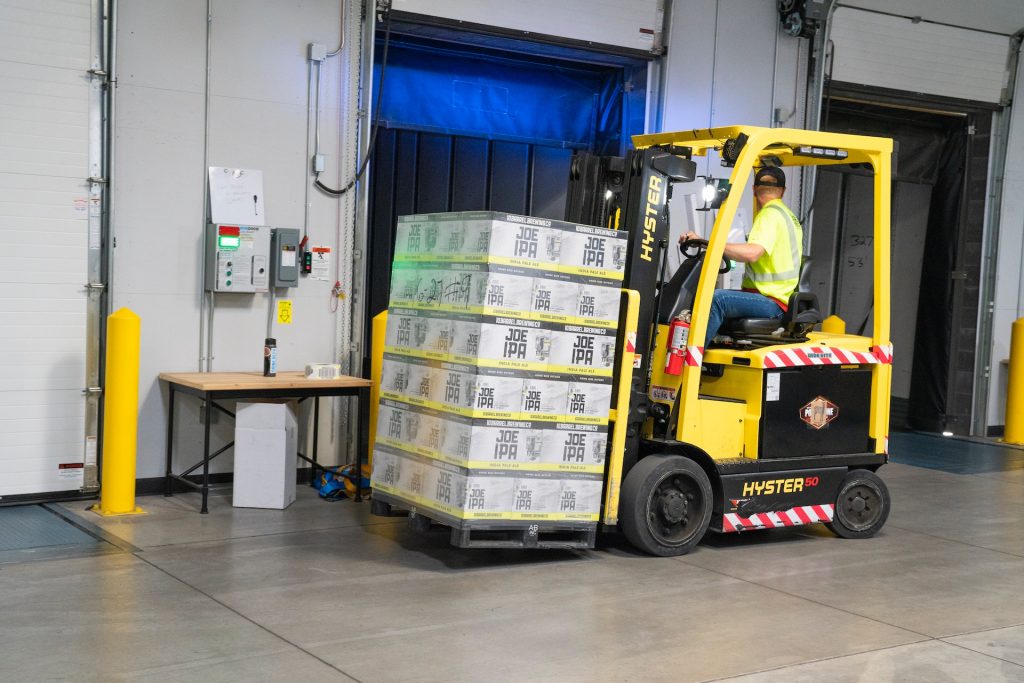

The warehouse utilizes counter-balance and reaches trucks as its equipment. These trucks actively lift pallets to a specific height during picking, enabling operators to avoid bending while placing boxes on the pallets. Additionally, the trucks serve the purpose of storing full pallets on shelves.
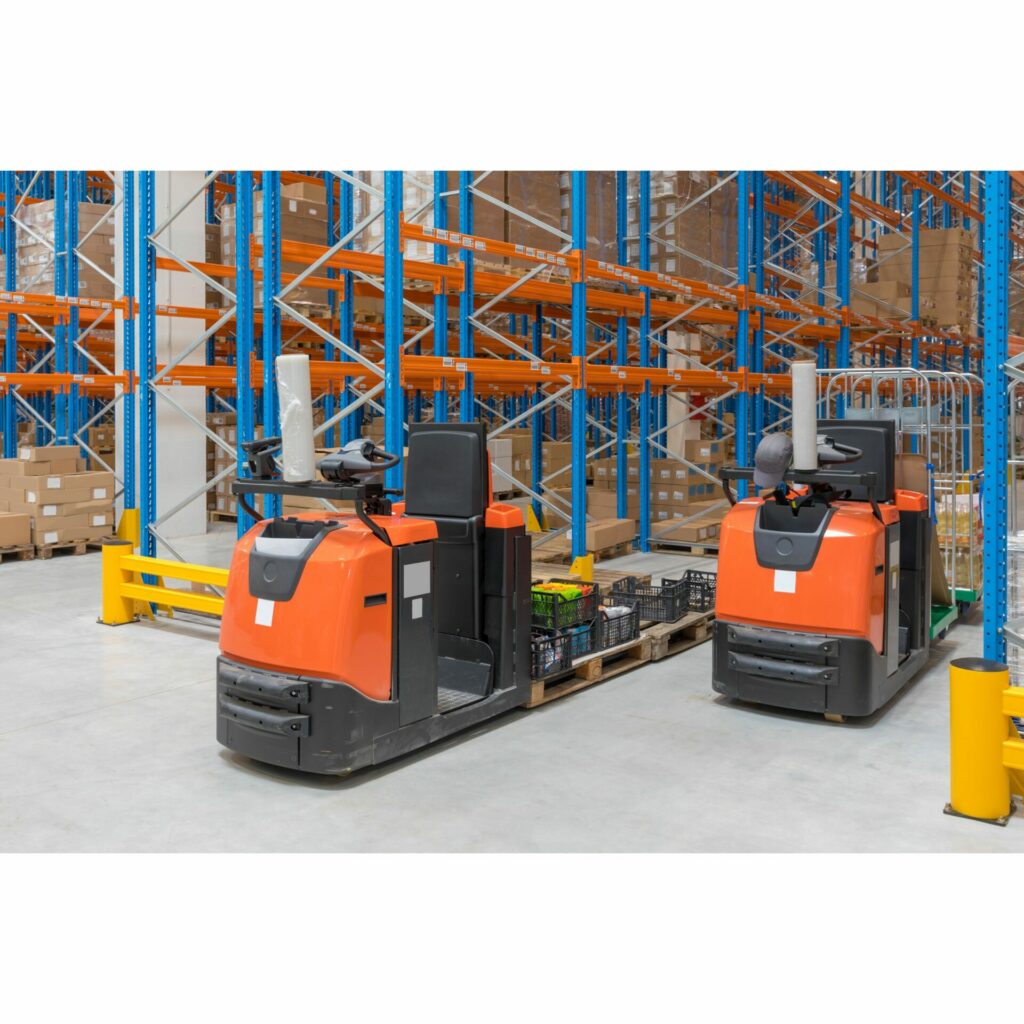

Low-Level Order Pickers (LLOP) are electric-powered warehouse machines that can simultaneously move two pallets to three roll cages along the picking aisle. These trucks work on the first and second levels. Towing tractors are great for moving things horizontally and picking orders at lower levels.
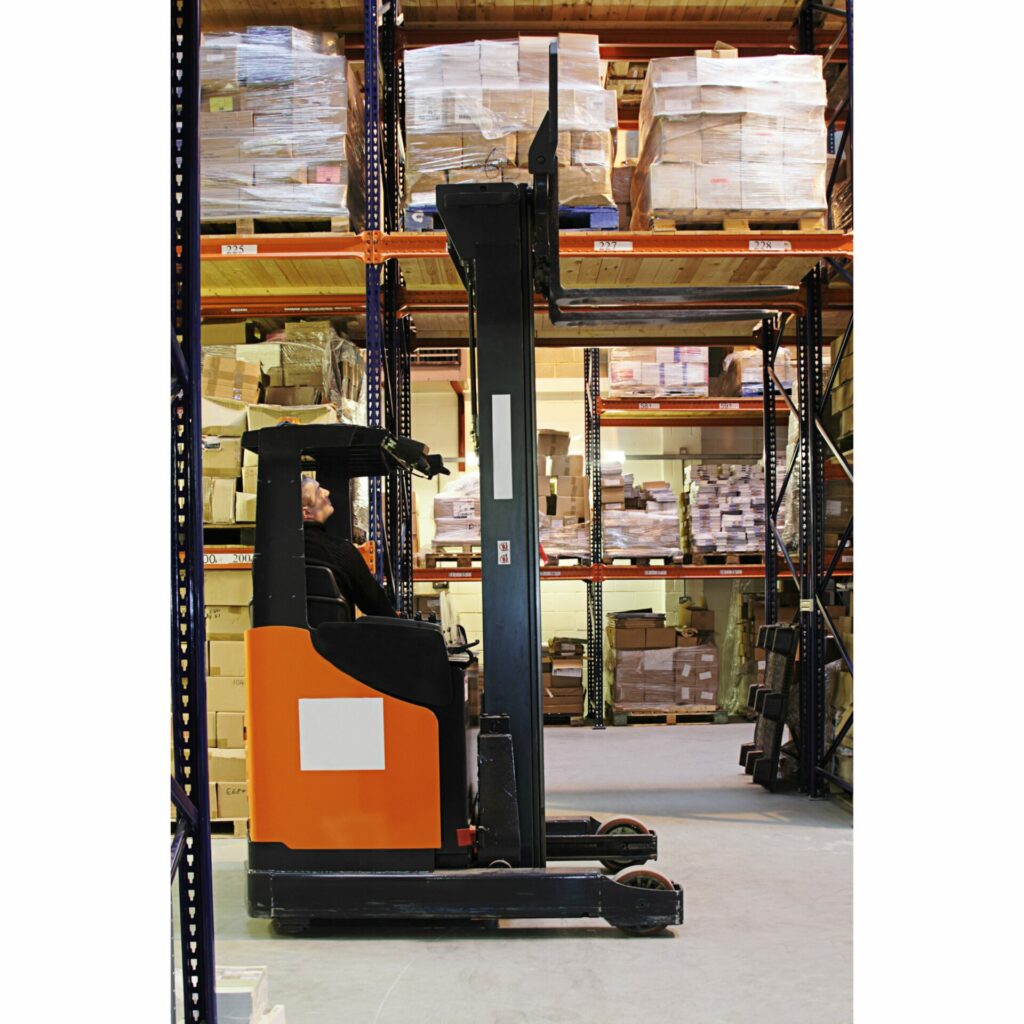

When you have many different products and insufficient space on the shelves, you need to get the products from storage above the ground. For this, you use high-level order pickers like the ones shown in the picture below.
This warehousing equipment is beneficial: it allows you to store many products in a small space using narrow aisles and trucks. HLOP can help you avoid moving things around using a random storage system.
However, there are some downsides to using these machines. The process of picking the products can be slower, and there is a risk of the aisles getting crowded. This system works best for operations with many slow-selling items and only a few goods needed per order.
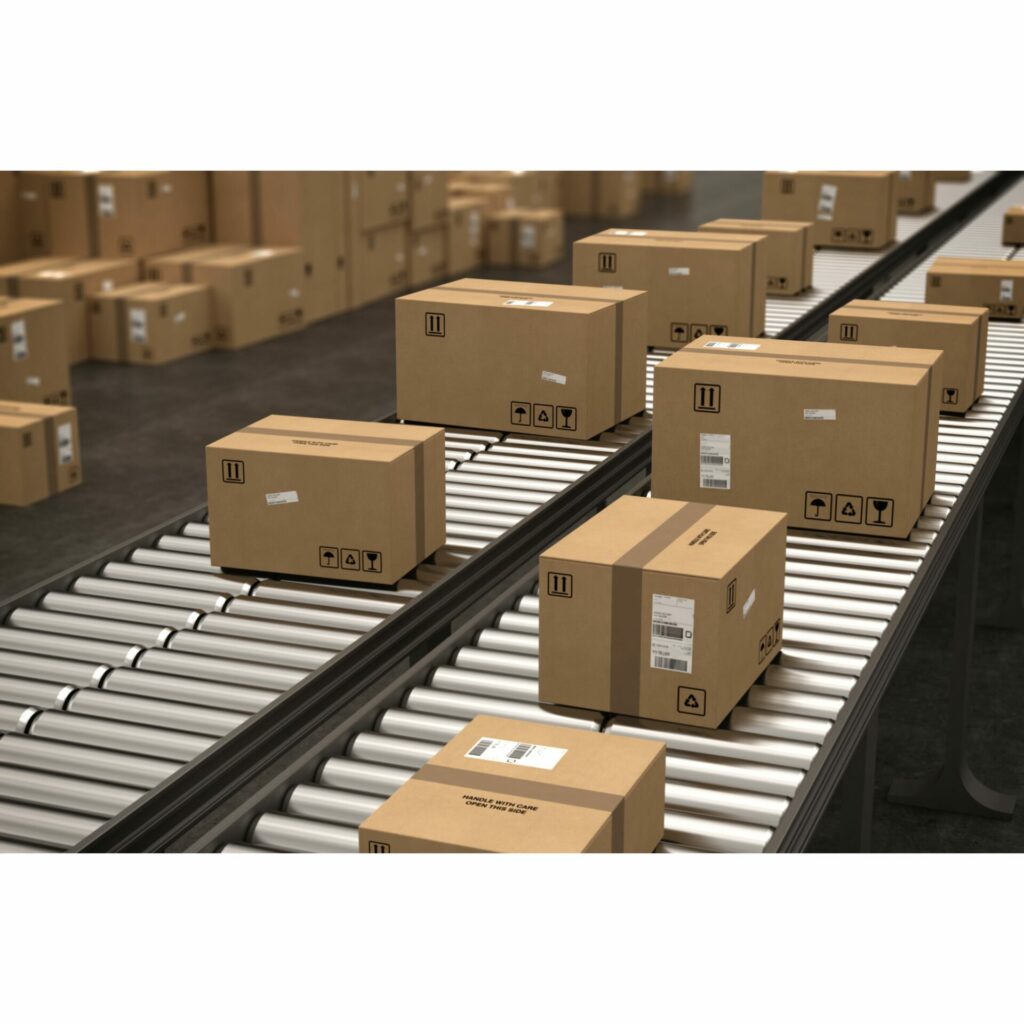

The last piece of warehousing equipment is the conveyor. It’s commonly used in the picking system to move products using either gravity or power. Conveyors are essential in goods-to-picker systems as they help transport boxes and totes between different areas and workstations.
Companies use powered conveyors to transport goods over long distances, utilizing belts, chains, blades, and rollers. Conversely, they employ gravity conveyors to move goods from the mezzanine floor to the shipping area, combining them with other items.
However, these conveyors have some disadvantages:
Companies can customize their picking strategies based on their specific requirements, resulting in variations in the types of picking and warehouse equipment needed.
Each picking method necessitates suitable warehouse equipment capable of handling all the associated processes. Therefore, companies must ensure that their warehouse conditions and budget align with the appropriate equipment.
Next, we will delve into the picking methods your company can implement.
Richard G. 2011. Warehouse Management. Great Britain: Kogan Page Limited.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

In the previous chapter, we talked about on-page SEO and how it helps your content show up better on search engine result pages. Now, let’s delve into another important aspect of website optimization: technical SEO.
Technical SEO is all about fine-tuning your website to meet the ever-changing requirements of search engines. It goes beyond just creating good content and focuses on the technical stuff affecting how well your site appears in search results. This article will explain why technical SEO is important and give practical tips to improve your website’s performance.
Read more: SEO Fundamentals: Key Definitions & 4 Best Practices
Technical SEO is all about optimizing the technical parts of your website to make it more visible and perform better in search engine rankings. It deals with the behind-the-scenes elements that search engines rely on to crawl, index, and understand your website’s content.
Technical SEO also involves various tasks to improve user experience and search engine friendliness. Some common activities include:
Focusing on these technical optimization tasks can improve your website’s visibility, user experience, and overall performance in search engine rankings. It’s a vital component of a successful SEO strategy to attract organic traffic to your website.
Creating good content isn’t enough in today’s digital landscape if people can’t find or see it. That’s where technical SEO comes into play.
Technical SEO helps search engines like Google recognize the value of your website. Technical optimization is important because search engines want to provide users with the best results for their search queries. Focusing on technical SEO ensures that your website meets the requirements and increases the chances of ranking higher in search results.
If your web pages take forever to load, visitors may become frustrated and leave your site. This negative user experience can signal search engines that your website isn’t up to par. On the other hand, if your website loads quickly, has no broken links, and is secure, it boosts search rankings.
In a nutshell, technical SEO is important because it helps search engines recognize the value of your website, improves user experience, and ultimately boosts your search rankings. By paying attention to technical aspects such as page speed, link quality, and website security, you increase your chances of being discovered by users and gaining visibility in search engine results.
Read more: On-Page SEO: Key Components and 4 Mistakes to Avoid
To improve your website’s technical performance, knowing what makes a technically sound website is important. A technically optimized website has certain important features that help it perform well. Let’s take a look at some key characteristics you should be aware of:
When it comes to technically optimized websites, one of the main goals is to make sure they load quickly. Page speed is important because it improves the experience for users who visit the site and also helps improve its ranking on search engines.
Ideally, websites should open within the space of three seconds. Optimizing images, minimizing code, using browser caching, and utilizing CDN (Content Delivery Network) can speed up your website and improve user experience.
As more people use mobile devices, technically optimized websites are created to work well on different screen sizes. These mobile-friendly websites provide a better user experience. Search engines prefer them, especially now that mobile-first indexing is in place.
A well-organized site structure is important for search engines to crawl and understand your website’s content effectively. Arrange your website logically and organized, using clear categories and menus that are easy to navigate.
It also involves creating user-friendly URLs that include relevant keywords to give search engines a clear idea of what each page is about. Having a well-structured site improves your website’s visibility. It makes it easier for search engines to index and rank your content.
Technically optimized websites prioritize security using HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) to protect data transmitted between the web server and the user’s browser. HTTPS ensures that information, like login credentials, is encrypted and safe from interception.
To enable HTTPS, you’ll need an SSL certificate. Search engines, like Google, recognize security’s importance and consider it a ranking factor. Secure websites have a higher ranking than those without proper security measures. Implementing HTTPS safeguards user data and boosts your website’s visibility in search engine results.
Technically optimized websites use a sitemap, like a file containing a list of all the pages on your website. Sitemaps help search engines find and understand your website’s content better, so it can appear more easily in search results. The sitemap categorizes content such as posts, pages, tags, and other types. It also provides information on the number of images on each page and when they were last updated.
Technically optimized websites use a special file called robots.txt. It’s like a set of instructions for search engine robots on how to explore your website. This file tells the robots which parts of your site they can or cannot visit. You can specify what actions are allowed or disallowed for different types of robots. By correctly setting up the robots.txt file, you can control what content search engines can see. It helps you keep irrelevant or sensitive pages hidden from search results.

Certain pages on your website shouldn’t show up on search engines. These pages usually include “thank you” pages, ads landing pages, not-so-great content pages, old blog archives, author and tag pages, and login pages.
To stop these pages from showing up in search results, you need to use something called a “noindex” tag. Place this small HTML code snippet in your web page’s <head> section. The tag tells search engines not to include specific pages in their results.

When Google sees the same content on different pages of your website, it can get confused about which page to put in its search results. This is where canonical tags help.
The canonical tag (you write it as rel=”canonical”) acts like a pointer to the main version of the content. It helps Google know which page to focus on for indexing and ranking.

Now that you understand the important elements for optimizing a website, let’s dive into the actionable steps to achieve it. The process involves following a structured approach consisting of eight steps.
The initial step towards technically optimizing your website is conducting a thorough technical audit of its elements. This process involves identifying issues such as broken
links, duplicate content, slow page loading, crawl errors, and problems with indexing.
To help with the audit process, you can utilize tools like Google Search Console, Bing Webmaster Tools, and other SEO auditing tools. These tools provide valuable insights and data to identify technical issues and areas that need improvement.
The next step is ensuring you have a sitemap that lists all the pages you want search engines to check. Confirm that the sitemap is properly formatted and submit it to search engines through their webmaster tools. Also, review and optimize your robots.txt file to ensure that important pages can be crawled and indexed by search engines without any restrictions.
Focus on enhancing user experience and search engine rankings. You can start by reducing the size of your images, making them smaller without compromising quality. Optimize your CSS and JavaScript files by removing unnecessary code or spaces.
Enabling browser caching allows visitors to store certain elements of your website locally so they don’t need to be downloaded again on subsequent visits. Another effective technique is to utilize content delivery networks (CDNs) that distribute your website’s content across various servers worldwide, enabling faster user access.
You can rely on tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to evaluate your website’s speed. These tools provide detailed reports and recommendations to improve performance. By taking these steps, you can enhance your website’s speed and provide a smoother experience for your visitors, positively impacting your search engine rankings.
It is important to ensure that your website is mobile-friendly, which means it should be easy to navigate and read on different screen sizes. You can achieve this by using a responsive design that automatically adjusts the layout to fit various screen resolutions.
You can use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to check if your website is mobile-friendly. If you discover issues, take the necessary steps to fix them and ensure a smooth experience for mobile users.
The next step in technical SEO is ensuring your website’s URLs are clean, descriptive, and easy for search engines to understand. Use hyphens to separate words in your URLs, and avoid using complicated codes or symbols. A better URL structure helps make your URLs user-friendly and search engine-friendly.
Additionally, it’s important to set up proper redirects, particularly 301 redirects, when you move or rename any of your website’s pages. This way, users or search engines will be automatically redirected to the new and correct page when they visit the old URL. By doing this, you can ensure a positive user experience, safeguard the value of your current links, and avoid any broken links.
Now, let’s add structured data to your content pages. This step helps Google better understand what’s on your webpage. When you use the correct structured data code, your pages can display special search result features.
These unique results are known as rich snippets. They provide additional information beneath the title and description in search results. Rich snippets are valuable because they set your pages apart from others. This distinction can encourage more people to click on your link when they come across it in search results.
Google supports various types of structured data codes. Choose the one that suits the content you want to enhance with structured data. For example, if you have a recipe website, you can utilize structured data to present details like cooking time and ratings directly in the search results.
The next step is to make sure your website is secure. To do this, obtain an SSL certificate and use the HTTPS protocol. This encryption helps protect users’ data on your site, such as personal information or passwords. It also builds trust with your visitors and can improve your rankings on search engines.
Additionally, it’s important to keep your website’s software and plugins up to date. Regularly updating them helps fix any security vulnerabilities, making it harder for hackers to exploit your site. By taking these steps, you can enhance the security of your website and provide a safer browsing experience for your users.
Finally, technical SEO is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring and updates. You should use different tools and analytics to monitor your website’s technical performance. The method includes reviewing reports on how search engine crawlers access your site, checking if all your pages are indexed properly, and monitoring other technical metrics affecting your site’s visibility.
By staying updated with the latest best practices and changes in search engine algorithms, you can adjust your technical SEO strategies accordingly. Search engines frequently make updates to improve their search results, so staying informed and adapting your website’s technical aspects is important. This optimization ensures your website remains in good shape and performs well in search engine rankings.
Read more: Search Engines: Inner Workings & 6 Ways to Rank Higher
Optimizing your website with technical SEO is important. It deals with the technical stuff affecting how your site appears in search results. When you do technical optimization, search engines like Google can better understand the value of your website.
A good site structure is key to getting noticed by users and ranking higher in search engines. If your web pages take forever to load or have broken links, it can frustrate visitors and tell search engines that your site isn’t up to par.
In the next chapter, we’ll talk about off-page SEO, specifically link-building and establishing authority. Off-page SEO is crucial for improving your online presence. By getting high-quality links from trustworthy sources and positioning your website as an authority in your industry, you can boost your search rankings and attract more organic traffic.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

Learning about effective strategies for selecting goods is essential to make warehouse picking more efficient.
The most expensive part of the picking process is moving between different locations to collect items. It’s essential to have a strategy that minimizes the time spent traveling within the warehouse. The diagram below illustrates how the picking process is connected and presents various options and designs.
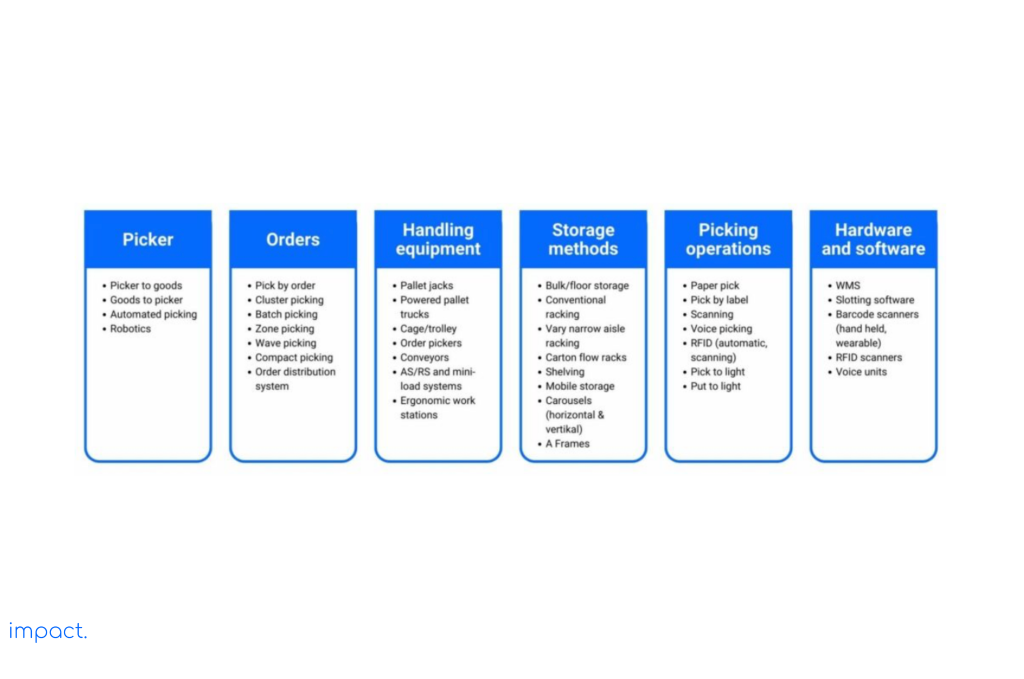
Since each company has different needs, they use different picking types and strategies. In this article, we will discuss various picking strategies that your company can consider.
Read more: Understanding Warehouses: Definition and its Importance
When managing a warehouse efficiently, picking strategies are crucial in ensuring that products are retrieved accurately and quickly. This section will explore three primary picking strategies: picker to goods, goods to picker, and automated picking. By understanding the unique features of each process, you can make an informed decision on which one suits your warehouse operations best.
Most warehouses lack automation. As a result, companies still rely on the picker-to-goods strategy to pick goods.
Pick-to-order moves goods from the warehouse to the delivery location with only one handling. The picker takes one order at a time and walks through the warehouse using trolleys, sacks, or forklifts. They follow a specific route by reading a list, using a radio device, or following voice commands. The orders can be individual items, full cartons, or full pallets.
The picker collects the order lines in a specific order and stores them in racks, carousels, or flow racks based on the size of the goods. Individual orders are easier to handle, but orders with multiple items and long distances can cause congestion during picking.
Cluster picking involves selecting individual compartments in trolleys or sacks while handling multiple orders. This method helps reduce travel time. To make cluster picking effortless, we can use equipment like pallet trucks, tugs, or tractors to lift two pallets simultaneously.
In cluster picking, we can also utilize conveyors. Here’s the process: The tote, a container, passes through a barcode reader to obtain a unique ID. Then, the pick-to-light terminal displays all the tote selections on a unique screen. Each terminal instructs us on the number of items to pick and the designated location for placing them.
For instance, if we need to place eight items in compartment B, it will show as “B8” on the screen. Once we pick items for all compartments in a specific area, we return the tote to the conveyor, which moves on to the next room.
The number of orders we can handle in each cluster depends on several factors. These include the number of lines, the number of items in each order, the total space required, and the capacity of the totes, sacks, or carts.
Read more: 6 Warehouse Performance Metrics & Tips for Choosing Them
Batch picking is a strategy where we simultaneously pick goods for multiple orders by breaking down the orders into product components and combining each product line. There are two options: pick by line or pick to zero.
In pick-by-line, there is a risk of returning excess goods to stock. In pick-to-zero, we allocate the correct number of items to customer orders until we exhaust units and lines.
The advantage of this strategy is that it reduces travel time and improves accuracy because two people are involved. However, it takes longer because there are two stages in the process. Batch picking can also increase the number of lines picked per hour, but we still need to count and check the items.
We can use batch picking in cross-dock processes to pick up and allocate products as soon as they arrive at the warehouse. By using batch picking, we can skip tasks like putaway and backfilling, which helps us work faster and more accurately.
We can group orders in different ways. For example, we can combine mail or e-commerce orders into a single charge. Similarly, we can combine orders that contain similar items. We can do this grouping manually, but many people now use Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) to make the batch-picking process easier and more efficient.
Zone picking is a simple strategy where each picker is assigned a specific area to collect goods. The number of zones given to each selector depends on how busy they are, and the WMS generates the instructions for picking.
Here’s how it works: we move orders from one zone to another until we complete all of them. We use different tools like bags, carts, pallets, or conveyors with rollers or gravity to make it easier to move boxes or totes. We must control the number of orders we send to each zone to avoid delays and ensure everyone has a fair workload.
Usually, each zone has 1-2 pickers, and each can handle multiple zones. Batch picking is practical when there are many different products, many orders, and a moderate number of items per order.
The most widely used strategy in this type of picking is “pick by light.” When an operator moves to the following order, a set of lights illuminates that zone, displaying the number of items to pick. Once the selector completes the picking, they turn off the light and move to the location with the subsequent illumination.
In addition, companies actively scan the product barcode before placing it in the tote to ensure it is the correct item. This scanning process speeds up operations and reduces errors. Companies commonly employ the pick-by-light strategy in their operations, especially when they have separate zones for different product lines, such as medicine, dangerous goods, and food.
We schedule the release of wave-picking orders at specific times, such as in the morning or at noon, to align with vehicle departures, recharge cycles, and shift changes. The timing may vary for different areas depending on the time required to select the orders.
The downside of this picking strategy is that it requires reassembling the partial orders in the next step. However, it also allows a second check on the product code and quantity.
The Goods-to-picker strategy is advantageous for various system configurations. Its benefits, as stated by Dematic (2009), include:
Read more: 9 Vital Warehouse Processes You Need to Know
An example of a goods-to-picker strategy is as follows:
The goods-to-picker compact picking system is excellent for handling slow-moving products in retail and wholesale warehouses. It’s also cost-effective for warehouses dealing with different parts and components, like the automotive industry.
Here’s how it works: the product is taken from storage and brought to the workstation using a conveyor. At the workstation, it’s combined with other items and packed into a cardboard box for delivery.
Read more: What is a Wholesaler? Definition, Benefits, and 4 Challenges
The order distribution system is excellent for businesses with many order lines with only a few different products. Carriers move boxes or containers with a single product to various locations where they assemble the orders using a unique light system. This system works well for companies that sell things through the mail or online.
In both of these operations, the workstation is essential. Vanderlande Industries has made a group of workstations that are good for people’s bodies and come in different sizes. They can handle anywhere from 100 to 1000 order lines every hour. Here are the main things about these workstations:
The Rapid Pick workstation by Dematic helps operators work efficiently and prevents injuries like Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) and fatigue. Operators can adjust the height of the workstation to fit their needs.
The workstation includes good lighting, controls that are easy to use, and visible buttons. You can adjust the screen on the workstation to a comfortable height and angle. The screen displays essential information such as the item’s size, a picture of the product, and where placement location. This feature helps us create a dependable and secure system for taking orders at every workstation.
The workstation also has a helpful feature that automatically organizes the order of picking items. It has two conveyor lines: one for bringing things to the operator and one for placing completed orders. The workstation presents the items to the operator in an easy-to-reach and handle manner.
The operator looks at the instructions on the screen and ensures each item is in the right place in the box by using a machine or pressing a button. Once the operator completes all the orders, the IT system actively sends out the boxes and totes. If the picking process encounters empty totes, the workstation retains them, and the IT system later directs their utilization.
This workstation can handle up to 1,800 units per hour at total capacity, making operations faster and more efficient.
Companies are using system automation to keep up with the competition. They want to be faster, more accurate, and more productive. In 2009, Vanderlande Industries introduced Automated Case Picking (ACP) to lower handling costs by 40%. This system caters to food retailers with high-capacity needs.
The ACP system automatically releases pallets from storage one layer at a time. The AS/RS system stores and transports these pallet layers, reducing the reliance on cranes. To expedite work, companies employ other AS/RS systems.
The ACP system has a lower initial cost and pays for itself quickly. It cuts up to 40% of order-picking expenses, making it a good choice. It also ensures enough stock at the picking area, processes orders fast, and improves service for retail food stores.
Using an automation system offers several advantages, including:
There are still some warehouses that use automation systems for picking. The picture below shows that automation doesn’t have much effect on the warehouse operator.
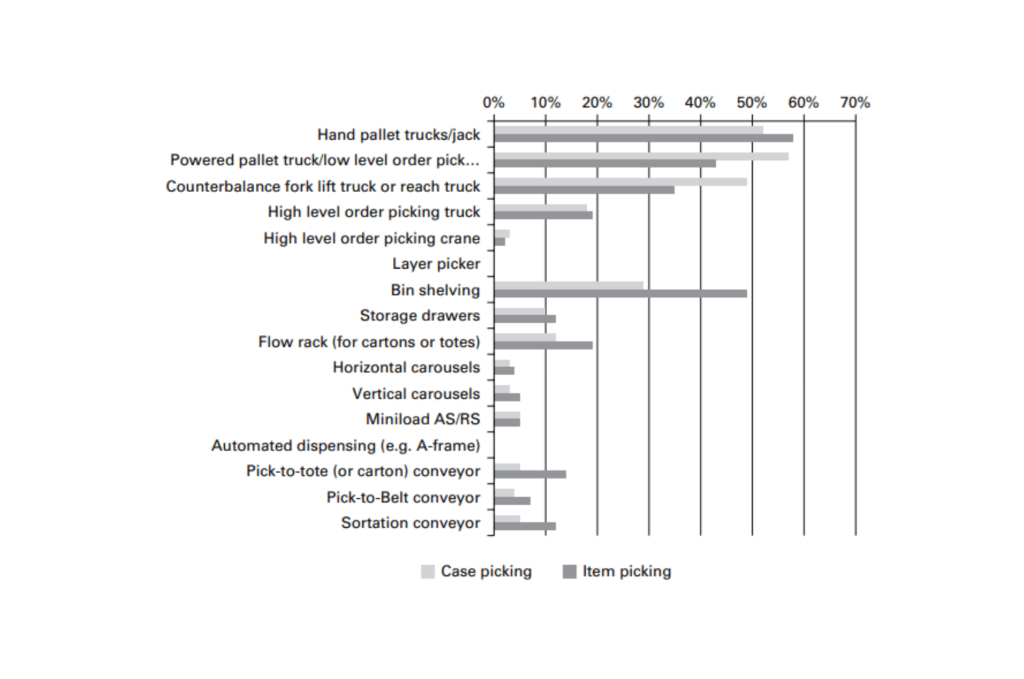
Source: Warehouse Management; Use of Equipment for Picking
Before switching to automation, ensure operations run smoothly without relying on technology. Once you have achieved this, you can explore using technology to enhance productivity. However, remember that automation necessitates adequate preparation and time for design, evaluation, and implementation.
Here are some drawbacks of automation to consider:
Read more: Warehouse Cost: 2 Determination Systems & Reduction Tips
To work more efficiently, you can use different picking strategies. It’s important to remember that every company has different needs, so their processes and tools will also differ.
The most common picking strategy used in warehouses today is when pickers go to the items. However, there’s another strategy where the goods come to the selector, which can be faster and more cost-effective if automated.
Each company may use different equipment in its warehouse, depending on their specific situation and needs. In the following article, we will talk about the equipment in warehouse operations.
Dematic C. 2009. Goods to Person Order Fulfilment. Dematic CorporationRichard G. 2011. Warehouse Management. Great Britain: Kogan Page Limited.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.
