Kanban: Definition, 6 Rules, and its Benefits
Kanban is a crucial part of the Just in Time (JIT) system, which we discussed…
Sean Thobias
May 17, 2025Our previous chapter discussed how important keyword research is for driving organic traffic to your website. Now, let’s shift our focus to page optimization, also known as on-page SEO.
This aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) can greatly improve your website’s visibility and ranking on search engine result pages (SERPs).
This article will define on-page SEO and discuss its key components. We will also share best practices to help you avoid common mistakes hindering your SEO efforts. So, let’s explore the world of webpage optimizations and see how these components and avoidable mistakes can greatly impact your website’s search engine performance.
On-page SEO, also known as on-site SEO, involves directly optimizing specific parts of a website. The main objective of on-site SEO is to make it simple for search engines and users to:
You should concentrate on a few essential factors to improve your website’s on-page SEO. These include your content, meta tags, URLs, headers, and internal links. By optimizing these elements, you make your website more appealing to both search engines and users.
Read more: SEO Fundamentals: Key Definitions & 4 Best Practices
Understanding the difference between on-page and off-page SEO is crucial to optimizing your website for search engines. By understanding these concepts, you can take a more comprehensive approach to improving your website’s visibility.
On-page SEO refers to the actions you can take directly on your web pages to enhance your search engine rankings. It involves optimizing various elements within your website itself. On the other hand, off-page SEO focuses on external factors that contribute to building your website’s reputation and authority.
Here’s a table that illustrates examples of on-page and off-page SEO techniques:
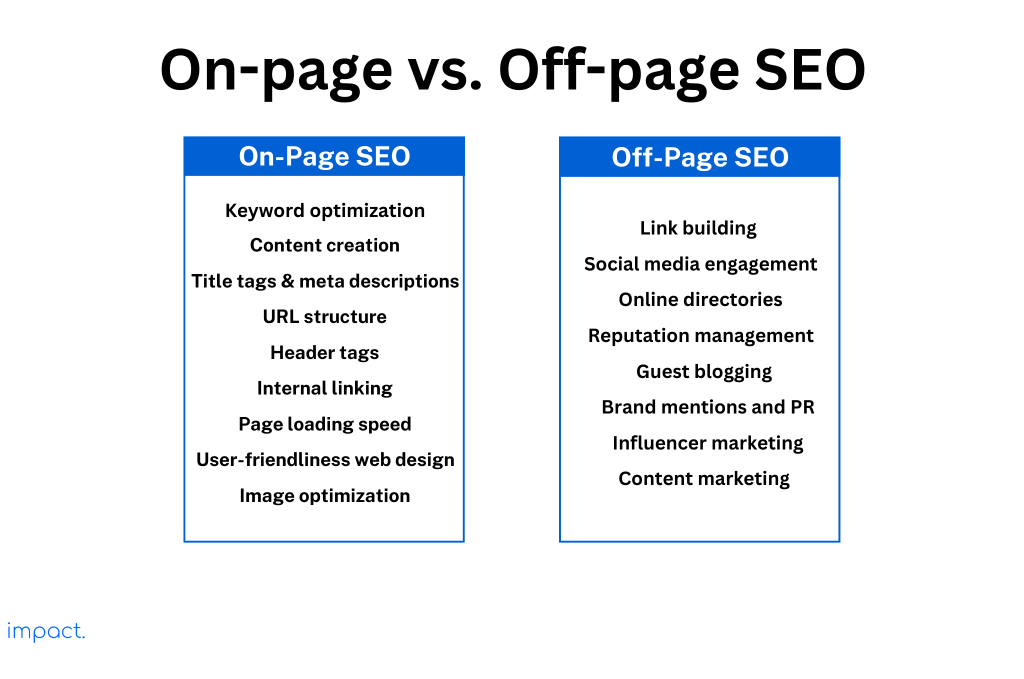
On-page SEO is crucial in achieving overall SEO success for your website. Here’s why it matters:
On-page SEO helps your site rank higher in search results, increasing organic traffic. Studies show that the first five organic results on a search page receive a whopping 67.60% of all clicks, while the next five only get 3.73%. It decreases further down the list.
On-page SEO helps search engines understand if your web pages are relevant to user searches. By optimizing your content and meta tags, you increase the chances of your website showing up in search results when people search for related topics. On-site SEO ensures that your website reaches the right audience and meets their needs.
When you do on-page SEO, you make your website better for users. You optimize URLs, headers, and internal links to improve navigation. These changes make it easier for visitors to find what they want and stay on your site. When people can navigate your site easily, they’re more likely to explore more pages and even become customers.
Proper on-page SEO optimization improves your website’s user-friendliness, reliability, and credibility. It creates a better user experience, builds trust in your brand, and increases the chances of visitors engaging with your content, trusting your products/services, and becoming leads or customers.
On-page SEO is the key to building a strong SEO strategy for your website. Regularly optimizing your content and website elements can create a sustainable plan to improve your search engine rankings. This results in more organic traffic, brand visibility, and ongoing business growth.
Read more: Search Engines: Inner Workings & 6 Ways to Rank Higher
Here are some important steps to optimize your on-page SEO:
The content of your page is crucial for on-page optimization. It communicates to search engines and readers what your website and business are about. To optimize it effectively, follow these steps:
The title tag is an important part of your webpage. The title appears in search results, social media, and the browser tab. To optimize it, ensure each page has a unique and descriptive title tag. This description helps people understand what your page is about.
Other tips include:
Meta descriptions are the short page descriptions that appear below the title in search results. They may not directly affect search engine rankings, but they are crucial in enticing users to click on your page.
When crafting meta descriptions, your goal is to create engaging summaries of your page content. Here’s what you should do:
When you structure your content, it’s important to use header tags. Header tags help hierarchically organize your content, making it easier for visitors to read and navigate.
The main heading, also known as H1, should include the primary keyword when it’s relevant to the content on the page. The keywords help search engines understand the main topic of your page.
For subheadings, you can use H2, H3, and so on. These subheadings further divide your content into sections, making it easier for readers to find specific information.
By using header tags effectively, you improve the readability and organization of your content, which can enhance the overall user experience on your website.
To optimize your URL structure, you must consider the following:
To optimize your images and make your website load faster, compress them. Compressing them will improve the overall user experience by reducing waiting times.
Your images must include descriptive file names and alt tags. Use relevant keywords in these descriptions to improve their visibility in search results. Additionally, provide alternative text that describes the images. This text helps users with difficulty viewing the photos and contributes to better search engine optimization (SEO) for your website.
Don’t forget this crucial step: create a value proposition for every page on your website. A value proposition is a clear and convincing statement that tells visitors what they’ll gain from that page or content.
Each page should have a goal beyond just ranking for a keyword. It’s not just about targeting keywords for SEO; each page should have a specific purpose or intent. It’s not just about driving traffic or ranking higher but providing unique value to visitors.
Create a logical internal linking structure to make it easier for visitors to navigate your website and improve their overall experience. When creating these links, use anchor text, the clickable text of a link containing relevant keywords.
An anchor text helps search engines understand the context of the linked page. It’s important to ensure that the internal links feel natural and provide value to the user. They should direct visitors to related and helpful content that adds to their understanding or provides further information on the topic they’re interested in.
Read more: Mastering Keyword Research in 8 Steps
You must avoid four common mistakes to optimize your on-page SEO and make your website more visible and user-friendly. These practices can harm your SEO efforts and hinder the overall experience for users. Here are the four things you should stay away from:
Thin content occurs when your web pages lack enough valuable information for users. They may have very little text or content that isn’t relevant or helpful. Search engines, like Google, really appreciate high-quality and informative content.
So, it’s imperative to avoid having thin content on your website to rank high in search results. Google aims to provide the best results matching users’ searches. To convince Google that your page is the best answer, you must provide comprehensive information on the topic you want to rank for.
Thin content rarely meets Google’s criteria for being the best result. Therefore, make sure your pages have important and useful content to achieve good search rankings and provide value to your visitors.
Duplicate content means having the same or very similar information on different web pages. This repetition can occur within your website or even across other websites.
Duplicate content causes three main issues for search engines:
Having unique and valuable content on each website page is crucial for maintaining strong SEO practices. Make sure you don’t repeat information that already exists on other pages, whether it’s within your site or on other websites.
Providing unique and informative content improves your chances of obtaining higher rankings in search results. It boosts your visibility and enhances the overall user experience by offering new and valuable information.
Keyword stuffing is when you put too many keywords on a webpage, even if they don’t make sense or are irrelevant. People do this to trick search engines into ranking their websites higher.
However, search engines see this as cheating and can punish your website by lowering its rankings. Instead, using keywords naturally and only when they fit well within your content is better. It makes your content more helpful and enjoyable for users.
For example, let’s say you have a website about healthy recipes. You want to include the keyword “healthy dinner recipes” in your content. Here’s an example of how you can incorporate it naturally versus keyword stuffing:
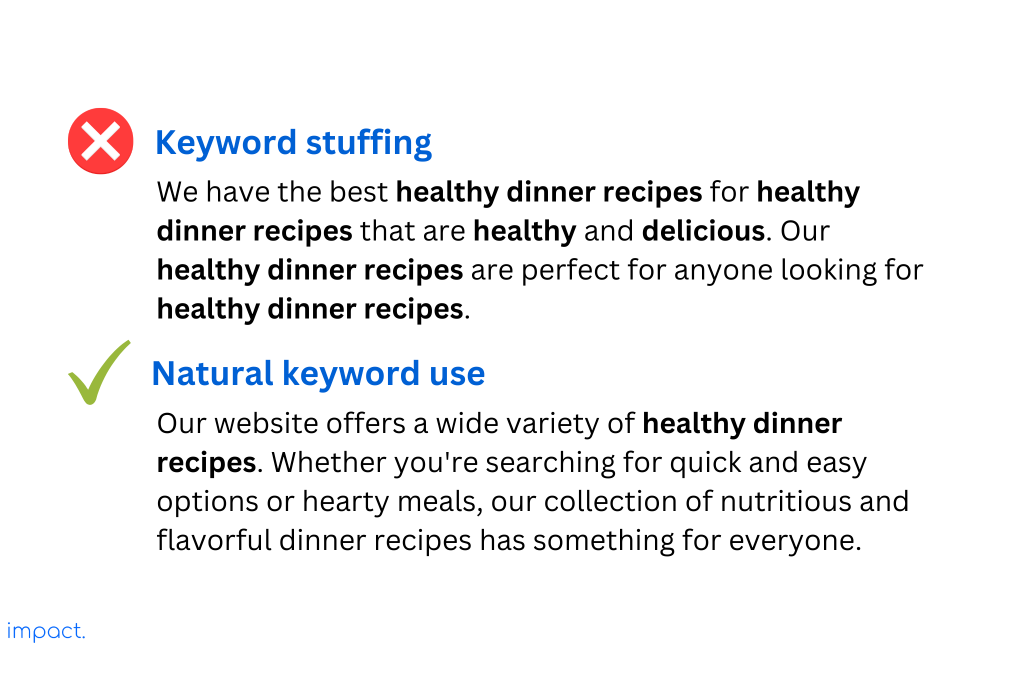
Cloaking is a sneaky tactic that involves showing different content to search engines and regular users. Here’s how it works: when search engines crawl your site, they see one set of optimized content designed to boost your rankings. However, when people visit your website, they see something completely different.
The reason behind this deceitful practice is to trick search engines and manipulate the search results in your favor. However, search engines don’t like this behavior because it’s all about trying to deceive and manipulate the search results. If you get caught using cloaking, it can seriously harm your website. Search engines might lower your rankings or, in some cases, even remove your site from their search results altogether.
It is important to make sure that the content displayed to both search engines and users is identical in order to prevent any unfavorable outcomes. Transparency is the key here. So, don’t try to outsmart search engines by using cloaking techniques. Instead, focus on creating valuable, relevant content that genuinely helps your users. That’s the best approach for long-term success in SEO.
On-page SEO is essential for improving your website’s visibility and ranking on search engines. It’s not just about keywords; you must also focus on other important factors. These include your content, meta tags, URLs, headers, and internal links. By optimizing these elements, you make your website more appealing to search engines and users.
To achieve effective on-page SEO, avoid four common mistakes: thin content, duplicate content, keyword stuffing, and cloaking. These practices can harm your SEO efforts and create a negative user experience. By removing these pitfalls, you can ensure your website is more visible and user-friendly, improving its search engine performance.
Next, we’ll explore technical SEO in the upcoming chapter. This SEO type deals with the technical aspects of your website that can impact its visibility and ranking. By understanding and implementing technical SEO best practices, you can enhance your website’s performance and make it search-engine friendly.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

Picking is when we take the items customers order from the warehouse shelves and send them out. It’s one of the most expensive parts of the warehouse process.
Picking has its challenges. It’s hard to automate, needs careful planning, and mistakes can happen quickly. Most importantly, it affects customer service directly. Despite these challenges, managers want to increase productivity in picking to reduce warehouse costs. They must consider the trade-offs between speed, price, and accuracy.
In the past 20 years, there has been a shift in order taking. Previously, we would gather items in large quantities. However, nowadays, it is more common to pick smaller amounts and have deliveries occur more frequently. Concepts such as Just in Time, the rise of online shopping, and the desire for shorter waiting times have driven this change.
We’ve talked about warehouse management before. This article focuses on picking orders and explaining them in more detail.
The 2009 Benchmarking Survey showed that Aberdeen Group uses specific measures to identify the best picking operations. They present the data in the table below:
| Metrics | Best Practices | Industry Average | Delays |
| Percentage of accurately picked orders | 99.8% | 97.7% | 88.4% |
| Percentage of orders delivered on time and as expected | 99.5% | 95.6% | 88.2% |
The figure below illustrates how labor, technology, equipment, and warehouse layout interrelate.
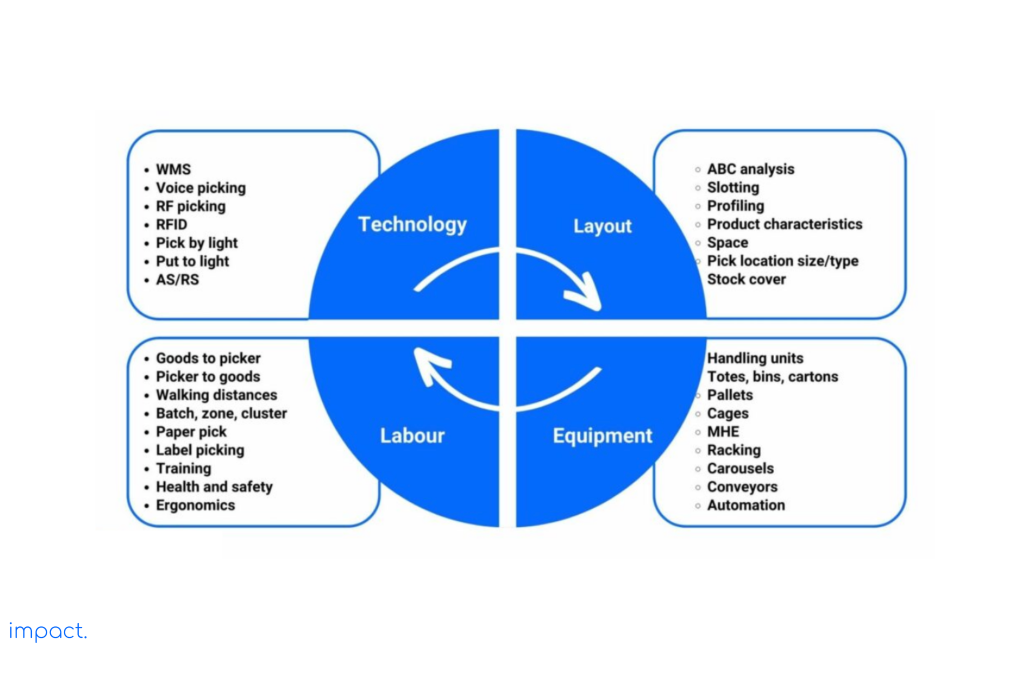
Moving between different picking spots is one of the most significant expenses in the picking process. Depending on the method, these charges can account for up to 60% of the time required to complete the picking process. That’s why managers need to choose the right way to do the picking based on the conditions in the warehouse to reduce these costs.
Read also: Warehouse Manager: Roles and 10 Challenges to Overcome
We use various strategies to handle orders, pick items, and determine the necessary equipment in the picking process. The picture below illustrates the methods and tools utilized in the picking process. We will delve deeper into this topic in the following article.
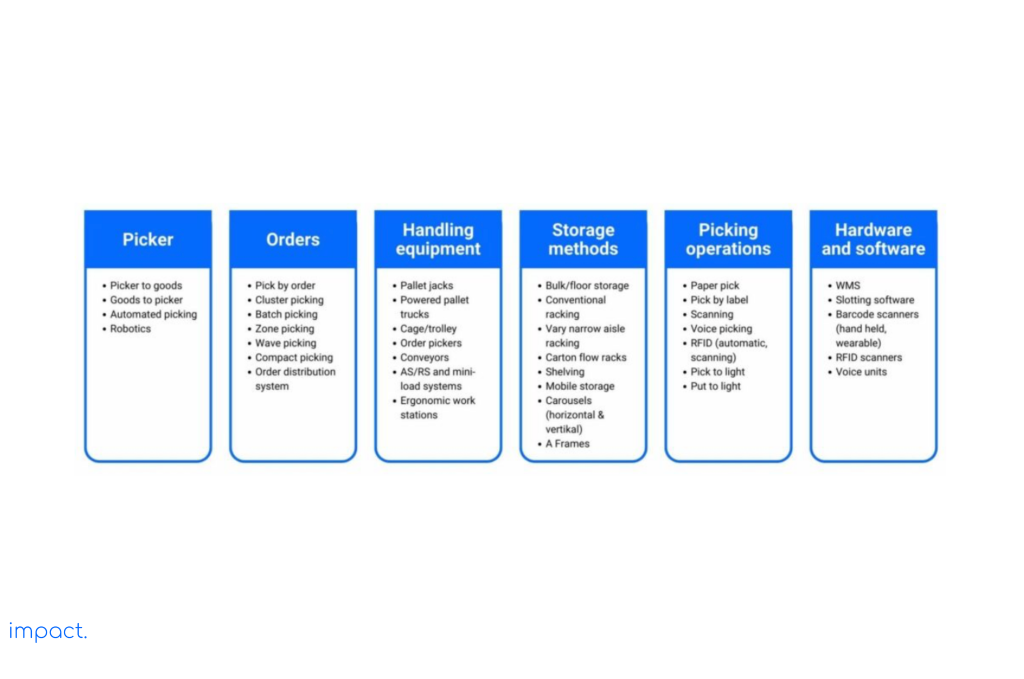
A little preparation can go a long way when it comes to getting your warehouse ready for efficient picking. Setting up the proper layout and organizing your space can streamline the picking process and save valuable time.
According to Frazelle (2002), only around 15% of SKUs are inefficient locations, which leads to higher costs due to increased travel time and unused spaces. To avoid this, you can take some steps before picking items. Start by using the right equipment, setting up a storage system, deciding on a picking method, and conducting an ABC inventory analysis.
Pareto’s Law, or the 80/20 rule, explains the ABC classification. This rule states that:
ABC classification is a way of organizing goods based on their importance using Pareto’s Law. Different companies and market sectors may have their classifications. When it comes to sales, here’s how ABC classification works:
Many companies use ABC analysis to optimize their warehouse layout effectively. Relying solely on traditional ABC analysis has limitations. It only provides a snapshot of the situation based solely on sales levels. As a result, relying exclusively on this analysis can reduce productivity.
Let’s look at an example that compares two products over a specific period using only ABC analysis:
| Product | Sales | Orders |
| Product A | 10,000 units | 4 |
| Product B | 1,000 units | 200 |
Although Product A achieved the highest sales, it received only four selections during that period. In contrast, Product B, despite having lower sales, received 200 orders. This data indicates that Product B demonstrates faster movement and warrants placement near the dispatch bay.
Right now, we have a system called dual ABC classification that combines two categories: volume and frequency. This system helps us create a nine-box lattice, like the one in the picture below.
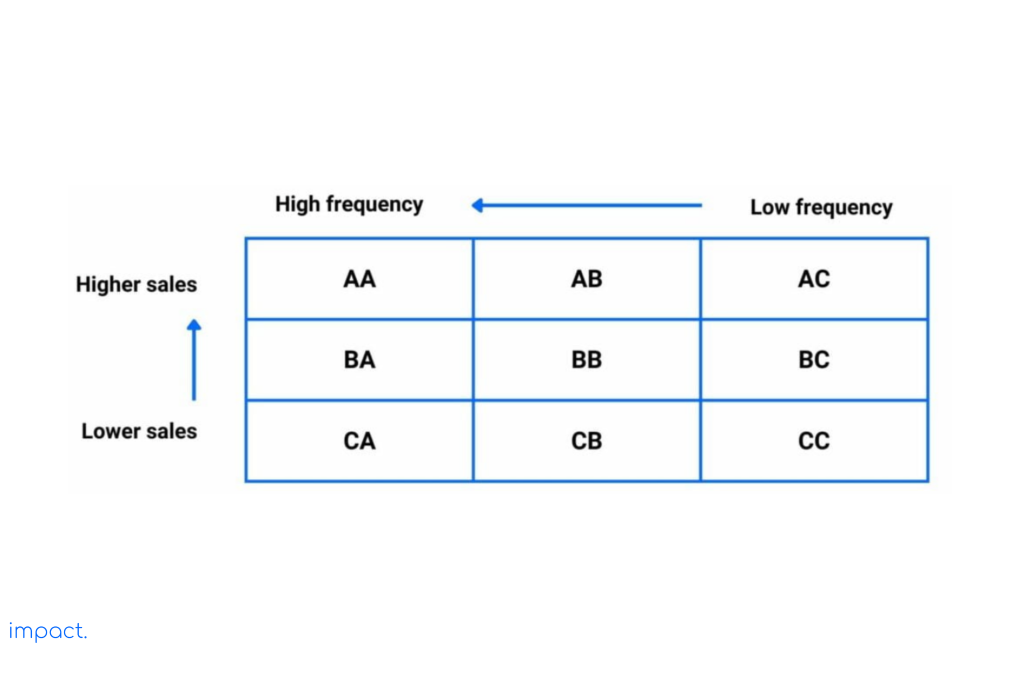
The figure reveals that AA products have the highest sales and frequent customer purchases. In contrast, CC products have the slowest sales rate. When you visit the picking location more frequently, the number of people present increases. Despite making up only 8% of the product suite, AA products contribute approximately 50% of the total sales.
The figure below explains the connection between how often a product sells and its value. It suggests that each sector requires a different approach. The strategy you choose can depend on the level of service, how often and how you order stock, how often you count your inventory, and the relationship between you and your customers and suppliers.
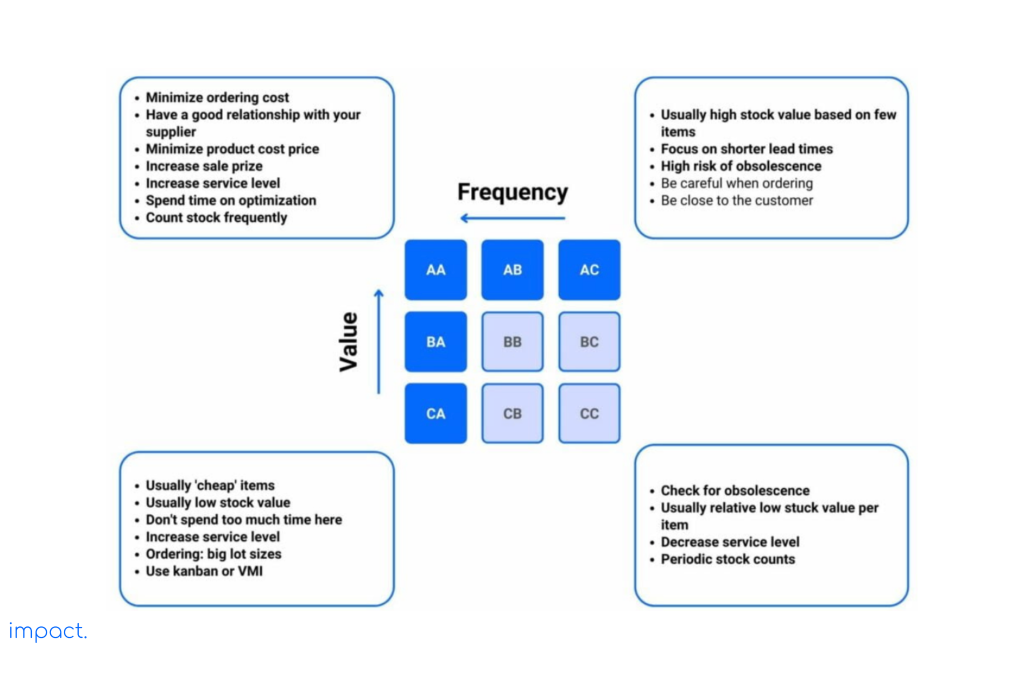
To make your warehouse more efficient, consider a few things.
First, calculate the weighted volume by multiplying the annual demand by the number of products on the shortlist. This calculation helps ensure that you don’t end up with too many products causing delays in the delivery area.
Remember that the more often you visit the pick face, the higher your labor costs will be. Traveling during picking can make up a significant portion of the total picking time. That’s why arranging your warehouse layout is essential based on the number of pick-face visits needed.
Another critical factor is slotting, which determines the best location for each product in the warehouse. It’s not just about placing fast-moving items near the delivery area. It’s also about grouping frequently shipped products together in the pick-face area. This way, you can reduce travel time and make picking more efficient.
Slotting can also help you determine how many pick faces you need for each product line and what size they should be. It’s a good idea to spread high-demand products across the front of the racking closest to the start and end of the picking run. Slotting prevents congestion and keeps things running smoothly.
Additionally, your system can identify small batches of products that can fulfill large orders. By looking at which items are popular and combining that with completed orders, you can allocate a specific area for those products. Slotting can also consider seasonal changes and suggest moving certain products during different times of the year.
This system can calculate other parameters and help determine the collection method by profiling goods and orders. It also facilitates the preparation and storage of products by strategically placing popular items in easily accessible locations.
Calculating the lines per order allows for the analysis of orders. It helps determine the number of orders per product code and the necessary pick-up locations. When a substantial number of items are on a single line, it is crucial to differentiate between standard and backorders. For standard charges, the appropriate method is the batch pick.
When picking goods, they are placed in smaller containers and combined in a designated area. The Cube per Order Index (COI) is a strategy that calculates the ratio of product line space requirements to the number of daily picks. This ratio helps determine the position of the picking run, with lower COI, indicating better utilization of product space.
Combining these factors enables us to determine the most suitable picking method for the warehouse. We can pick up small cube orders using roll cages or trolleys, while larger ones require trucks or pallet jacks.
By analyzing demand variations, we can determine the pick face size and the quantity to hold for each product type. This analysis ensures we maintain an adequate stock level to meet a day’s demand and reduce refills’ frequency. Calculating the average daily direction and standard deviation allows us to obtain demand figures for each item.
Ensuring sufficient space in the picking area is crucial to accommodate the required stock quantities is vital. The space calculation considers the total warehouse capacity, floor area, and reserve stock storage requirements.
Take a look at the image below. It shows a simple layout that uses ABC analysis from a pick-face visit. To make the warehouse run better, we need to minimize the number of trips when picking orders.
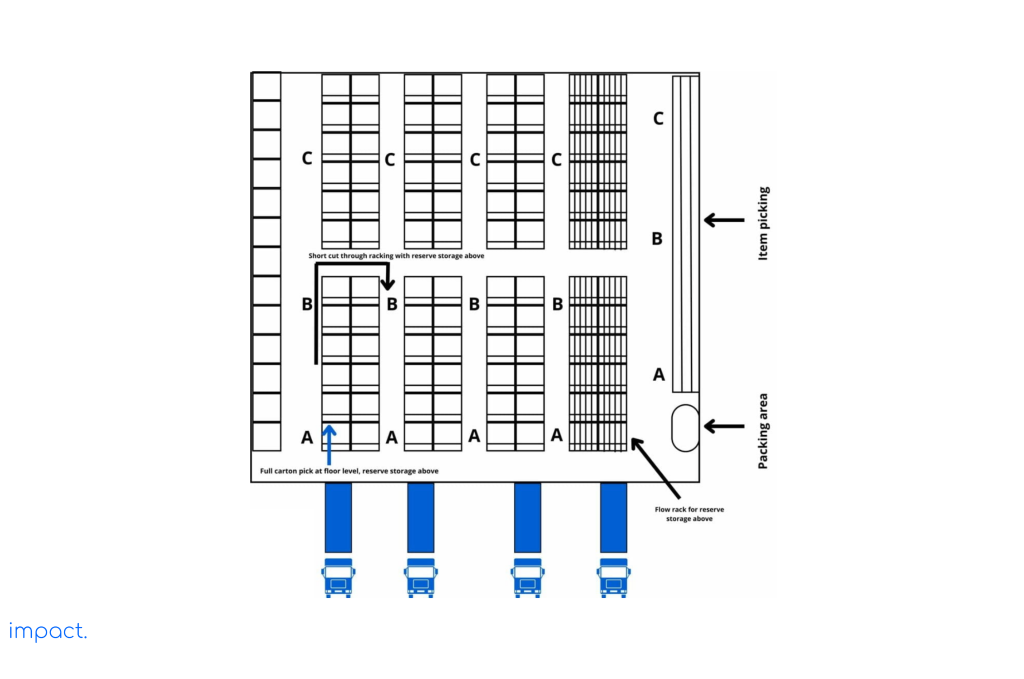
When choosing picker routes for order preparation, consider the following:
Warehouse layouts typically include racks or freestanding storage areas for spare pallets. The positioning of these storage areas depends on the number of different products and the available floor space. It is vital to avoid having pickers retrieve full pallets from the picking area since they require replacement.
Creating a separate area in the warehouse specifically for these product parts is more cost-effective when multiple orders require them. This approach simplifies picking individual items, especially when small quantities are needed, and provides a designated space for storing unused items.
To improve the picking process:
When planning the warehouse layout, thinking about the space needed for other services like labeling, packaging, and packing things together is essential. That area should be near where items are picked and delivered to avoid long trips. It’s also necessary to think about the people working in the warehouse and choose equipment and work areas that are safe and comfortable for them.
To figure out the best picking system, you’ll need the following information:
Once you’ve gathered this data during profiling, you can choose the most effective retrieval system.
We must make essential preparations to ensure an efficient and productive picking process. These preparations involve understanding the products and sales patterns and using available data to analyze them using ABC analysis.
By placing the products in the right spots, we can reduce the distance the operator needs to travel and make their job less stressful. This method will increase productivity and save money overall. So, we have to consider how to arrange the warehouse layout carefully.
The next chapter will discuss the picking process in more detail.
Aberdeen Group. 2009b. Warehouse Operations: Increase Responsiveness through Automation. Boston: Aberdeen Group
Richard G. 2011. Warehouse Management. Great Britain: Kogan Page Limited.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

Improving the system begins with simplifying processes and procedures. Still, it should be done in the best way possible to get the most out of it. When done correctly, these processes can boost productivity and reduce operational costs.
Warehouses may vary in size, type, function, location, and ownership, but the basic processes remain the same. One way to make warehouse operations more efficient is by using the latest technology.
The chart below shows the costs associated with different warehouse activities. It highlights the importance of pick, pack, and dispatch operations in day-to-day activities. These numbers can vary depending on the type of operation.
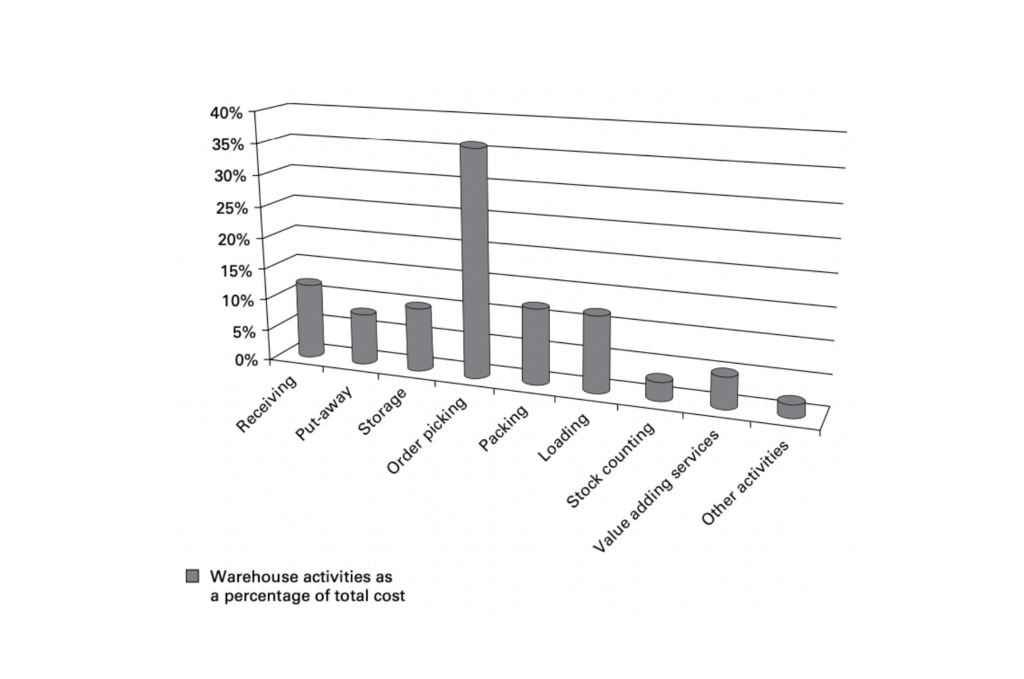
Source: Gwynne Richards; Warehouse Management; Warehouse processes: receiving and put-away
Apart from those three steps, pre-receipt and receiving are also important. If the wrong product is received or placed in the wrong spot, it can cause big problems.
This article will discuss the warehouse process from before receiving goods (pre-receipt) to the put-away stage. Put away means everything in the warehouse between getting goods from suppliers and storing them on the shelves.
Read more: Understanding Warehouses: Definition and its Importance
In warehouse management, 9 vital processes ensure the smooth functioning of operations. These processes are like gears that work together to keep the warehouse running efficiently. Let’s take a closer look at each of these processes and understand how they contribute to the overall success of warehouse management.
To ensure the buyer gets the correct quality goods, the supplier must deliver them correctly to the warehouse. The buyer doesn’t know how the goods are received, so they should receive goods that match the description.
The warehouse manager plays a crucial role in this process. They have to choose and give the okay for the packaging, decide how many items go in each box, how many packages go on each pallet, any unique labels needed, and the transportation method.
Read more: Warehouse Manager: Roles and 10 Challenges to Overcome
In the end, containers with many products still need to be sorted in the receiving area. It includes products on pallets and those without pallets, just loose in the container.
When the loose products arrive in the container, someone must place them on a pallet before storing them on the shelf. These boxes should be stacked neatly on the pallet without sticking out or being at risk of getting damaged.
Using ready-made software can make improving how we load the products more accessible. Pallets not only look nice, but they also help reduce the chances of the products getting damaged.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has rules about the size of pallets. These rules are in ISO 6780: Flat pallets for moving things worldwide – main sizes and limits. The table below shows the six dimensions that ISO specifies.
| Dimensions in mm (Width x Length) | Dimensions in inches (Width x Length) | Countries that use |
| 1219 x 1016 | 48.00 x 40.00 | North America |
| 1000 x 1200 | 39.37 x 47.24 | UK and Asia, commonly referred to as industrial pallet |
| 1165 x 1165 | 44.88 x 44.88 | Australia |
| 1067 x 1067 | 42.00 x 42.00 | Most countries |
| 1100 x 1100 | 43.30 x 43.30 | Asia |
| 800 x 1200 | 31.50 x 47.24 | Europe, commonly known as euro pallet |
To figure out how to arrange the racks, you need a solution that can handle different sizes of pallets. One option is to use plastic pallets called iGPS. These pallets are unique — you can recycle them, and weigh 30% less than wooden ones.
The good thing about iGPS pallets is that they don’t need any maintenance, which makes them great for moving groceries in warehouses.
Labeling products in boxes is essential to ensure easy identification. One way to do this is by using barcodes. These barcodes are like special codes that machines can read. They store information such as the product code, description, and how many packages there are.
In the supply chain, it’s essential to have consistency. You must ensure that the number of packages provided, stored, and sold matches the demand. This way, there won’t be too much or too little product available.
Many products often arrive at the warehouse in poor condition, with improper packaging, incorrect labels, or the wrong number of items. Therefore, it’s important to discuss certain things before placing an order. These include:
Selecting shipping methods that align with the warehouse’s available equipment is crucial to ensure smooth operations. For instance, if there is no loading bay, it is necessary to use vehicles equipped with tail-lift or side-unloading capabilities.
Shipping many goods overseas increases container traffic. You must choose between loose loading or palletizing your cargo as a business owner. Using pallets protects your stock from loss and damage during handling. It reduces the number of people needed to load and unload containers.
However, there’s a downside. Pallets take up space in the container, using up to 10% depending on the type used. Some pallets can’t be stacked, which further reduces space.
Due to the reduced space, pallets can increase shipping costs by 15-33%, depending on the load. However, it also lowers costs for delivery. It decreases the chances of damage to your products and injuries to your staff.
To reduce this drawback, you can use slip sheets instead of pallets. Slip sheets are made of thick cardboard or thin plastic and have a width of about 2 centimeters.
In this method, you place the load on a slip sheet inside the container. When the goods arrive, a special forklift attachment removes the slip sheet and the pack and then puts them on a pallet for storage.
The number of packages will depend on the product’s value, weight, and size. It’s important to note that boxes cannot weigh more than 20 kg, as legal restrictions exist. We must maintain a consistent product flow to ensure we count our stock accurately and reduce mistakes when picking items.
We need to have discussions with warehouses, procurement, customer service, and suppliers. For instance, we should talk to suppliers about our specific requirements and ask them to change their usual processes.
Another vital thing to remember is the 80/20 rule. This principle means roughly 20 percent of our suppliers provide about 80 percent of our stock. Likewise, around 20 percent of suppliers are responsible for 80 percent of the problems we encounter with our goods. It’s something we should keep in mind.
Problems often arise because suppliers may not realize how their actions affect our operations. So, it’s better to address the issue directly and work with the supplier to fix it.
Warehouse managers face the challenging responsibility of aligning work hours with the workload. They can reduce the hours needed and achieve cost savings by minimizing the time required to handle products.
Labor costs are the most considerable expense for warehouses, making up around 48% to 60% of the total cost, depending on automation levels. Handling activities alone account for roughly 20% of the overall expenses in retail warehouses.
To prepare correctly, make sure the supplier sends the product to the warehouse when you decide, not when it’s convenient for them, except when the shipping company is struggling to deliver on time.
To provide delivery times, match the time slot with how long you estimate it will take to complete the task.
For example, unloading a 45-foot pallet trailer might take 30 minutes, and moving the pallets to a storage area could take another 15 minutes. Depending on the number of items and available staff, unloading a loosely packed 20-foot container could take up to three hours.
Keep track of the time required for each type of delivery and share this information with the ordering team. The ordering team can plan more efficiently by understanding the necessary labor and equipment.
The warehouse staff needs to know the products being sent, the type of vehicle used, and the equipment required for unloading. Once everything is confirmed and the time is calculated, assign appropriate order slots and provide order references to the supplier.
Also, make sure you understand the details of the pallet exchange agreement. If you’re using a pallet rental system, both parties need to record the movement of pallets in the system accurately.
Providing advance notice of the shipped products is also a good idea. It allows the Warehouse Management Software (WMS) to enter the details and prepare for the arrival of the products.
When the goods arrive, you must check the vehicle’s condition and compare the seal with the order reference. Then, assign the vehicle to the loading bay or a spot in the yard.
Before you change the vehicle’s temperature for unloading, check how hot or cold it has been during the trip and how hot or cold the goods are right now. Once the vehicle is in the room or yard for unloading, ensure the team has enough people and the tools to do the job quickly and satisfactorily.
The most common way to lower pallets into the loading bay is using a powered pallet truck, hand pallet truck, or pallet jack. Some companies use counter-balanced forklift trucks, but be careful because accidents can happen if the truck, driver, or floor weights are weak or damaged.
To speed up this process, we have installed an automatic unloading system that can unload 26 pallets in just 5 minutes. The picture below shows one of the unloading methods, which uses tracks.
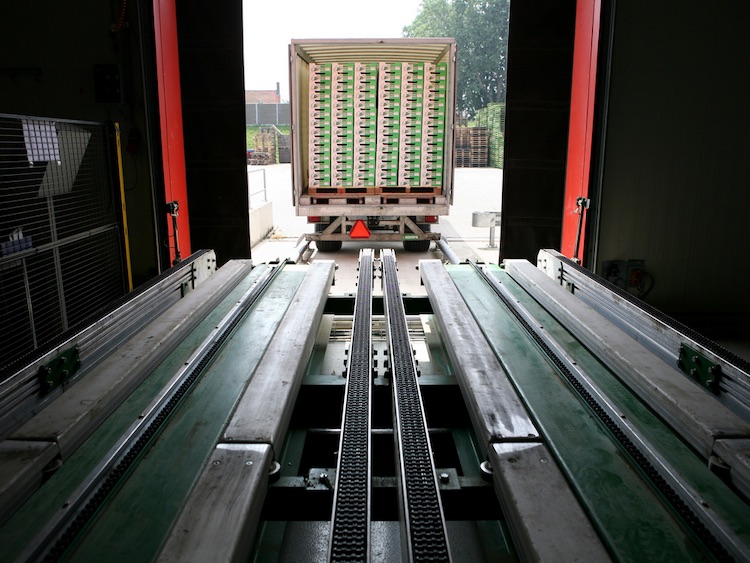

Image source: Robotics and Automation News
Unloading loose-loaded containers consumes much time. It takes at least two people to unload and place the goods onto pallets. At the same time, another person waits to transport the stacked pallets to the inspection area.
This process lacks productivity. Staff inside the containers must wait to replace full pallets with empty ones. At the same time, forklift drivers await the construction of the pallets.
Containers often contain a mix of products, so sorting is necessary at the unloading dock. This sorting process is inefficient and poses risks to staff constantly bending and stretching in the confined space and near Material Handling Equipment (MHE). Moreover, the lighting is poor, making the conditions unfavorable.
Pallets or stillages can be placed on either side of the conveyor and stacked with the right items to improve this operation. The operator can reduce the amount of bending and stretching required by using platforms that adjust to the height of the pallet they are building.
Instructing suppliers to load the same product in each container is crucial for smooth operation. This change could increase productivity gains by up to 50%.
Using more automation will make the cartons more consistent. We now use robots to build pallets when we bring items in and send them out. We also have other equipment like forklift trucks with clamp attachments for unloading big appliances and larger boxes. And we have forklift trucks with slip sheet attachments for unloading containers.
Read more: Warehouse Cost: 2 Determination Systems & Reduction Tips
Once you unload the goods, you must decide whether to check them before storing them. Ideally, move incoming goods directly from the loading bay to the storage or discharge areas if they are cross-docked.
The problem with this process is trust unless you’re sure the supplier can deliver the right product. There’s a solution to this problem: you can randomly inspect some of the products instead of checking everything.
Some retailers employ a method known as Good Faith Receiving (GFR). In GFR, they receive products at the distribution center without conducting immediate checks. They randomly inspect the products and report any issues to the supplier in proportion. This approach allows drivers to continue making deliveries and pressures suppliers to enhance accuracy.
Managers can establish rules and inspection requirements if they don’t use GFR. The manager measures supplier performance based on the accuracy of their recent shipments.
New suppliers may feel concerned when their first shipment undergoes a check. Still, you will continue checking until you have confidence in their accuracy. As for experienced suppliers, you can inspect 10% of each shipment. If an issue arises, you can check the next 10%.
There’s a trade-off between the time it takes to inspect shipments, the number of problems found, and the time it takes to deal with them.
Barcodes have accelerated inspections and increased accuracy. When we scan products, we can instantly compare their details in real-time if we have wireless capability.
After scanning, we can move the goods directly to the next step, such as checking quality, selecting items, storing them, or shipping them out. Using RFID technology will make inspections even faster in the reception area. When products with the proper tags come into the warehouse, we can quickly recognize and count them, sending the information immediately to the warehouse management system.
Aberdeen Group (2009b) found that 70% of the best companies prefer receiving goods without paper documents. They use barcodes, RFID, or voice technology instead.
Noting and reporting discrepancies in the received goods is crucial in the admissions process. It plays a vital role. Here’s an example of a report for goods that do not meet the requirements.
| Receiving Date | Supplier | Product Code | Purchase Order Number | Order Reference | Non-Compliance |
| 03/04/21 | ABC | 59193 | 26620 | 1128 | Barcode cannot be scanned |
| 03/04/21 | ABC | 105729 | 26620 | 1128 | Outer carton exceeds 20 kg |
| 06/04/21 | DEF | 541037 | 29901 | 2832 | Barcode located outside, not inside |
| 07/04/21 | FHI | 925739 | 29992 | 3314 | Quantity does not match expectations |
| 07/04/21 | FHI | 017592 | 29992 | 3314 | Barcode cannot be scanned |
| 08/04/21 | JKL | 752948 | 3210 | 2109 | No price sticker present |
Most warehouses want to move products quickly and hold less stock. Cross docking is a way to move products straight from receiving to shipping without storing them in the warehouse or picking them up.
For cross-docking to work, suppliers must ensure clear labeling of products and provide timely notifications of their arrival and delivery. We also need systems to identify products and processes that encourage shipments.
After checking the products, we transport them directly to the delivery area. We actively track the temporary storage locations of these products in the system, enabling staff to be aware of their readiness for delivery. Additionally, we maintain comprehensive records for auditing purposes.
It’s essential to have enough space in the entry and exit areas. Having enough space helps us move products quickly and safely. If there are any bottlenecks in these areas, it slows down the process and can cause tension between teams.
Additionally, it’s crucial to establish a marked area for the placement of products before shipping them. Drive-in rack areas can assist in organizing loads for specific collections.
Companies widely employ cross-docking in the supply chain to transport perishable goods. Retailers actively utilize this system at their distribution centers to receive products from various suppliers, sort them, and dispatch them to different stores.
The just-in-time system also relies on cross-docking to send parts to a central location for assembly and delivery in a specific order. The image below shows an example of how cross-docking works.
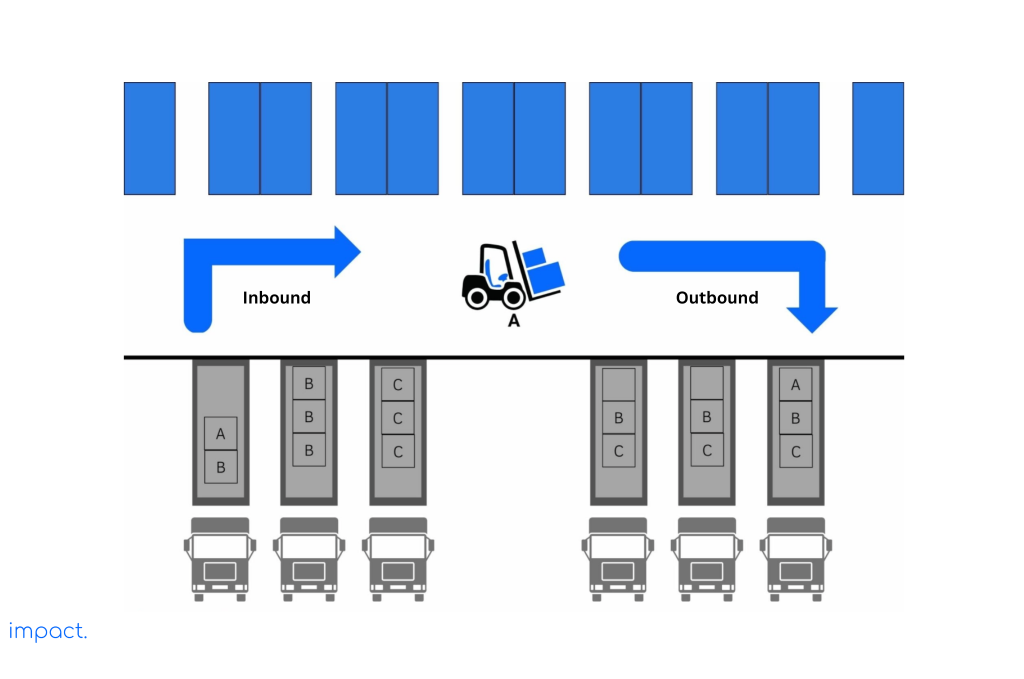
Every product needs records beyond the usual information like product code, description, and quantity when it arrives. It can include extra details such as batch or slot numbers and serial numbers.
Certain products require stricter acceptance checks. These include high-value items, food, dangerous goods, and products that need specific temperatures, like medicines.
Create a designated area close to the receiving point to check goods upon arrival. It’s crucial to carry out this process with speed and efficiency to avoid any hold-ups and ensure prompt integration of the products into the system.
If there’s a problem with a product, put it in a separate area for quarantine. If the issue is with the storage room, put the product there but label it as damaged or wait for test results.
Most WMS systems actively block access to blocked products and prohibit their selection. Adding physical markings on the site provides an additional measure to ensure proper handling of the products.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) actively assign product locations beforehand and instruct workers where to place goods. Workers can perform this task directly at the dispatch area for cross-docking, at the pick face to restock, or in backup storage.
To ensure the effective functioning of this system, we must input a wealth of information. This information encompasses various aspects such as:
Without a system, the warehouse manager has to figure out the best spots for goods and tell the operators where to put them. When you use fixed locations, you have to assign a specific area for each product. Random locations mean putting pallets where they fit best.
When placing products, it is crucial to consider certain factors. We must allocate dangerous goods to a specific area and provide special storage for valuable items that we can lock or place on a secure carousel.
It’s best to put the fastest-selling items in the middle row when putting boxes away. That way, the people picking orders don’t have to bend or stretch too much. Slower-selling goods can go on the top and bottom shelves.
The warehouse manager also needs to group similar items. Some warehouse systems combine putting things away with picking pallets, called insertion duty. The system tells the operator where to store pallets while they gather the full ones needed to restock.
Read more: 6 Warehouse Performance Metrics & Tips for Choosing Them
All warehouses follow a similar process, although they may vary in size, function, ownership, and location. As discussed, the receiving and setup process is vital for an efficient warehouse operation.
Ensuring the smooth running of this process is crucial to achieving optimal results and cost reduction. To enhance productivity in the receiving and setup area, here are five steps you can take:
In the following article, we’ll explore another important aspect of warehouse operations: the picking process.
Aberdeen Group. 2009b. Warehouse Operations: Increase Responsiveness through Automation. Boston: Aberdeen Group
Richard G. 2011. Warehouse Management. Great Britain: Kogan Page Limited.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

In our previous chapter, we explored search engines and how they work. Now, we shift our focus to the crucial role of keyword research in driving SEO outcomes.
Keywords are the foundation of effective SEO strategies. They act as a compass, guiding search engines and connecting users with relevant information, products, or services. However, selecting the right keywords is a common struggle for businesses, often leaving them lost amidst fierce online competition.
This comprehensive guide presents eight simple steps to master keyword research. Whether you’re a digital marketer, a small business owner, or an SEO enthusiast, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to bring your SEO efforts to new heights.
Keywords are crucial in SEO. They are words or phrases that describe the main topic of the content. When people search for something, they enter keywords into search engines.
Search engines analyze web pages to determine if they are relevant and of good quality. They look at the content and the keywords used. This analysis affects how well a website or web page appears in search engine results.
As a website owner or content creator, you want the keywords on your page to match what people are searching for. This similarity enhances the likelihood of your audience finding your content on the search engine result page (SERP). By optimizing your website or content with relevant keywords, you improve its visibility in search results when users search for those terms.
Read more: SEO Fundamentals: Key Definitions & 4 Best Practices
Strategically placing your keywords in different areas on your website or web page can help improve its visibility. Here are some key locations where you should include your keywords:
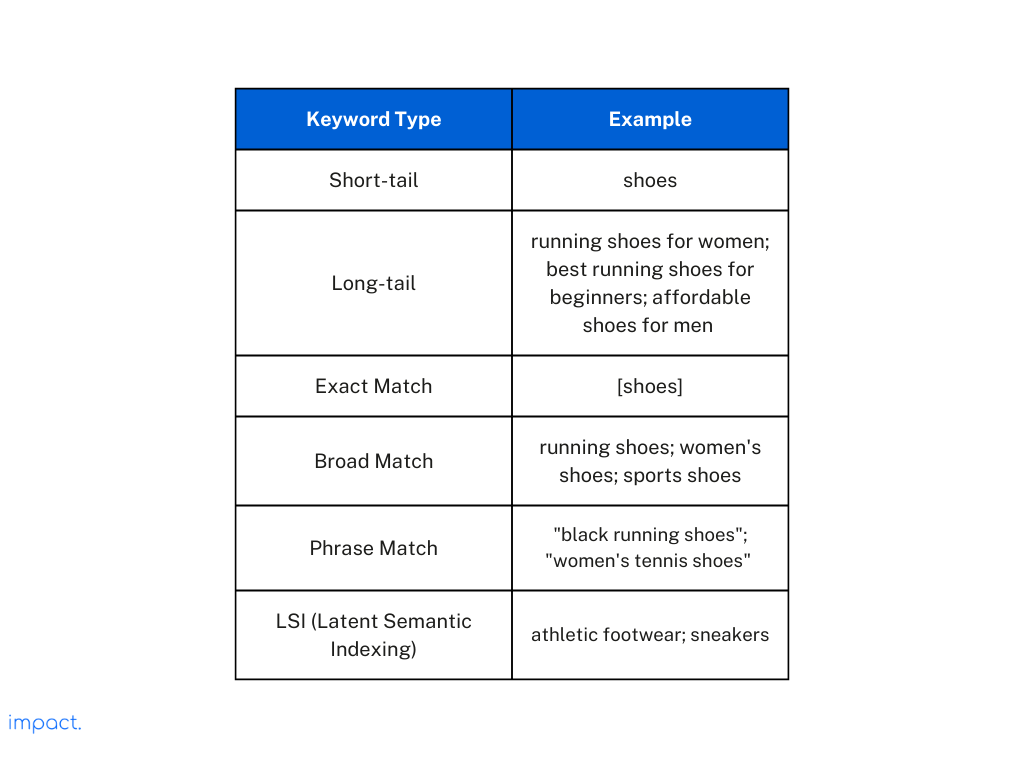
There are different types of keywords you can use for SEO. Here are some common ones, along with their examples:
Now, let’s head to the keyword research process. When conducting your research, you must consider these three main elements:
When you use search engines like Google, they focus on showing you the most relevant content. To understand what people are looking for, they consider search intent, which is the reason behind a search. There are four types of search intent:
Your content will only rank well for a keyword if it fulfills what searchers seek. Moreover, your content needs to be the best among other resources available. Otherwise, Google won’t prioritize it over more valuable content on the web.
Google values authoritative sources, so it’s crucial to establish yourself as one. To rank higher on Google, you must:
Ranking on the first page for a keyword won’t help if nobody searches for it. It’s like having a store in a deserted town. MSV (monthly search volume) measures the number of times everyone searches for a keyword each month.
Read more: Search Engines: Inner Workings & 6 Ways to Rank Higher
To conduct effective keyword research and improve your website’s visibility in search engine results, you need to follow a strategic approach. Following these eight steps, you can identify the keywords that match your goals and target audience. Let’s explore each step in detail:
To begin, grasp the purpose of your keyword research. Clearly define your objectives and identify your target audience.
You can customize your keyword strategy by understanding what they are searching for. Set clear goals for your keyword targeting to guide your research process efficiently.
Create a list of seed keywords representing your main topic or business. These core terms capture the essence of your content or business.
To expand on this list, consider the phrases and words your potential customers will likely use when searching.
Additionally, it may benefit you to research related search terms and analyze your competitors’ use of keywords. By doing so, you can uncover new keyword opportunities.
Now that you have a list of potential keywords grouped by topics you want to focus on, it’s time to evaluate their search volume. Search volume tells how many people search for a particular keyword monthly.
Look for keywords with high monthly searches, as they can increase your website’s traffic.
Besides search volume, it’s crucial to consider the relevance of keywords to your website and target audience.
Choose keywords that match your goal, content, products, or services. Relevance helps attract the right audience more likely to engage with your website and become customers.
Think about the purpose behind the keywords and how well they fit with what you offer.
It’s worth noting that user intent can be inferred through the process of analyzing the top-ranking pages associated with those keywords
Keyword difficulty measures how tough it is to compete for a specific keyword. Assessing keyword difficulty is crucial to see if you can realistically rank for those keywords.
Higher-difficulty keywords are more competitive, making it challenging to reach the top ranks. Targeting a mix of high and low-difficulty keywords is a good idea. Low-difficulty keywords offer better chances for visibility and ranking.
In contrast, as you gain authority and enhance your SEO efforts, you can target high-difficulty keywords.
Select keywords that match your goals and target audience after analyzing search volume, relevance, and difficulty.
Give priority to keywords that balance search volume and relevance to your content or business. Remember the competition for these keywords and ensure they align with your available resources and capabilities.
After selecting your keywords, it’s important to map them to your website’s right pages or content.
Assign keywords to specific pages or articles that are closely related to them. Optimize important on-page elements like titles, headings, meta descriptions, and URLs by naturally including these keywords.
This seamless integration improves the user experience and helps search engines find and rank your content better.
Keyword research is a continuous process. Use analytics tools to monitor how your chosen keywords perform.
Monitor changes in search volume, competition, and keyword rankings. Analyze how your keywords drive traffic, engagement, and conversions. Based on the results, adjust your keyword strategy as needed.
Stay flexible to adapt to new trends, user behavior, and search engine updates. It will help you improve your SEO efforts and reach your goals.
When it comes to keyword research, there are several highly recommended tools available online. Here are five popular options:
These tools have different features and capabilities to help you find valuable SEO or content strategy keywords. Look at each to see which suits your needs and budget the best.
Mastering keyword research is crucial for successful SEO outcomes. Keywords are a compass connecting users with relevant information, products, or services. However, selecting the right keywords can be challenging due to the intense online competition.
In the next chapter, we will explore on-site optimization or on-page SEO. This aspect of SEO focuses on optimizing individual web pages to improve search engine rankings and enhance user experience.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.

In our previous discussions about Search Engine Optimization (SEO), we learned the basic concept to help boost your online presence. Now, we will look closely at search engines and how they decide which websites appear at the top of search results.
Search engines have become a big part of our daily lives. We use them to find answers to questions, research topics we’re interested in, and discover products and services. However, have you ever wondered how search engines work behind the scenes? How do they pick which websites deserve the best spots on their search result pages?
In this article, we will explore the inner workings of search engines and the complex algorithms and processes they use to make those decisions. We will also give you six ways to rank higher on their results page.
A search engine is a special set of programs that helps you find things on the internet. It looks through an extensive database of information and tries to find items that match what you’re looking for.
You enter a few keywords to describe what you are searching for. The engine lists relevant web pages, images, videos, or other online content that closely matches your search. This list of results is called a search engine results page (SERP). It shows you all the relevant content the search engine found based on your search.

Search engines are significant for SEO (Search Engine Optimization). They decide how visible and high-ranking websites are on search results pages. SEO techniques help improve websites so that they meet the requirements of search engines and have a better chance of ranking higher.
Search engines look at keywords, how easy it is to use a website, how trustworthy it is, and how authoritative it is. Based on these factors, search engines determine which websites are the most relevant for a user’s search. By using SEO strategies, website owners can make their websites more visible, get more people to visit them, and have a better chance of reaching their target audience.
Read more: SEO Fundamentals: Key Definitions & 4 Best Practices
There are various search engines available today that help you find information on the internet. Some popular examples include Google, Bing, and Yahoo!, each offering unique features and services.
Google is the biggest search engine in the world, handling over 99,000 searches every second and more than 8.5 billion searches daily. It’s so popular that it has become synonymous with searching the internet, with people often saying, “I googled it” when looking something up online.
Bing is Microsoft’s search engine, created as an alternative to Google and released in 2009. It comes as the default search engine in Microsoft’s web browser. While Bing aims to improve, it still has much ground to cover to rival Google. Bing offers various services like image, web, video search, and maps. One notable feature introduced by Bing is “Places,” which provides information about local businesses and locations.
Yahoo! has been a strong competitor in the world of search engines. However, instead of doing all the work, it relied on other companies to handle its searchable index and web crawling. At first, it used Inktomi and then Google from 2001 to 2004. Later, in 2009, Yahoo! teamed up with Microsoft, allowing Bing to take over the tasks of providing the search index and crawling the web.
In China, Baidu is the country’s most popular search engine and acts as an alternative to Google, which is banned there. Founded in January 2000, Baidu provides web search results for websites, audio files, and images. In addition to search, Baidu offers various services like maps, news, cloud storage, and over 55 other internet-related services.
Yandex is a prevalent search engine in Russia and ranks as the fourth most visited website there. It is also widely used in Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Belarus, and Turkey. Besides its search function, Yandex offers services like maps, navigation, music streaming, e-commerce, mobile apps, and online advertising.
Ask.com, previously known as Ask Jeeves, is a question-and-answer community that provides answers based on a simple question-and-answer format. It incorporates many archived data to address users’ queries. However, it relies on an external search provider for search results. As a result, the information may not be as up-to-date as other search engines.
DuckDuckGo (DDG) is a search engine that values your privacy. Unlike other search engines, it doesn’t track or customize your search results based on personal information. Instead, it gives the same results to everyone. DDG also focuses on showing you high-quality search results; its interface is clean and free of too many ads.
A search engine comprises three essential components that help you find online information. Let’s take a closer look at each of them:
Search engines on the internet use complex algorithms to give you the right search results. But let’s break down the main process into three stages:
Now, let’s dive into each stage and learn more about them.

Search engines on the internet use complicated algorithms to provide you with accurate search results. Let’s simplify the main process. A typical Google search consists of three stages, although not all inquiries go through each step:
Here’s how Google’s crawling process works:
When the crawler discovers information, it must arrange, sort, and save it for later use by the ranking algorithm. Search engines store important details like the page title, description, content type, related keywords, incoming and outgoing links, and other factors that help determine a page’s ranking.
After crawling, Google’s indexing process follows these steps:
After collecting and organizing information from websites, the search engine determines the order of search results through ranking. The process involves assessing the relevance and quality of web pages. Here are some common factors used in ranking:
It’s important to understand that search engine algorithms constantly change as they undergo regular updates and improvements. The ultimate goal is to provide users with the most accurate and helpful search results, taking into account their intent, location, and personal preferences.
If you want your business to appear at the top of a Search Engine Results Page (SERP), you must take certain steps. Most people, around 90%, click on the results displayed on that page. To guarantee a high ranking when people search for your website, follow these guidelines:
Keyword relevance is one of the many factors that determine the rank of your website in a search engine. Therefore, you need to focus on using the right keywords. These keywords should be relevant to your website’s content and what your target audience is searching for. Conduct thorough research using keyword tools to find popular keywords that match your website’s theme.
Improving the elements on your website’s pages is important to rank higher on search engines. These elements include the title tags (the main heading of each page), meta descriptions (summaries of the page’s content), headers (subheadings that break up the text), and URL structures (the web addresses of your pages).
When optimizing these on-page elements, ensure you include your target keywords naturally and organically. The placement helps search engines understand your content and increases the chances of your pages appearing in relevant search results.
To rank higher on search engines, create valuable and engaging content for your visitors. Your content should be original and well-researched.
Additionally, it’s essential to understand why people are searching in the first place. When you know what your target audience is looking for, you can create content that meets their needs. By implementing this, you can increase your chances of obtaining a higher ranking and attracting the appropriate type of traffic.
Read more: Content Marketing: 7 Steps to Strategize for Success
To rank higher on search engines, having a strong and trustworthy network of links to your website is essential. You can do this by getting links from reputable websites in your industry.
Look for chances to write guest blog posts, collaborate with influencers, or form partnerships to help you gain valuable links. Remember, it’s better to focus on getting high-quality links rather than getting lots of low-quality links, as those could hurt your rankings.
Make sure your website loads quickly and works well on mobile devices. People expect websites to load within about 3 seconds. Around 40% of users may leave your site if it takes longer. Fast and mobile-friendly sites are more likely to appear higher in search results.
Improve website performance by compressing images, enabling browser caching, and minimizing unnecessary scripts. Also, logically organize your website and submit a sitemap to search engines.
By implementing these steps, you can enhance the overall performance of your website and make it easier for search engines to explore and list your site — increasing your website’s ranking.
Keep an eye on how your website is doing using tools like Google Analytics. Look at important numbers like how many people visit your site through search engines, how many leave right away, how many visitors turn into customers, and where your keywords rank in search results. Study this data to find out what needs to be improved and use it to make smart choices for your website.
Understanding how search engines work and the factors influencing website rankings is essential for improving your online presence. We’ve covered the inner workings of search engines, including crawling, indexing, and ranking. Using effective SEO strategies, website owners can optimize their sites to meet search engine requirements, making them more visible and increasing their chances of reaching their target audience.
In the next chapter, we’ll dive into the crucial topic of keyword research. Keywords are the words and phrases users type into search engines to find information or solutions. We’ll discuss how to conduct thorough keyword research to identify the most relevant and valuable keywords for your website.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
Ask about digital transformation, our products, pricing, implementation, or anything else.
We are excited to be part of your transformation journey from day one.
